Understanding Hormones: A Key Element in Reproductive Endocrinology
Hormones play a vital role in our body’s reproductive system and overall health. They are chemical messengers that are produced by the endocrine glands and are responsible for regulating various bodily functions. In the field of reproductive endocrinology, hormones are of utmost importance, as they control the reproductive processes in both men and women.
In this blog post, we will delve deeper into the world of hormones and their impact on reproductive endocrinology. We will discuss the different types of hormones, their functions, and how they work together to ensure successful reproduction. So, let’s get started!
1. What are hormones?
2. Types of hormones and their functions
3. The role of hormones in reproductive endocrinology
4. Common hormone-related conditions in reproductive endocrinology
5. How to maintain hormonal balance for optimal reproductive health
1. What are hormones?
Hormones are chemical substances that are produced by the endocrine glands and are released into the bloodstream. They act as messengers, carrying signals from one part of the body to another and regulating various bodily functions. The endocrine glands, such as the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, and adrenal gland, secrete hormones in response to signals from the brain or other organs.
2. Types of hormones and their functions
There are different types of hormones in the body, each with a specific function. Some of the most important hormones in reproductive endocrinology include:
Understanding Hormones: A Key Element in Reproductive Endocrinology
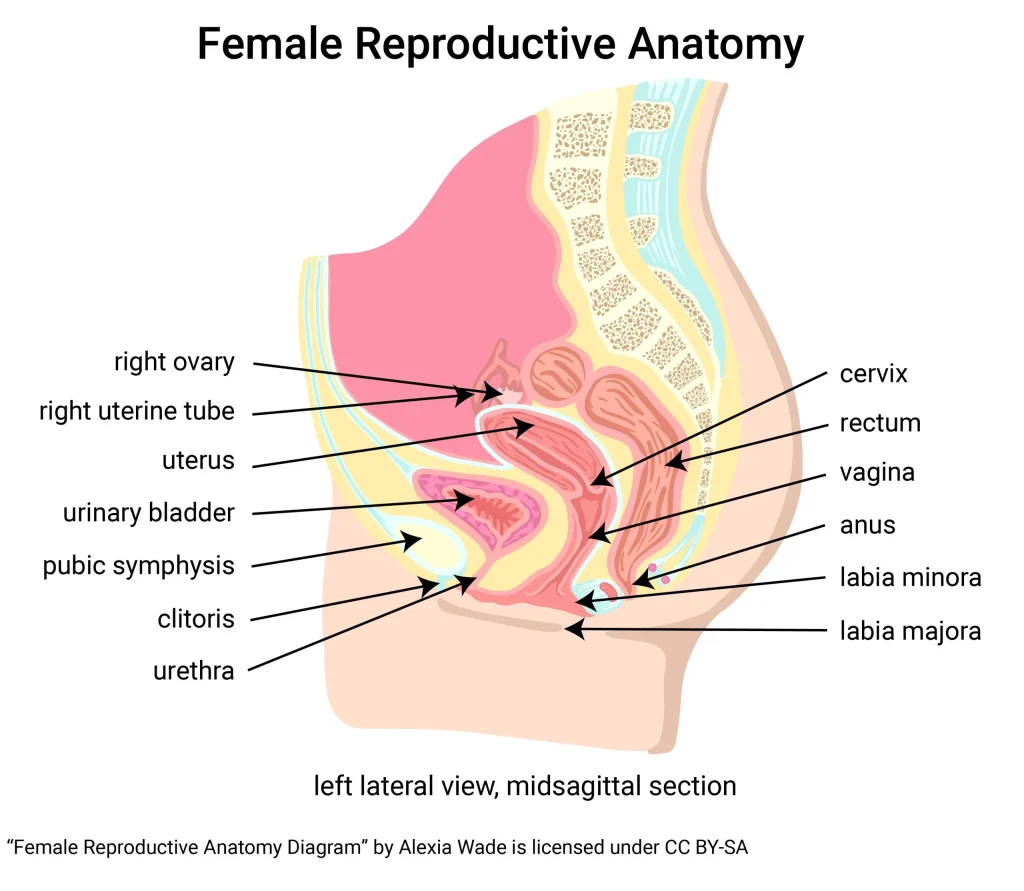
– Estrogen: This hormone is primarily produced by the ovaries in women and is responsible for the development of female sexual characteristics, such as breast growth and regulation of the menstrual cycle.
– Progesterone: Another hormone produced by the ovaries, progesterone plays a crucial role in preparing the uterus for pregnancy and maintaining a healthy pregnancy.
– Testosterone: This is the main male sex hormone, responsible for the development of male sexual characteristics, such as facial hair and muscle mass.
– Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH): Produced by the pituitary gland, FSH plays a crucial role in the development of eggs in women and sperm in men.
– Luteinizing hormone (LH): Also produced by the pituitary gland, LH triggers ovulation in women and stimulates the production of testosterone in men.
3. The role of hormones in reproductive endocrinology
Hormones play a critical role in reproductive endocrinology, as they regulate the reproductive processes in both men and women. In women, hormones control the menstrual cycle, ovulation, and pregnancy. In men, hormones are responsible for sperm production and sexual function. Without the proper balance of hormones, these processes can be disrupted, leading to fertility issues and other reproductive problems.
4. Common hormone-related conditions in reproductive endocrinology
Hormonal imbalances can lead to various conditions in reproductive endocrinology. Some of the most common conditions include:
– Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): This is a hormonal disorder that affects women of reproductive age and can cause irregular periods, difficulty getting pregnant, and excessive hair growth.
– Hypogonadism: A condition in which the body does not produce enough hormones, which can lead to infertility and other reproductive problems.
– Endometriosis: This is a condition in which the tissue that lines the uterus grows outside of it, causing hormonal imbalances and fertility issues.
– Erectile dysfunction: A common condition in men, where the body does not produce enough testosterone, leading to difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection.
– Thyroid disorders: The thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate metabolism and can affect fertility if not functioning properly.
5. How to maintain hormonal balance for optimal reproductive health
Maintaining hormonal balance is crucial for optimal reproductive health. Some ways to achieve this include:
– Eating a balanced and nutritious diet: A healthy diet can help regulate hormone production and maintain a healthy weight, which is vital for reproductive health.
– Exercising regularly: Regular exercise can help regulate hormone levels and improve overall health.
– Managing stress: Chronic stress can affect hormone production, so it’s essential to find healthy ways to cope with stress.
– Getting enough sleep: Sleep is crucial for hormone regulation, so it’s important to get 7-9 hours of sleep each night.
– Seeking medical help: If you suspect you have a hormonal imbalance, it’s essential to seek medical help from a qualified reproductive endocrinologist who can diagnose and treat any underlying conditions.
In conclusion, hormones play a crucial role in reproductive endocrinology and are essential for successful reproduction. Understanding the different types of hormones, their functions, and how to maintain hormonal balance can help individuals achieve optimal reproductive health and address any issues that may arise. By taking care of our hormonal health, we can improve our overall well-being and increase our chances of building a healthy family.