The menstrual cycle is a complex and highly individualized process that plays a crucial role in a woman’s reproductive health. It involves a series of physiological changes and hormonal fluctuations that prepare the body for pregnancy each month. As such, understanding and tracking the menstrual cycle is essential for family planning, whether it be avoiding or achieving pregnancy. While many factors can affect the menstrual cycle, including lifestyle and health conditions, genetics play a significant role in its regulation and regularity.
Genetics refers to the study of heredity and how traits are passed down from parents to offspring. Every individual has a unique set of genetic information that determines various characteristics, including physical traits, health conditions, and even reproductive functions. In the context of the menstrual cycle, genetic variations can influence the length, regularity, and symptoms experienced during the cycle. Understanding these genetic factors can help women and couples better track their cycles for family planning purposes.
One of the primary genetic factors that can affect the menstrual cycle is the length of the cycle. The average menstrual cycle lasts around 28 days, but for some women, it can be shorter or longer. This is due to genetic variations in the length of the follicular phase, which is the first part of the cycle when the egg matures. Studies have shown that genetic variations in the genes involved in follicle development can affect the length of the menstrual cycle. For example, mutations in the FSHR gene, which regulates follicle-stimulating hormone, can lead to shorter or longer cycles.
Aside from cycle length, genetics also plays a role in the regularity of the menstrual cycle. Regularity refers to how predictable the cycle is, with most women having a cycle that ranges from 25 to 32 days. However, some women experience irregular cycles, which can affect their ability to track their ovulation and plan for pregnancy. Studies have found that genetic variations in the genes responsible for ovulation, such as the LH and FSH genes, can affect the regularity of the menstrual cycle. Mutations in these genes can result in decreased levels of these hormones, leading to ovulation disorders and irregular cycles.
Genetics also plays a role in the symptoms experienced during the menstrual cycle, such as cramping, bloating, and mood changes. Women with a family history of severe menstrual symptoms are more likely to experience them as well. Studies have identified genetic variations in the genes involved in the production and regulation of hormones, such as estrogen and progesterone, to be linked to severe menstrual symptoms. These variations can affect the levels of these hormones, leading to more intense symptoms.
Furthermore, genetics can also affect a woman’s fertility and the timing of ovulation. Ovulation is the release of an egg from the ovary and is essential for pregnancy to occur. Studies have shown that genes involved in the production and regulation of hormones, such as AMH and AMHR2, can influence the timing of ovulation. Mutations in these genes can lead to fertility issues, such as irregular ovulation or premature ovarian failure. Understanding these genetic factors can help women and couples better plan for pregnancy by tracking ovulation more accurately.
In addition to understanding the role of genetics in the menstrual cycle, advancements in technology have made it possible to track these genetic variations through DNA testing. Companies like 23andMe and AncestryDNA offer at-home DNA testing kits that can provide information on genetic variations related to reproductive health, including menstrual cycle length, regularity, and fertility. This information can be beneficial for women and couples who are trying to conceive or avoid pregnancy.
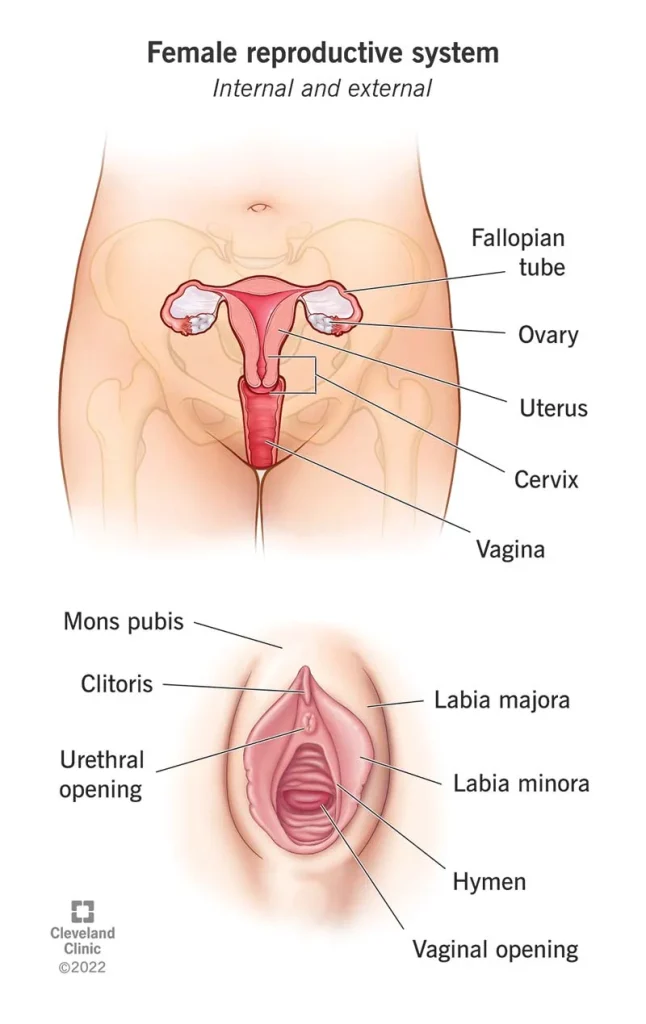
The Role of Genetics in Menstrual Cycle Tracking for Family Planning
In conclusion, genetics plays a crucial role in the menstrual cycle and can significantly affect family planning. Understanding the genetic factors that influence cycle length, regularity, symptoms, and fertility can help women and couples better track their cycles and plan for pregnancy. Furthermore, advancements in technology have made it possible to identify these genetic variations, providing valuable information for reproductive health. By considering the role of genetics in menstrual cycle tracking, women and couples can make more informed decisions about their family planning journey.
Search Queries:
1. How does genetics affect the menstrual cycle?
https://makeamom.com/how-genetics-affects-menstrual-cycle/
2. What are the genetic factors that influence the menstrual cycle?
https://makeamom.com/genetic-factors-menstrual-cycle/
3. Can DNA testing help with menstrual cycle tracking for family planning?
https://makeamom.com/dna-testing-menstrual-cycle-tracking/
4. Why is it important to understand the role of genetics in family planning?
https://makeamom.com/understanding-genetics-family-planning/
5. How can genetic variations affect fertility and ovulation?
https://makeamom.com/genetics-fertility-ovulation/
Summary:
The menstrual cycle is a complex process influenced by various factors, including genetics. Understanding the role of genetics in the cycle can help women and couples better track their cycles for family planning purposes. Genetic variations can affect cycle length, regularity, symptoms, and fertility, and advancements in technology have made it possible to identify these variations through DNA testing. By considering genetics in menstrual cycle tracking, individuals can make more informed decisions about their reproductive health.