Blog Post:
The process of self-insemination, or self-inseminating at home, has become a popular option for individuals or couples looking to start a family. This method involves using a donor’s sperm to fertilize an egg, without the need for medical intervention. While there are various methods of self-insemination, one key component in this process is the hormone progesterone.
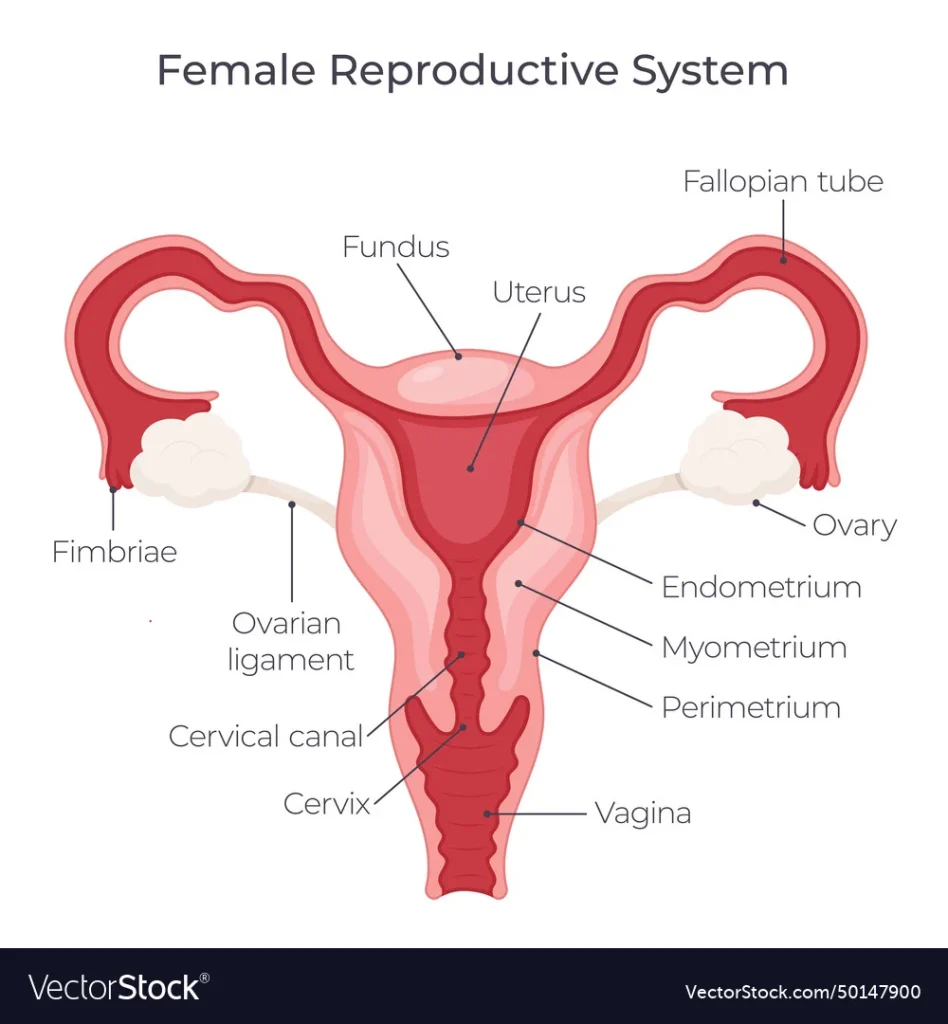
Progesterone is a hormone naturally produced by the body, specifically by the ovaries in females. It plays a crucial role in the menstrual cycle and pregnancy. In the context of self-insemination, progesterone helps to thicken the lining of the uterus, making it a more hospitable environment for the fertilized egg to implant and grow.
In this blog post, we will discuss the role of progesterone in self-insemination, and provide a step-by-step process for those considering this method of conception.
Step 1: Know Your Cycle
Before attempting self-insemination, it is essential to understand your menstrual cycle. This includes tracking your ovulation, which is when an egg is released from the ovaries. This usually occurs around day 14 of a 28-day cycle, but can vary from person to person. There are various methods for tracking ovulation, such as using ovulation predictor kits or tracking your basal body temperature.
Understanding your cycle will help you determine the best time for self-insemination, as it is crucial to have a thickened uterine lining for the fertilized egg to implant.
Step 2: Obtain Donor Sperm
The next step is to obtain donor sperm. This can be done through a sperm bank or by using a known donor. It is essential to ensure that the donor has been screened for any potential genetic or infectious diseases. It is also recommended to have the donor undergo a semen analysis to ensure the sperm is healthy and viable.
The Role of Progesterone in Self-Insemination: A Step-by-Step Process
Step 3: Prepare for Self-Insemination
Before self-insemination, it is necessary to prepare the body by increasing the levels of progesterone. This can be done through various methods, such as taking progesterone supplements, using natural progesterone creams, or consuming foods that are high in progesterone, such as avocado, nuts, and seeds.
It is also recommended to use an ovulation induction medication, such as Clomid, to stimulate the ovaries and increase the chances of ovulation.
Step 4: Self-Insemination
Once the body is prepared, it is time for self-insemination. This can be done using a syringe or a cervical cap. The sperm is placed near the cervix, and the person undergoing insemination can use their fingers to help guide the sperm into the cervix.
Step 5: Rest and Relax
After self-insemination, it is crucial to rest and relax for at least 20 to 30 minutes to allow the sperm to travel to the uterus. This will also help to increase the chances of successful fertilization.
Step 6: Monitor and Follow-Up
After self-insemination, it is essential to monitor the body for any signs of pregnancy. This can include tracking your basal body temperature, taking a pregnancy test, or monitoring any changes in your body. It is also recommended to follow up with a healthcare provider to confirm pregnancy and receive proper prenatal care.
In summary, self-insemination is a method of conception that involves using donor sperm to fertilize an egg without medical intervention. The hormone progesterone plays a crucial role in this process, as it helps to thicken the lining of the uterus for successful implantation and pregnancy. By understanding your menstrual cycle, obtaining donor sperm, preparing the body, and following the step-by-step process outlined in this blog post, individuals or couples can increase their chances of successful self-insemination and starting a family.