The Science of Ovulation: Understanding the Optimal Timing for Self-Insemination
Ovulation is a crucial part of the menstrual cycle and is essential for conception. Understanding the science behind ovulation and its optimal timing is crucial for individuals or couples who are planning to self-inseminate. In this blog post, we will dive into the science of ovulation and explore the factors that affect its timing. We will also provide tips and techniques for self-insemination to increase the chances of successful conception.
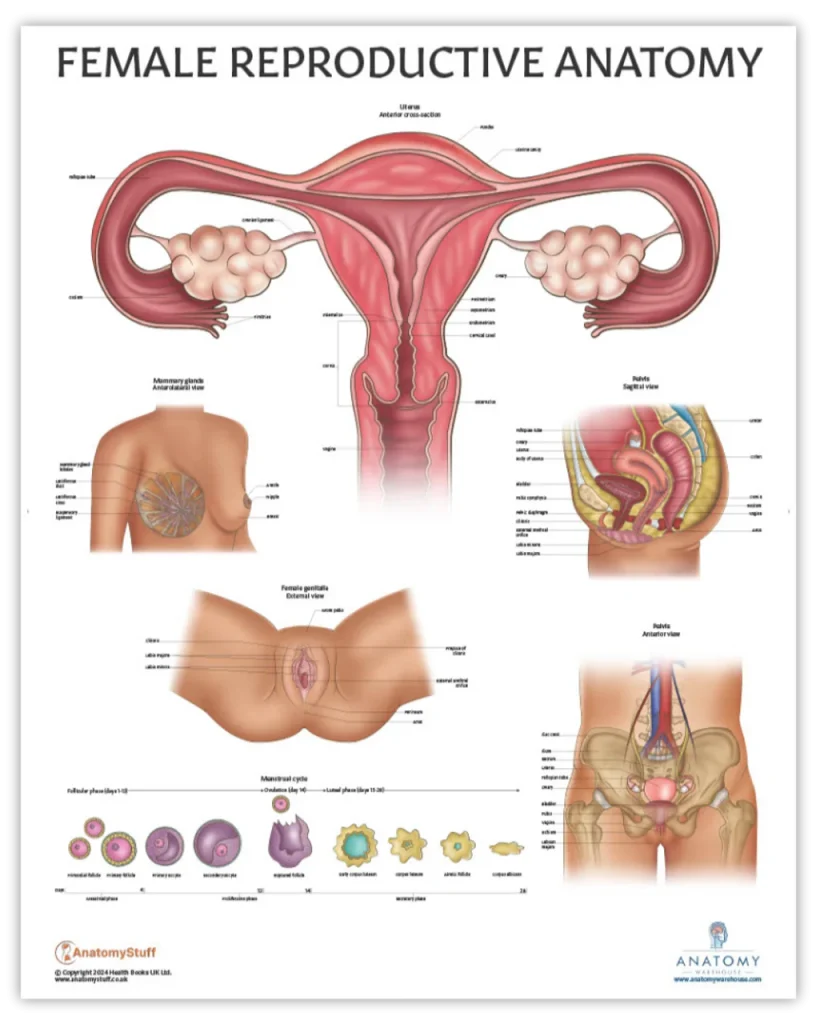
To begin with, ovulation is the process where a mature egg is released from the ovary and travels down the fallopian tube, where it can be fertilized by sperm. It usually occurs once a month, around the middle of the menstrual cycle. However, the exact timing can vary from person to person and can even vary from cycle to cycle. This is why understanding the science behind ovulation is crucial for self-insemination.
So, what factors affect the timing of ovulation? The most significant factor is the length of the menstrual cycle. The average menstrual cycle is 28 days, but it can range from 21 to 35 days. Ovulation typically occurs around day 14 for individuals with a 28-day cycle. For those with longer or shorter cycles, ovulation can occur earlier or later in the cycle.
Another essential factor is hormonal fluctuations. The menstrual cycle is regulated by the hormones estrogen and progesterone, produced by the ovaries. These hormones work together to control the development and release of the egg. Estrogen levels rise in the first half of the cycle, stimulating the growth of the uterine lining. As ovulation approaches, estrogen levels peak, triggering a surge of luteinizing hormone (LH), which causes the egg to be released. This surge in LH can be detected through ovulation predictor kits, which can help to pinpoint the optimal timing for self-insemination.
The Science of Ovulation: Understanding the Optimal Timing for Self-Insemination
Aside from the menstrual cycle and hormonal fluctuations, other factors can also affect the timing of ovulation. These include stress, illness, and changes in routine or diet. It is essential to keep track of these factors and their potential effects on ovulation to increase the chances of successful self-insemination.
Now that we understand the science behind ovulation and its timing let’s discuss the techniques for self-insemination. The most common method is the “turkey baster” method, where the sperm is collected and inserted into the vagina using a clean, sterile syringe. However, this method is not always successful since the sperm may not reach the uterus or fallopian tubes, where fertilization occurs.
A more effective technique is intrauterine insemination (IUI), where the sperm is inserted directly into the uterus using a catheter. This method is usually performed by a healthcare professional but can also be done at home with the help of a donor or partner. IUI has a higher success rate compared to the “turkey baster” method, as it bypasses the cervix and places the sperm closer to the egg.
Timing is crucial when it comes to self-insemination. The best time to self-inseminate is around the time of ovulation, as this is when the egg is released and ready to be fertilized. However, sperm can survive inside the female reproductive tract for up to five days, so it is also recommended to self-inseminate a few days before ovulation to increase the chances of success.
In conclusion, understanding the science of ovulation and its optimal timing is crucial for self-insemination. Factors such as the length of the menstrual cycle, hormonal fluctuations, and lifestyle can affect the timing of ovulation. By keeping track of these factors and using techniques like ovulation predictor kits and IUI, individuals or couples can increase their chances of successful self-insemination. Remember, timing is everything when it comes to conceiving, so be sure to plan and track carefully.
Search Queries:
1. “How to self-inseminate using the turkey baster method”
2. “Ovulation predictor kits for self-insemination”
3. “Understanding the science behind ovulation for self-insemination”
4. “Tips for successful self-insemination”
5. “Intrauterine insemination at home: a step-by-step guide”