Keywords: Hormones, Self-Insemination, Women, Low Ovarian Reserve, Fertility, Reproductive Health, Artificial Insemination, Ovulation, FSH, LH, Progesterone, IVF
The Role of Hormones in Self-Insemination for Women with Low Ovarian Reserve
For many women, the dream of becoming a mother is one of the most important and meaningful desires in life. However, for women with low ovarian reserve, the chances of conceiving naturally can be significantly reduced. This can be a challenging reality for those who are hoping to start a family, but thanks to advancements in reproductive health, there are now ways to increase the chances of pregnancy, such as self-insemination. In this blog post, we will discuss the role of hormones in self-insemination for women with low ovarian reserve and how it can help them achieve their dream of motherhood.
Self-insemination, also known as self-IVF or self-injection, is a method of artificial insemination that allows women to inseminate themselves at home. This method is particularly useful for women with low ovarian reserve because it eliminates the need for multiple visits to a fertility clinic, which can be time-consuming and costly. Instead, women can track their ovulation and administer the necessary hormones and medications themselves with the guidance of a medical professional.
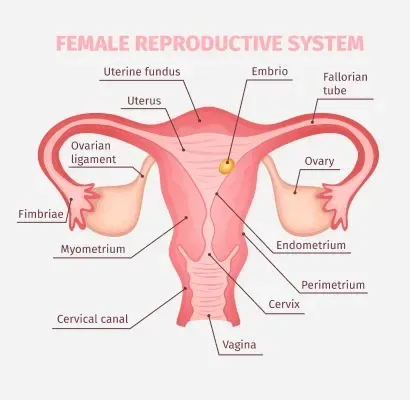
One of the key hormones involved in self-insemination is follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). This hormone is responsible for stimulating the growth and development of follicles, which contain the eggs. In women with low ovarian reserve, the number of follicles is reduced, which can make it difficult to conceive. However, by administering FSH injections, the ovaries can be stimulated to produce more follicles, increasing the chances of ovulation and pregnancy.
The Role of Hormones in Self-Insemination for Women with Low Ovarian Reserve
Another hormone involved in self-insemination is luteinizing hormone (LH). This hormone is responsible for triggering ovulation, or the release of an egg from the ovary. In women with low ovarian reserve, LH levels may be low, making it difficult for the egg to be released. By tracking LH levels and administering LH injections, the chances of ovulation and pregnancy can be improved.
Progesterone is another hormone that plays a vital role in self-insemination for women with low ovarian reserve. After ovulation, the ruptured follicle turns into a structure called the corpus luteum, which produces progesterone. This hormone helps prepare the uterine lining for the implantation of a fertilized egg. In women with low ovarian reserve, the corpus luteum may not produce enough progesterone, making it difficult for a fertilized egg to implant. By administering progesterone supplements, the chances of a successful pregnancy can be increased.
Self-insemination for women with low ovarian reserve involves a combination of hormone injections and medications to prepare the body for pregnancy. These hormones work together to stimulate the ovaries, trigger ovulation, and prepare the uterus for implantation. This method is often used in conjunction with techniques like intrauterine insemination (IUI) or in vitro fertilization (IVF) to further increase the chances of pregnancy.
It is essential to note that self-insemination should only be done under the guidance and supervision of a medical professional. Hormone levels need to be monitored closely, and the timing of the injections is critical for the success of the procedure. Additionally, women with low ovarian reserve may also have other underlying fertility issues that need to be addressed, and self-insemination may not be the most suitable option for everyone.
In conclusion, the role of hormones in self-insemination for women with low ovarian reserve is crucial in increasing the chances of pregnancy. FSH, LH, and progesterone work together to stimulate the ovaries, trigger ovulation, and prepare the uterus for implantation. However, it is essential to consult with a medical professional and undergo thorough testing before embarking on this journey. With the right guidance and support, self-insemination can be a successful option for women with low ovarian reserve to achieve their dream of motherhood.
Search Queries:
1. How can hormones help with self-insemination for women with low ovarian reserve?
2. What is the role of FSH in self-insemination for women with low ovarian reserve?
3. Can self-insemination be a successful option for women with low ovarian reserve?
4. What are the benefits of self-insemination for women with low ovarian reserve?
5. What are the potential risks of self-insemination for women with low ovarian reserve?