The Role of Hormones in Ovulation and Conception
When it comes to reproduction, hormones play a crucial role in the female body. One of the most important processes that hormones regulate is ovulation, which is the release of an egg from the ovaries. This is a necessary step for conception, as the egg must be fertilized by sperm in order for pregnancy to occur. In this blog post, we will explore the role of hormones in ovulation and conception, and how they work together to facilitate the miraculous journey of creating new life.
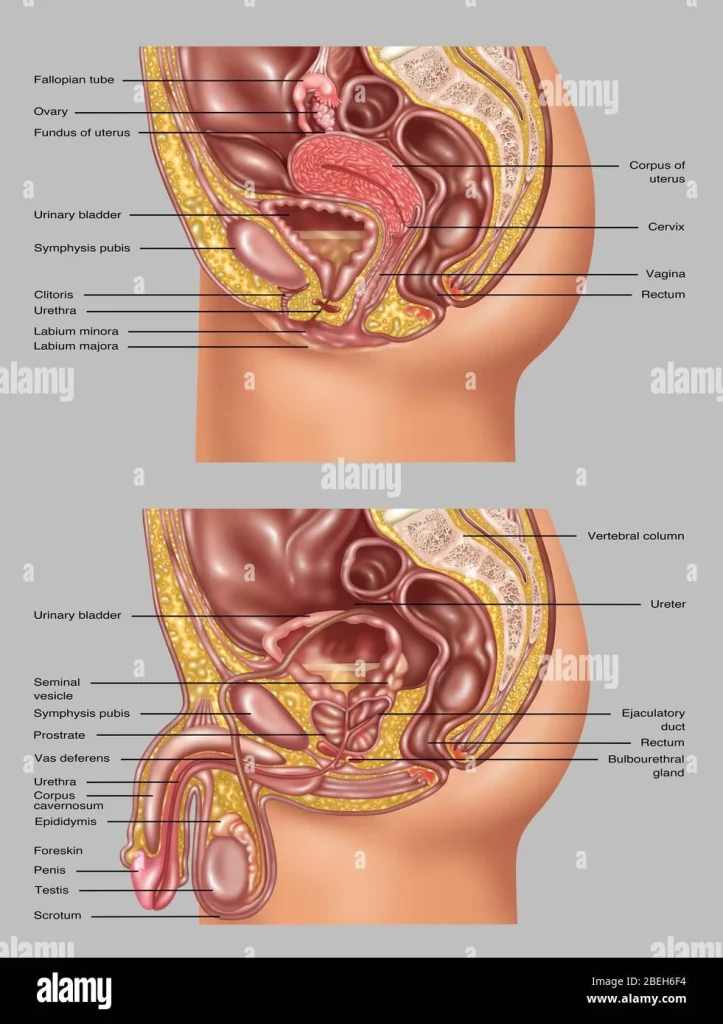
Before we dive into the details of hormones and their role in ovulation and conception, it is important to have a basic understanding of the female reproductive system. The ovaries are two small, almond-shaped organs located on either side of the uterus. They are responsible for producing and releasing eggs as well as producing hormones such as estrogen and progesterone. The uterus, or womb, is where a fertilized egg implants and a baby grows during pregnancy. The fallopian tubes are the passageways that connect the ovaries to the uterus, and they are where fertilization typically occurs.
Now, let’s take a closer look at the hormones involved in ovulation and conception.
Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
The first hormone to be released in the menstrual cycle is follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). This hormone is produced by the pituitary gland in the brain and is responsible for stimulating the growth of follicles in the ovaries. Follicles are small fluid-filled sacs that contain immature eggs. Each month, multiple follicles begin to develop, but usually only one will continue to grow and mature into an egg.
Estrogen
As the follicle grows, it produces estrogen, which helps to thicken the uterine lining in preparation for a potential pregnancy. Estrogen also triggers a surge of luteinizing hormone (LH), which is the hormone that ultimately causes ovulation.
Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
Luteinizing hormone (LH) is produced by the pituitary gland and is responsible for triggering ovulation. This hormone causes the mature follicle to rupture and release the egg from the ovary, where it then travels through the fallopian tube towards the uterus.
The Role of Hormones in Ovulation and Conception
Progesterone
After the egg is released, the follicle that contained it transforms into a structure called the corpus luteum. The corpus luteum produces progesterone, which helps to maintain the uterine lining and prepares it for potential implantation of a fertilized egg. If conception does not occur, the corpus luteum will eventually break down and the levels of progesterone will decrease, leading to the start of a new menstrual cycle.
The Role of Hormones in Conception
If a sperm is able to fertilize the egg in the fallopian tube, the fertilized egg, now called a zygote, will continue to travel towards the uterus. As it travels, it will continue to divide and grow, eventually implanting in the thickened uterine lining. This process is known as conception and marks the beginning of a pregnancy.
After conception, the corpus luteum continues to produce progesterone to support the growing embryo. Once the placenta takes over hormone production, progesterone levels will increase even further to maintain the pregnancy and prevent the uterus from contracting and potentially causing a miscarriage.
Hormonal Imbalances and Ovulation/Conception Difficulties
As you can see, hormones play a crucial role in ovulation and conception. Any disruptions or imbalances in these hormones can lead to difficulties with ovulation and conception. For example, if a woman has Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), she may have high levels of androgens (male hormones) that can interfere with the regular production of FSH and LH, leading to irregular ovulation or no ovulation at all. Additionally, a decrease in progesterone levels can result in a thin uterine lining, making it difficult for a fertilized egg to implant and grow.
In some cases, hormonal imbalances can be treated with medication or lifestyle changes. For women who struggle with infertility due to hormonal issues, fertility treatments such as ovulation induction or in vitro fertilization (IVF) may be recommended.
Summary:
Hormones play a crucial role in the process of ovulation and conception. Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) stimulates the growth of follicles, estrogen thickens the uterine lining, luteinizing hormone (LH) triggers ovulation, and progesterone prepares the uterus for pregnancy. If conception occurs, progesterone levels increase to support the pregnancy. Hormonal imbalances can lead to difficulties with ovulation and conception, but there are treatments available to help women achieve their dream of becoming a mother.
Search Queries:
1. What are the hormones involved in ovulation and conception?
2. How do hormones regulate ovulation and conception?
3. What role does estrogen play in ovulation and conception?
4. What are the consequences of hormonal imbalances on ovulation and conception?
5. What are the treatment options for hormonal-related infertility?