Hormones play a crucial role in the reproductive system of women, specifically in ovulation and pregnancy. These chemical messengers send signals to different parts of the body, regulating various processes and ensuring the success of pregnancy. In this blog post, we will delve deeper into the role of hormones in ovulation and pregnancy success, and how understanding them can help women in their journey towards motherhood.
One of the primary hormones involved in ovulation is follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). Produced by the pituitary gland, FSH stimulates the growth and development of follicles in the ovaries, which contain the eggs. As the follicles mature, they produce another hormone called estrogen. Estrogen is responsible for thickening the uterine lining, preparing it for a potential pregnancy.
As the follicles continue to grow, they produce even more estrogen, which triggers a sudden surge of luteinizing hormone (LH). This surge is essential for ovulation to occur. LH causes the dominant follicle to burst, releasing the mature egg into the fallopian tube. This is the process of ovulation, which usually happens around day 14 of a woman’s menstrual cycle.
Once the egg is released, the remaining follicle transforms into the corpus luteum, which produces progesterone. Progesterone is crucial for preparing the uterus for implantation and maintaining the pregnancy. It thickens the uterine lining further, making it an ideal environment for the fertilized egg to implant and grow.
If fertilization does not occur, the corpus luteum will start to break down, leading to a drop in progesterone levels. This drop triggers the start of the next menstrual cycle. However, if the egg is fertilized, it will implant in the thickened uterine lining, and the corpus luteum will continue to produce progesterone to support the pregnancy.
Aside from FSH, LH, estrogen, and progesterone, there are other hormones involved in ovulation and pregnancy success. These include human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), which is produced by the fertilized egg after implantation. hCG signals the corpus luteum to continue producing progesterone until the placenta takes over this function.
Another essential hormone is prolactin, which is responsible for milk production during pregnancy and after birth. It also plays a role in suppressing ovulation, ensuring that a woman does not get pregnant while breastfeeding. Oxytocin, known as the “love hormone,” helps with contractions during labor and stimulates the release of milk during breastfeeding.
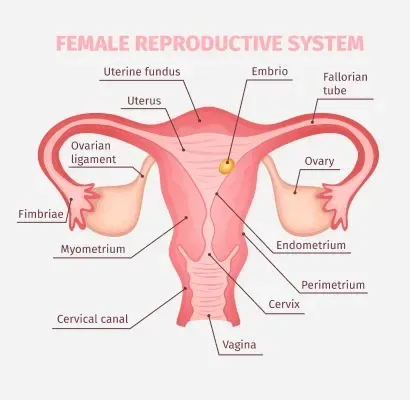
The Role of Hormones in Ovulation and Pregnancy Success
Moreover, the thyroid gland also produces hormones that are crucial for fertility and pregnancy success. An overactive or underactive thyroid can disrupt the delicate balance of hormones, affecting ovulation and pregnancy. The same goes for insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas that regulates blood sugar levels. Insulin resistance, a condition where the body cannot use insulin effectively, can lead to hormonal imbalances and difficulties with ovulation.
Hormones also play a role in the success of assisted reproductive techniques, such as in vitro fertilization (IVF). In IVF, medications are used to stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs for fertilization. These medications contain hormones that mimic the natural hormone levels during ovulation, increasing the chances of pregnancy.
Understanding the role of hormones in ovulation and pregnancy success is essential for women who are trying to conceive. Tracking ovulation and knowing when the fertile window occurs can help increase the chances of pregnancy. Women can use ovulation predictor kits or track their basal body temperature and cervical mucus to determine when they are ovulating.
Moreover, women who have irregular cycles or difficulty ovulating can seek medical help from a fertility specialist. Through various tests and evaluations, doctors can identify hormonal imbalances and prescribe appropriate treatments to help improve ovulation and increase the chances of pregnancy.
In conclusion, hormones play a crucial role in ovulation and pregnancy success. These chemical messengers regulate the reproductive system and ensure that everything is in place for a healthy pregnancy. Understanding how these hormones work together can help women in their journey towards motherhood, whether it is through natural conception or assisted reproductive techniques.
Possible search queries related to the post subject:
1. What are the key hormones involved in ovulation and pregnancy success?
2. How do hormones regulate ovulation and prepare the uterus for pregnancy?
3. Can hormonal imbalances affect ovulation and pregnancy?
4. What is the role of hormones in assisted reproductive techniques?
5. How can women track ovulation and increase their chances of pregnancy?