The Science Behind Frozen and Fresh Sperm Insemination: A Comprehensive Guide
In recent years, the use of sperm insemination has become an increasingly popular method for couples struggling with fertility. This procedure involves the placement of sperm directly into the uterus or cervix of a woman in order to increase the chances of fertilization. While fresh sperm insemination has been the traditional method, the use of frozen sperm has also gained traction. In this blog post, we will delve into the science behind both frozen and fresh sperm insemination, exploring their differences, effectiveness, and potential benefits.
Search Queries:
1. “What is the difference between frozen and fresh sperm insemination?”
2. “How does sperm insemination work?”
3. “What are the success rates of frozen and fresh sperm insemination?”
4. “Is frozen sperm as effective as fresh sperm for insemination?”
5. “What are the benefits of using frozen sperm for insemination?”
Fresh Sperm Insemination:
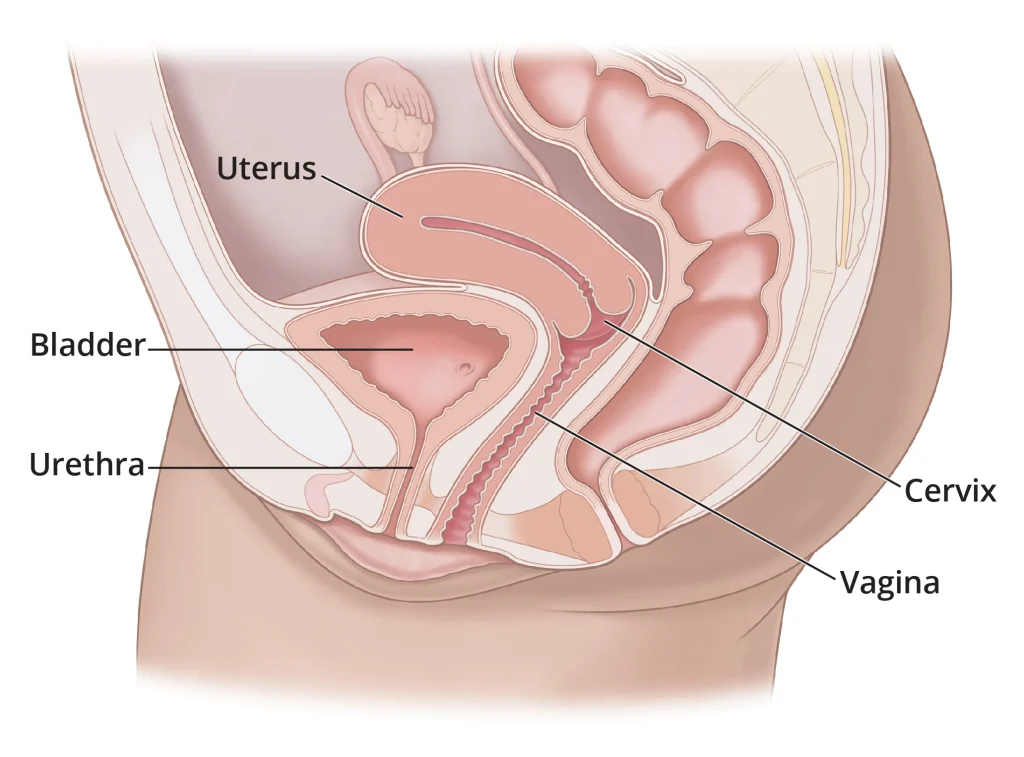
Fresh sperm insemination, also known as intrauterine insemination (IUI), involves the insertion of freshly collected sperm directly into the uterus. This is typically done around the time of ovulation, in order to increase the chances of the sperm reaching and fertilizing the egg. The process of collecting the sperm involves masturbation, and the sample is then washed to remove any potentially harmful substances. The sperm is then injected into the uterus using a thin catheter.
One of the main benefits of fresh sperm insemination is that it can be timed according to the woman’s ovulation cycle, which increases the chances of fertilization. Additionally, fresh sperm has a higher concentration and motility, making it more likely to successfully fertilize an egg. However, there are also some drawbacks to using fresh sperm. The sperm must be collected on the day of the insemination, which can be inconvenient and stressful for both partners. There is also the risk of contamination or infection during the collection process.
The Science Behind Frozen and Fresh Sperm Insemination
Frozen Sperm Insemination:
Frozen sperm insemination, also known as cryopreserved sperm insemination, involves the use of sperm that has been frozen and stored in a sperm bank. This method is typically used when the male partner is unable to produce a fresh sample or if there is a need to preserve the sperm due to medical reasons. The frozen sperm is thawed prior to the insemination procedure and then inserted into the uterus in the same manner as fresh sperm insemination.
While frozen sperm may not have the same high concentration and motility as fresh sperm, it can still be effective for insemination. The freezing process can cause some damage to the sperm, but modern techniques have improved the chances of successful fertilization. Additionally, using frozen sperm allows for more flexibility in timing, as the sperm can be stored for future use. This method can also be less stressful for both partners, as the sperm can be collected in advance and does not require a specific schedule.
Comparing Success Rates:
Both fresh and frozen sperm insemination have been found to be effective methods for increasing the chances of pregnancy. Success rates vary depending on factors such as the age of the female partner, the quality of the sperm, and any underlying fertility issues. According to research, the success rates for fresh sperm insemination range from 10-20%, while the success rates for frozen sperm insemination range from 5-15%. However, it is important to note that success rates can also be affected by the expertise of the medical team performing the insemination.
Benefits of Frozen Sperm Insemination:
There are several potential benefits to using frozen sperm for insemination. As mentioned, it allows for flexibility in timing and can be less stressful for both partners. Additionally, using frozen sperm can be more cost-effective, as it eliminates the need for frequent visits to the clinic for fresh sperm collection. It can also be beneficial for couples who need to delay pregnancy due to personal or medical reasons, as the sperm can be stored for longer periods of time.
In summary, both frozen and fresh sperm insemination can be effective methods for increasing the chances of pregnancy. While fresh sperm has a higher concentration and motility, frozen sperm offers more flexibility and convenience. Success rates can vary and are dependent on various factors, but both methods have been found to be successful in helping couples conceive. Ultimately, the choice between frozen and fresh sperm insemination will depend on the specific needs and preferences of each couple.