Blog post:
When a couple is trying to conceive, there are various methods available to help increase their chances of conception. One of these methods is self-insemination, which involves the process of manually placing sperm into the vagina in order to fertilize an egg. This method can be used by heterosexual couples, same-sex couples, and single women who are looking to start a family. In this blog post, we will delve into the science behind self-insemination and how it can increase your chances of conception.
The Science Behind Self-Insemination
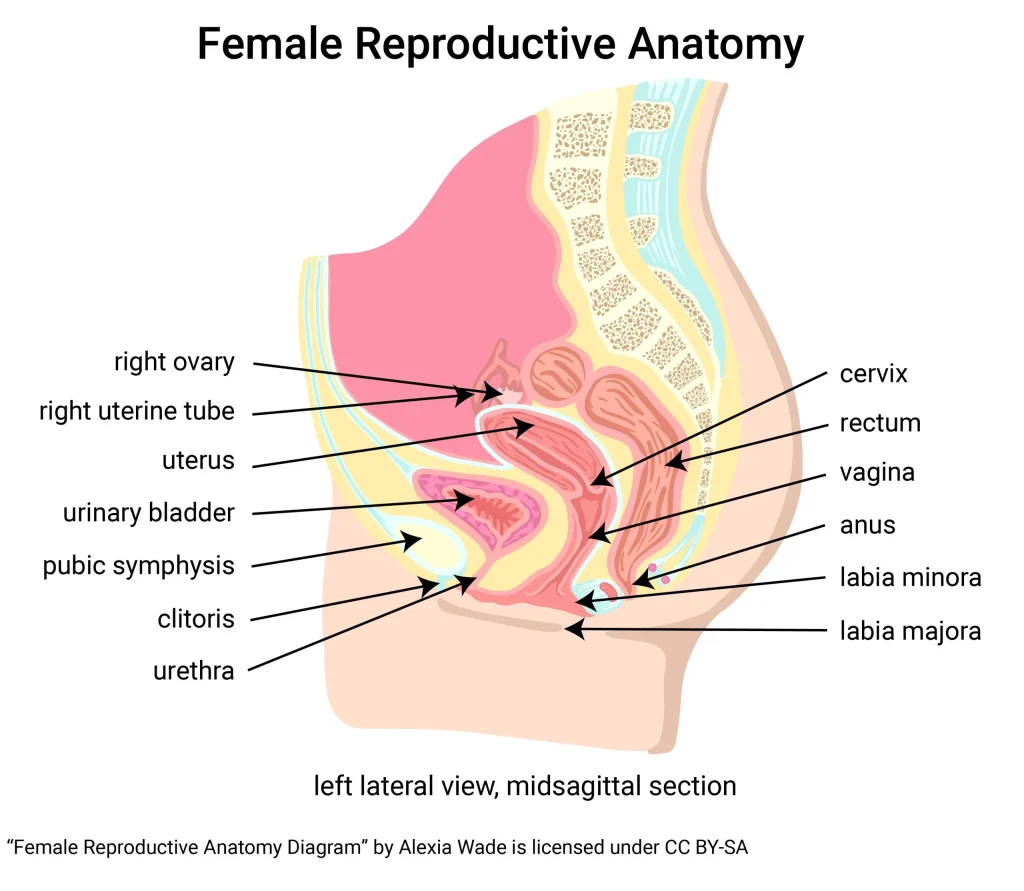
Self-insemination, also known as self-insemination at home or self-insemination with donor sperm, is a process that involves the use of a syringe or a cervical cap to manually place sperm into the vagina. This method can be done at home without the need for medical assistance, making it a more convenient and cost-effective option for many couples.
The key to successful self-insemination is timing. Sperm can survive in the female reproductive tract for up to five days, so it is important to track ovulation and have intercourse or self-insemination during the most fertile days of the menstrual cycle. This can be done using ovulation predictor kits or by tracking basal body temperature and cervical mucus changes.
Using fresh or frozen sperm from a known donor or a sperm bank, the sperm is collected and placed into a sterile cup or syringe. The woman then inserts the sperm into her vagina, close to the cervix, using a syringe or a cervical cap. The sperm can then travel to the fallopian tubes and fertilize an egg, just like in natural conception.
Increasing Your Chances of Conception with Self-Insemination
Self-insemination can be a successful method of conception for many couples. However, there are certain factors that can affect its success rate. These include:
1. Ovulation Timing: As mentioned earlier, timing is crucial when it comes to self-insemination. It is important to track ovulation accurately and have intercourse or self-insemination during the most fertile days of the menstrual cycle.
The Science Behind Self-Insemination: Increasing Your Chances of Conception
2. Sperm Quality: The quality of the sperm used for self-insemination can also affect its success rate. Fresh sperm is usually more viable than frozen sperm, so using fresh sperm can increase the chances of conception.
3. Cervical Mucus: Cervical mucus plays an important role in conception as it helps sperm travel to the fallopian tubes. Having the right consistency and amount of cervical mucus can make it easier for sperm to reach the egg.
4. Underlying Health Conditions: Certain health conditions such as PCOS, endometriosis, or blocked fallopian tubes can affect the success of self-insemination. It is important to address any underlying health issues before attempting self-insemination.
5. Age: As women age, their fertility decreases, making it more difficult to conceive. This can also affect the success rate of self-insemination, especially for women over the age of 35.
Overall, self-insemination can be a successful method of conception for many couples, but it is important to keep in mind that it may not work for everyone. It is always recommended to consult with a fertility specialist or a doctor before attempting self-insemination to ensure that all factors are considered and increase the chances of success.
Search Queries:
1. “How to increase chances of conception with self-insemination”
2. “Self-insemination: The science behind it”
3. “Tips for successful self-insemination”
4. “Using ovulation kits for self-insemination”
5. “Self-insemination vs. traditional insemination: Which is more effective?”
Summary:
Self-insemination is a method of conception that involves manually placing sperm into the vagina. It can be used by couples, same-sex couples, and single women who are looking to start a family. Timing, sperm quality, cervical mucus, underlying health conditions, and age are all factors that can affect the success of self-insemination. It is important to track ovulation accurately and address any underlying health issues before attempting self-insemination.