Thinking Outside the Box: Self-Insemination for Women with Blocked Fallopian Tubes
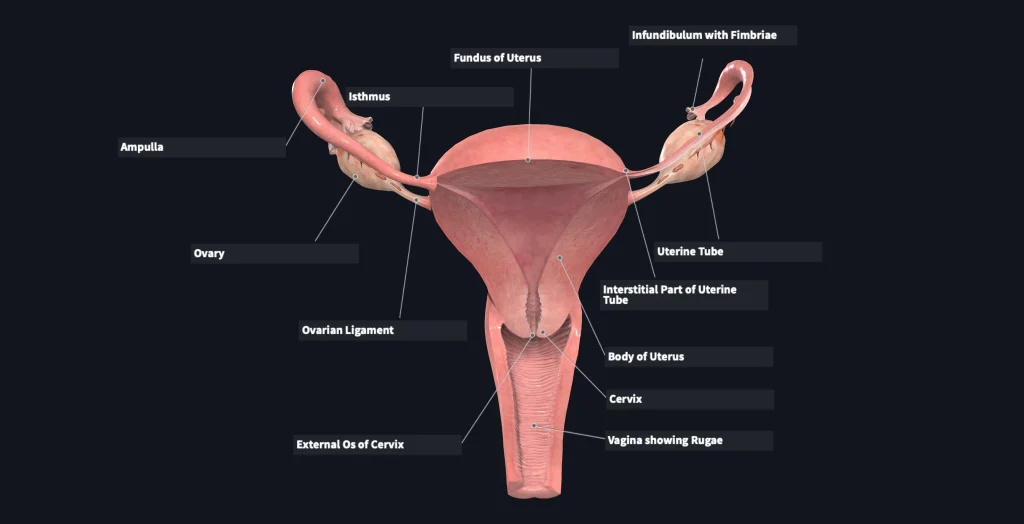
Trying to conceive can be a challenging and emotional journey for many women, especially those who have been diagnosed with blocked fallopian tubes. This condition can make it difficult or even impossible for natural conception to occur, leaving women feeling frustrated and hopeless. However, there is a lesser-known method of conception that can give women with blocked fallopian tubes a glimmer of hope – self-insemination.
Self-insemination, also known as at-home insemination, is the process of using a syringe or other device to place sperm into the vagina in order to fertilize an egg. This method is often used by single women or same-sex couples, but it can also be a viable option for women with blocked fallopian tubes. In this blog post, we will explore the ins and outs of self-insemination for women with blocked fallopian tubes, including the benefits, risks, and step-by-step process.
Benefits of Self-Insemination for Women with Blocked Fallopian Tubes
The most obvious benefit of self-insemination for women with blocked fallopian tubes is the possibility of getting pregnant without the need for invasive medical procedures. This can be a huge relief for women who may have been told that their only option for conception is in vitro fertilization (IVF) or other fertility treatments. Self-insemination is a much more affordable and less invasive option, making it a more accessible choice for many women.
Another advantage of self-insemination is that it can be done in the comfort and privacy of one’s own home. For some women, the thought of undergoing medical procedures or going to a fertility clinic can be overwhelming and stressful. Self-insemination allows women to take control of their own fertility journey and perform the procedure in a familiar and comfortable setting.
Self-insemination also gives women with blocked fallopian tubes the opportunity to have a biological connection to their child. In cases where the male partner’s sperm is used, this method allows for both partners to play a role in the conception process. For single women or same-sex couples, self-insemination can give them the chance to have a genetically related child without the need for a sperm donor.
Risks and Considerations
As with any medical procedure, self-insemination does come with some risks and considerations. The most important factor to consider is the source of the sperm. It is crucial to use sperm from a reliable and healthy donor in order to reduce the risk of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and other health complications. It is recommended to use sperm from a sperm bank or a known and trusted donor.
Another potential risk of self-insemination is the risk of infection. Women should take precautions to ensure that the syringe or other device used for insemination is clean and sterile. It is also important to follow proper hygiene practices before and after the procedure to reduce the risk of infection.
The success rate of self-insemination for women with blocked fallopian tubes can vary. Factors such as the timing of ovulation, the quality of the sperm, and the technique used can all affect the likelihood of conception. It is important to manage expectations and be prepared for the possibility of multiple attempts before achieving a successful pregnancy.
Thinking Outside the Box: Self-Insemination for Women with Blocked Fallopian Tubes
Step-by-Step Guide to Self-Insemination
Now that we have discussed the benefits and risks of self-insemination for women with blocked fallopian tubes, let’s take a closer look at the step-by-step process.
1. Determine the timing: The first step is to track your ovulation cycle in order to determine the best time for insemination. This can be done through various methods such as tracking basal body temperature, using ovulation predictor kits, or monitoring cervical mucus.
2. Prepare the sperm: If using sperm from a sperm bank, follow the instructions provided to thaw and prepare the sample. If using sperm from a known donor, make sure it has been recently tested and is free of any potential infections.
3. Prepare the syringe: Use a clean and sterile syringe or device to collect the sperm. Some women prefer to use a menstrual cup or soft cup instead of a syringe for easier insertion.
4. Insert the sperm: Lie down with your hips elevated and insert the sperm into the vagina using the syringe or device. It is recommended to keep the sperm inside the vagina for at least 15 minutes to allow it to travel toward the fallopian tubes.
5. Relax and monitor: After the sperm has been inserted, it is important to relax and avoid any strenuous activities for the next few hours. You can also monitor your body for any signs of ovulation and track your cycle for potential pregnancy symptoms.
Possible Search Queries:
1. “Self-insemination for women with blocked fallopian tubes”
2. “At-home insemination for blocked fallopian tubes”
3. “Can women with blocked fallopian tubes get pregnant through self-insemination?”
4. “Step-by-step guide to self-insemination for blocked fallopian tubes”
5. “Benefits and risks of self-insemination for women with blocked fallopian tubes”
Summary:
Self-insemination can be a viable option for women with blocked fallopian tubes who are trying to conceive. This method offers a more affordable and less invasive alternative to traditional fertility treatments. It also allows women to take control of their own fertility journey and have a biological connection to their child. However, it is important to consider the risks and follow proper precautions when performing self-insemination. By tracking ovulation and following a step-by-step process, women can increase their chances of successful conception through self-insemination.