Ovulation is a crucial part of a woman’s menstrual cycle, as it is the main process responsible for fertility and conception. It is the release of an egg from the ovary, which then travels down the fallopian tube where it can be fertilized by sperm. However, ovulation can be a tricky thing to track, especially for women who have irregular menstrual cycles. This is where understanding the role of hormones in ovulation tracking becomes essential.
Hormones play a significant role in regulating and signaling ovulation. These chemical messengers are produced by the endocrine glands and are responsible for various bodily functions, including the menstrual cycle. In this blog post, we will dive deeper into the role of hormones in ovulation tracking and how understanding your body’s signals can help you plan for pregnancy or simply keep track of your menstrual cycle.
1. What are hormones, and how do they regulate ovulation?
2a. What are the different hormones involved in ovulation tracking?
2b. How do these hormones work together to signal ovulation?
3. How does ovulation tracking work?
4. What are the different methods for tracking ovulation?
5. How can understanding your body’s signals help in ovulation tracking?
Hormones are chemical messengers that are produced by various endocrine glands in the body. They are responsible for regulating and controlling various bodily functions, such as metabolism, growth, and reproduction. In terms of ovulation, hormones play a crucial role in signaling when an egg is released from the ovary.
The main hormone responsible for ovulation is called luteinizing hormone (LH). This hormone is produced by the pituitary gland and is responsible for stimulating the ovary to release an egg. LH levels rise sharply just before ovulation, typically around day 14 of a 28-day menstrual cycle. This surge in LH triggers the release of an egg from the ovary, which can then travel down the fallopian tube.
Another hormone involved in ovulation is follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). This hormone is also produced by the pituitary gland and is responsible for stimulating the growth and development of follicles in the ovary. Follicles are small sacs that contain eggs. As FSH levels increase, the follicles grow in size until one of them becomes dominant and releases an egg during ovulation.
Estrogen and progesterone are two other hormones that play a crucial role in ovulation. These hormones are produced by the ovaries and are responsible for preparing the uterus for a potential pregnancy. Estrogen levels rise during the first half of the menstrual cycle, leading up to ovulation. After ovulation, progesterone levels rise, causing the lining of the uterus to thicken in preparation for a fertilized egg to implant.
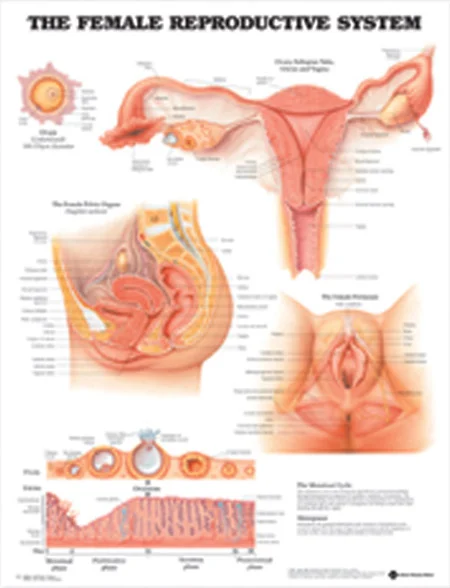
The Role of Hormones in Ovulation Tracking: Understanding Your Body's Signals
These hormones work together in a carefully orchestrated dance to signal ovulation. As the follicles grow and produce estrogen, it triggers a surge in LH, which then causes the dominant follicle to release an egg. After ovulation, progesterone levels rise, maintaining the thickness of the uterine lining and preparing the body for a potential pregnancy. If fertilization does not occur, the levels of estrogen and progesterone eventually drop, and menstruation occurs, starting a new cycle.
Ovulation tracking is the process of monitoring your menstrual cycle to determine when you are most likely to ovulate. This can be helpful for women who are trying to conceive, as well as those who want to understand their bodies better. There are various methods for tracking ovulation, including:
1. Basal body temperature (BBT) tracking: This involves taking your temperature every morning and tracking any changes. After ovulation, the body’s temperature rises slightly due to an increase in progesterone levels. Tracking these temperature changes can help pinpoint when ovulation occurs.
2. Cervical mucus monitoring: The consistency and color of your cervical mucus can also indicate where you are in your menstrual cycle. As ovulation approaches, cervical mucus becomes thinner and more slippery, making it easier for sperm to travel through the cervix.
3. Ovulation predictor kits: These kits measure the levels of LH in your urine and can help predict when ovulation will occur. They work similarly to a pregnancy test and are available over the counter at most drug stores.
4. Menstrual cycle tracking apps: There are various apps available that help track your menstrual cycle, including ovulation. These apps use data such as your period start date, BBT, and cervical mucus to predict when you are most likely to ovulate.
Understanding your body’s signals is essential in ovulation tracking. By paying attention to changes in your body, such as cervical mucus, BBT, and other symptoms, you can better predict when ovulation will occur. Additionally, tracking your cycle over several months can help you identify patterns and determine if your hormones are in balance.
In conclusion, hormones play a crucial role in ovulation tracking by signaling the release of an egg from the ovary. By understanding the different hormones involved and how they work together, women can better track their ovulation and plan for pregnancy or simply keep track of their menstrual cycle. With various methods available, understanding your body’s signals can help you take control of your fertility and reproductive health.