The Role of Androgens in Female Reproductive Health
Androgens, commonly known as male hormones, play a crucial role in the reproductive health of females. While traditionally thought to only affect men, androgens also have important functions in women, particularly in the development and maintenance of the female reproductive system. In this blog post, we will explore the role of androgens in female reproductive health and how imbalances or deficiencies can impact a woman’s overall well-being.
To begin, it is important to understand what androgens are and how they differ from female hormones. Androgens are a group of steroid hormones that are primarily produced by the testes in men and the ovaries in women. The most well-known androgen is testosterone, but there are others such as androstenedione and dihydrotestosterone (DHT). In women, androgens are mainly produced by the adrenal glands and ovaries.
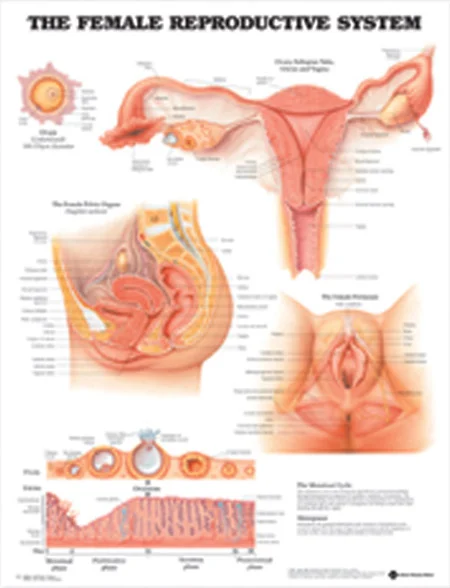
Androgens play a crucial role in the development of the female reproductive system. During fetal development, androgens are responsible for the development of the external genitalia, as well as the formation of the ovaries. In puberty, androgens contribute to the growth and maturation of the reproductive organs, including the uterus, fallopian tubes, and breasts. Androgens also play a role in regulating the menstrual cycle, as well as in maintaining bone health and muscle mass.
One of the key functions of androgens in women is their role in fertility. Androgens stimulate the growth and maturation of follicles in the ovaries, which are responsible for producing and releasing eggs. In addition, androgens play a role in the production of cervical mucus, which helps sperm travel through the reproductive tract to reach the egg for fertilization.
The Role of Androgens in Female Reproductive Health
While androgens are essential for female reproductive health, imbalances or deficiencies can have significant impacts on a woman’s well-being. High levels of androgens, known as hyperandrogenism, can lead to conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), which is characterized by irregular periods, excess hair growth, and acne. PCOS is one of the most common causes of female infertility and can also increase the risk of developing diabetes and heart disease.
On the other hand, low levels of androgens, known as hypoandrogenism, can also have adverse effects on a woman’s health. Hypoandrogenism is often seen in menopausal women, where the decline in androgen production can lead to symptoms such as low libido, vaginal dryness, and decreased bone density. In addition, androgen deficiencies can also occur in younger women and may lead to decreased fertility, low energy levels, and mood swings.
Supplementation with androgens, particularly testosterone, has been shown to have positive effects on female reproductive health. In women with hypoandrogenism, testosterone therapy can improve sexual function, bone density, and overall well-being. In women with PCOS, androgen suppression therapy has been shown to improve insulin resistance and regulate menstrual cycles. However, it is crucial to note that androgen supplementation should be closely monitored by a healthcare professional, as excessive levels of androgens can have adverse effects, such as masculinization.
In conclusion, androgens play a pivotal role in the female reproductive system, from fetal development to menopause. Imbalances or deficiencies in androgens can have significant impacts on a woman’s overall health and fertility. While androgen supplementation may be beneficial, it should always be done under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Search Queries:
1. “What is the role of androgens in female reproductive health?”
2. “How do androgens affect female fertility?”
3. “What are the symptoms of androgen imbalances in women?”
4. “Can androgen supplementation improve female reproductive health?”
5. “What are the risks of excessive androgens in women?”