The Role of Hormones in Your Menstrual Cycle and Fertility
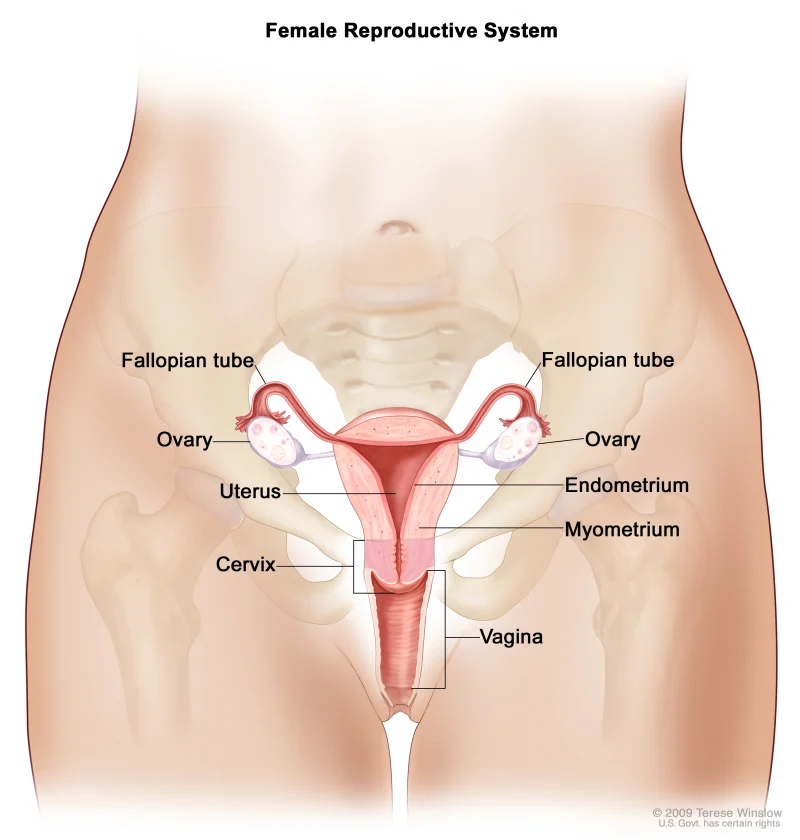
The female reproductive system is a complex and intricate system that is regulated by a delicate balance of hormones. These hormones play a crucial role in the menstrual cycle and fertility of a woman. Understanding the role of hormones in the female reproductive system is essential for women to understand their bodies and reproductive health. In this blog post, we will dive deeper into the hormones involved in the menstrual cycle and fertility and how they impact a woman’s reproductive health.
Hormones and the Menstrual Cycle
The menstrual cycle is the monthly process that occurs in a woman’s body to prepare for pregnancy. The average menstrual cycle lasts about 28 days, but it can range from 21 to 35 days. During this cycle, the body goes through several changes, including the thickening of the uterine lining, the release of an egg from the ovaries, and the shedding of the uterine lining if pregnancy does not occur. All of these changes are controlled and regulated by hormones.
The main hormones involved in the menstrual cycle are estrogen, progesterone, follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), and luteinizing hormone (LH). Each of these hormones plays a specific role in the menstrual cycle.
Estrogen
Estrogen is a vital female sex hormone that is responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system. During the first half of the menstrual cycle, estrogen levels increase, which causes the uterine lining to thicken in preparation for pregnancy. Estrogen also stimulates the production of FSH, which is responsible for the growth and development of the ovarian follicles.
Progesterone
Progesterone is another essential hormone in the menstrual cycle. After the ovulation of an egg, the ruptured follicle transforms into a structure called the corpus luteum. The corpus luteum produces progesterone, which helps to maintain the thickened uterine lining and prepares the uterus for pregnancy. If pregnancy does not occur, the corpus luteum disintegrates, and progesterone levels drop, leading to the shedding of the uterine lining and the start of a new menstrual cycle.
Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
FSH is a hormone that is released by the pituitary gland in the brain. It plays a crucial role in the development of the ovarian follicles, which are tiny fluid-filled sacs in the ovaries that contain the eggs. During the menstrual cycle, FSH levels rise, stimulating the growth and maturation of the follicles. As the follicles mature, they produce estrogen, which further stimulates the thickening of the uterine lining.
The Role of Hormones in Your Menstrual Cycle and Fertility
Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
LH is also released by the pituitary gland and works in conjunction with FSH to regulate the menstrual cycle. As the follicles mature, LH levels increase, leading to the release of an egg from the ovaries, also known as ovulation. LH also stimulates the production of progesterone by the corpus luteum, which is essential for maintaining a thick uterine lining.
Hormones and Fertility
Hormones play a crucial role in a woman’s fertility by regulating the menstrual cycle and preparing the body for pregnancy. A woman’s fertility is at its peak during her reproductive years, which typically start at puberty and end with menopause. During this time, the body goes through monthly cycles in preparation for pregnancy, and hormones play a vital role in this process.
Fertility is directly linked to the levels of estrogen and progesterone in a woman’s body. If these hormones are not in balance, it can lead to irregular menstrual cycles or even difficulty conceiving. For example, a decrease in estrogen levels can cause irregular ovulation, making it challenging to get pregnant. On the other hand, an excess of estrogen can lead to the development of conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), which can also affect fertility. It is crucial for women to have balanced hormone levels for optimal fertility and reproductive health.
Hormonal Imbalances and Reproductive Health
Hormonal imbalances can also have a significant impact on a woman’s reproductive health. Irregularities in hormone levels can cause a variety of issues, such as irregular menstrual cycles, heavy or painful periods, and even difficulty conceiving. Hormonal imbalances can be caused by various factors, such as stress, diet, exercise, and underlying health conditions.
For example, thyroid disorders can disrupt the production of hormones and affect a woman’s menstrual cycle and fertility. Similarly, conditions such as PCOS and endometriosis can also cause hormonal imbalances and affect reproductive health. It is essential to address any hormonal imbalances promptly and seek medical advice if necessary to maintain optimal reproductive health.
In conclusion, hormones play a vital role in the menstrual cycle and fertility of a woman. They regulate the monthly changes in the female reproductive system and prepare the body for pregnancy. A balanced hormonal system is crucial for optimal reproductive health, and any imbalances should be addressed promptly. By understanding the role of hormones in the menstrual cycle and fertility, women can take better control of their reproductive health and overall well-being.
Probable Search Queries:
1. What are the hormones involved in the menstrual cycle?
2. How do hormones affect fertility?
3. What are the main hormones involved in female reproductive health?
4. Can hormonal imbalances affect fertility?
5. What are the symptoms of hormonal imbalances in women?