The Science of Self-Insemination: How Progesterone Plays a Part
Self-insemination is a method of conception where a person uses their own sperm or a known donor’s sperm to fertilize their own egg. This method has become increasingly popular among individuals and couples who are unable to conceive through traditional methods. While there are many factors that play a role in successful self-insemination, one key player is progesterone. In this blog post, we will explore the science behind self-insemination and how progesterone plays a crucial role in this process.
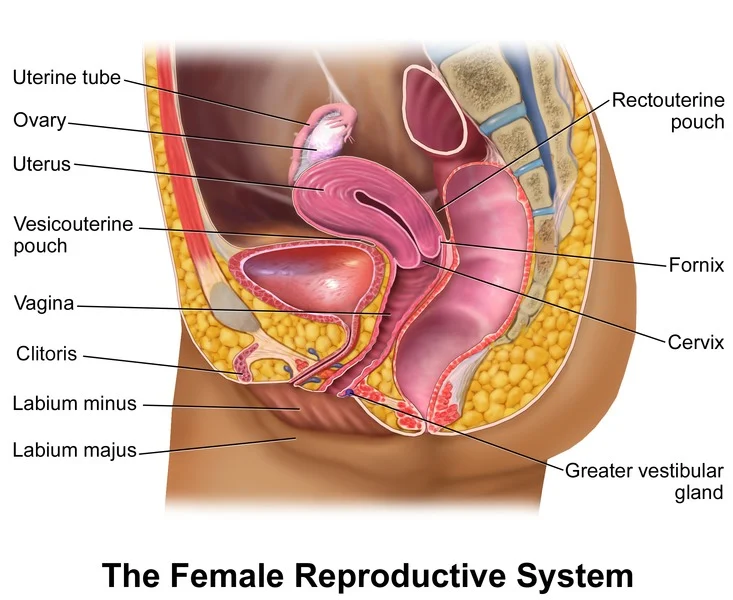
First, it is important to understand what progesterone is and how it functions in the body. Progesterone is a hormone produced by the ovaries in females and the testes in males. In females, it plays a vital role in the menstrual cycle and pregnancy. During the first half of the menstrual cycle, estrogen is the dominant hormone and helps to prepare the uterus for potential pregnancy. In the second half of the cycle, progesterone takes over and helps to maintain the uterine lining, preparing it for the implantation of a fertilized egg.
When it comes to self-insemination, progesterone plays a crucial role in two main ways. First, it helps to create an environment in the uterus that is conducive for fertilization and implantation. This is because progesterone causes the uterine lining to thicken, creating a nourishing environment for a fertilized egg to implant and grow. Without enough progesterone, the uterine lining may not be thick enough, making it difficult for a fertilized egg to successfully implant.
The Science of Self-Insemination: How Progesterone Plays a Part
Secondly, progesterone helps to regulate the timing of ovulation. Ovulation is the process where an egg is released from the ovary and travels down the fallopian tube, where it can potentially be fertilized by sperm. In a typical menstrual cycle, ovulation occurs around day 14. However, in self-insemination, timing is crucial as sperm can only survive in the female reproductive tract for a limited amount of time. Progesterone levels rise just before ovulation, signaling the release of an egg. By tracking progesterone levels, individuals can better predict when ovulation will occur and increase their chances of successful self-insemination.
So, how can individuals track their progesterone levels? One method is through the use of ovulation predictor kits (OPKs). These kits measure the levels of luteinizing hormone (LH) in urine, which surges just before ovulation occurs. However, in self-insemination, it is important to also track progesterone levels after ovulation has occurred. This can be done through blood tests or saliva tests. Blood tests measure the levels of progesterone in the blood, while saliva tests measure the levels of progesterone in saliva. Both of these methods can provide valuable information about an individual’s progesterone levels and help them determine the best time for self-insemination.
In addition to tracking progesterone levels, there are other factors that can affect the success of self-insemination. These include the quality and quantity of sperm, the timing of insemination, and the overall health of the individual. It is important to have a healthy lifestyle and to consult with a healthcare provider before attempting self-insemination.
While self-insemination can be a successful method of conception, it is important to note that it may not be suitable for everyone. Individuals with certain health conditions or fertility issues may not be good candidates for self-insemination. It is always recommended to consult with a healthcare provider before attempting this method.
In conclusion, progesterone plays a crucial role in self-insemination. It helps to create a favorable environment in the uterus for fertilization and implantation, and it also helps to regulate the timing of ovulation. By tracking progesterone levels, individuals can increase their chances of successful self-insemination. However, it is important to note that self-insemination may not be suitable for everyone and it is always best to consult with a healthcare provider before attempting this method.