The decision to start a family through self-insemination can be an exciting and empowering one. It allows individuals and couples to take control of their fertility journey and create a family on their own terms. However, just like any other method of conception, proper preparation is essential for a successful outcome. One crucial aspect of this preparation is nutrition. In this blog post, we will explore the role of nutrition in preparing for self-insemination and how it can improve your chances of achieving a healthy and successful pregnancy.
Before we dive into the specifics, it’s important to understand the basics of self-insemination. Self-insemination, also known as self-impregnation, is the process of manually placing sperm into the vagina in order to achieve pregnancy. This can be done using a variety of methods, such as a turkey baster, syringe, or cervical cap. It is a popular choice for same-sex couples, single individuals, and couples struggling with fertility issues.
Nutrition plays a crucial role in the success of self-insemination for several reasons. First and foremost, a healthy and balanced diet is essential for overall fertility and reproductive health. Proper nutrition can help regulate hormones, improve egg quality, and increase sperm count and motility. Additionally, certain nutrients are specifically beneficial for conception and pregnancy.
One of the most important nutrients for self-insemination is folic acid. Folic acid is a B vitamin that is crucial for fetal development and can help prevent birth defects. It is recommended for women to start taking folic acid at least one month before trying to conceive. Good sources of folic acid include leafy green vegetables, legumes, and fortified cereals.
Another important nutrient for self-insemination is iron. Iron plays a vital role in the production of healthy eggs and sperm. It is also essential for maintaining a healthy pregnancy and preventing anemia. Good sources of iron include lean meats, leafy green vegetables, and fortified cereals.
Omega-3 fatty acids are also crucial for self-insemination. These healthy fats can help regulate hormones and improve sperm quality. They can also reduce the risk of complications during pregnancy, such as preeclampsia. Good sources of omega-3s include fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts.
In addition to specific nutrients, a healthy and balanced diet is essential for self-insemination. This includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. It is also important to limit or avoid processed foods, trans fats, and excessive amounts of caffeine and alcohol.
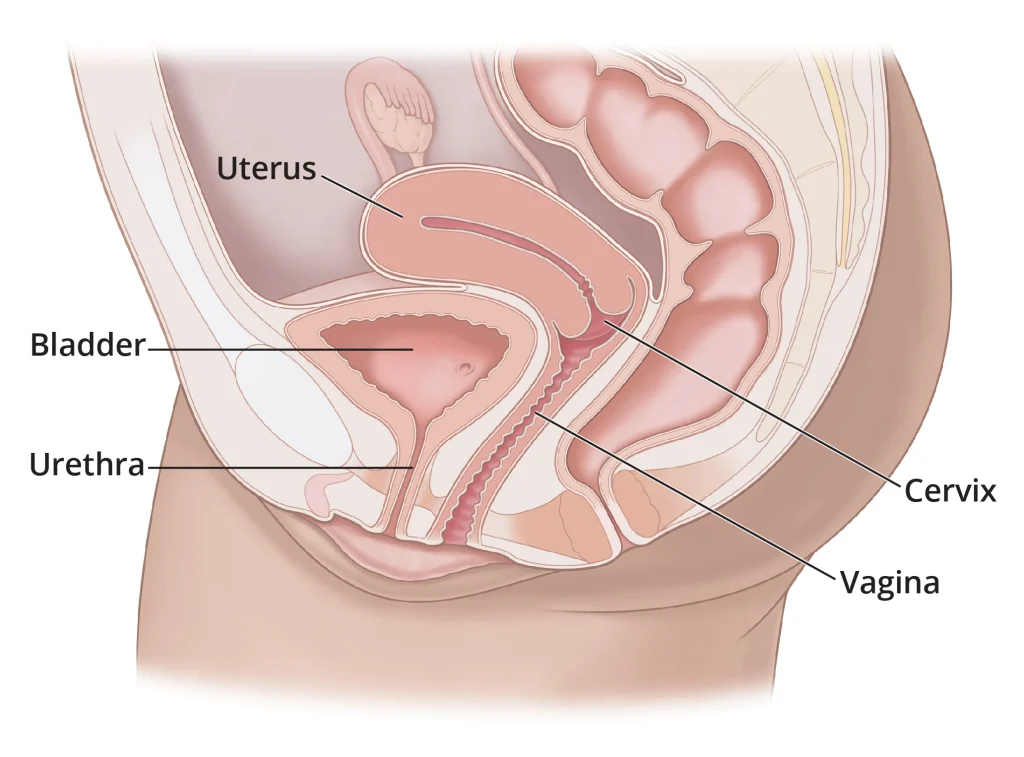
The Role of Nutrition in Preparing for Self-Insemination
In addition to nutrition, maintaining a healthy weight is also important for self-insemination. Being overweight or underweight can affect hormone levels and disrupt ovulation. It is recommended to aim for a body mass index (BMI) between 18.5-24.9 for optimal fertility.
In some cases, supplements may be recommended to support self-insemination. These may include prenatal vitamins, coenzyme Q10, and vitamin D. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplements.
Aside from nutrition, there are other lifestyle factors that can impact the success of self-insemination. These include stress management, exercise, and avoiding harmful substances. Finding healthy ways to cope with stress, such as yoga or meditation, can help regulate hormone levels and improve fertility. Moderate exercise can also be beneficial, but it is important not to overdo it, as excessive exercise can also affect fertility.
Avoiding harmful substances, such as tobacco and recreational drugs, is crucial for self-insemination. These substances can not only decrease fertility but can also increase the risk of complications during pregnancy. It is also recommended to limit caffeine intake and avoid alcohol completely during the conception and pregnancy process.
In addition to proper nutrition and lifestyle habits, it is also important to track ovulation and time self-insemination accordingly. This can be done using ovulation predictor kits or tracking basal body temperature. It is also recommended to have regular check-ups with a healthcare provider to monitor overall health and fertility.
In conclusion, nutrition plays a crucial role in preparing for self-insemination. A healthy and balanced diet, along with proper lifestyle habits, can improve overall fertility and increase the chances of a successful pregnancy. By focusing on key nutrients and maintaining a healthy weight, individuals and couples can take proactive steps to prepare for self-insemination and achieve their dream of starting a family.
Search Queries:
1. “How can nutrition improve self-insemination success?”
2. “What nutrients are important for self-insemination?”
3. “Can a healthy diet increase chances of self-insemination?”
4. “Tips for preparing for self-insemination”
5. “The link between nutrition and fertility in self-insemination”