Blog Post Title: The Pros and Cons of Using Fresh vs. Frozen Sperm for Self-Insemination
Summary:
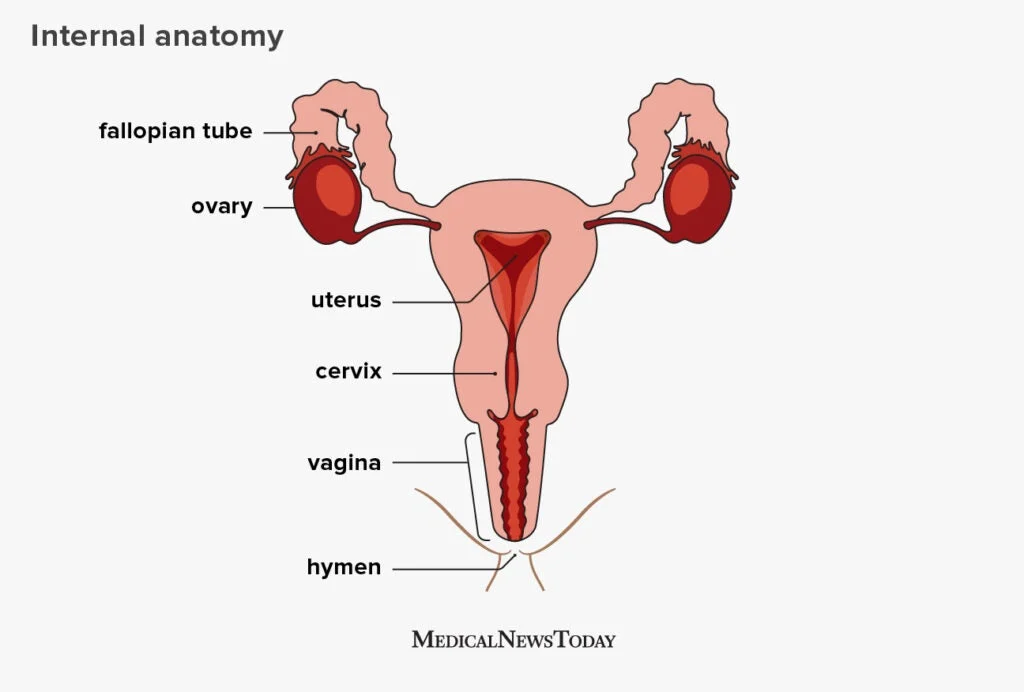
For couples and individuals who are trying to conceive, the options for self-insemination have expanded in recent years. One of the more popular methods is using either fresh or frozen sperm for self-insemination. While both options have their own set of advantages and disadvantages, it is important to weigh them carefully before making a decision. In this blog post, we will explore the pros and cons of using fresh vs. frozen sperm for self-insemination.
Pros of Using Fresh Sperm:
1. Higher Chance of Success: Fresh sperm has a higher chance of success compared to frozen sperm. This is because fresh sperm is usually collected and used within a short period of time, increasing its viability and motility.
2. Cost-Effective: Using fresh sperm for self-insemination can be more cost-effective, as you do not have to pay for the additional cost of freezing and storing the sperm.
3. More Natural: Some people prefer using fresh sperm as it is considered to be a more natural way of conceiving. It is collected and used in the same way as it would be during intercourse.
Cons of Using Fresh Sperm:
1. Limited Availability: One of the biggest disadvantages of using fresh sperm is the limited availability. It can only be collected on specific days and times, making it difficult for those with busy schedules to plan for insemination.
2. Shorter Shelf Life: Fresh sperm has a shorter shelf life compared to frozen sperm, which can be stored for a longer period of time. This means that fresh sperm must be used immediately or within a few hours of collection, making it less convenient for some individuals.
3. Higher Risk of Infection: Fresh sperm carries a higher risk of infection compared to frozen sperm. This is because it has not been tested and screened for any potential diseases or infections.
The Pros and Cons of Using Fresh vs. Frozen Sperm for Self-Insemination
Pros of Using Frozen Sperm:
1. Convenient: Frozen sperm can be stored for a longer period of time, making it more convenient for those who cannot plan for insemination on specific days and times. It also allows for flexibility in the timing of insemination.
2. Lower Risk of Infection: Frozen sperm has been tested and screened for any potential diseases or infections, making it a safer option for self-insemination.
3. More Available: Unlike fresh sperm, frozen sperm is readily available and can be shipped to your doorstep, eliminating the need to coordinate with a donor for collection.
Cons of Using Frozen Sperm:
1. Lower Success Rate: Frozen sperm has a lower success rate compared to fresh sperm. This is because the freezing process can damage some of the sperm cells, affecting their viability and motility.
2. Additional Cost: Using frozen sperm for self-insemination comes with additional costs, such as purchasing and storing the sperm, as well as shipping fees.
3. Requires Planning: Unlike fresh sperm, which can be used immediately, frozen sperm requires planning ahead of time as it needs to be thawed before use. This can be challenging for those who are not able to predict their ovulation cycle.
Conclusion:
Both fresh and frozen sperm have their own set of advantages and disadvantages when it comes to self-insemination. While fresh sperm may have a higher success rate, it is limited in availability and carries a higher risk of infection. On the other hand, frozen sperm is more convenient and has a lower risk of infection, but it may have a lower success rate and comes with additional costs. Ultimately, the decision should be based on an individual or couple’s personal preferences and needs.
Search Queries:
1. What are the pros and cons of using fresh vs. frozen sperm for self-insemination?
2. Is fresh sperm more effective for self-insemination than frozen sperm?
3. What are the risks associated with using fresh sperm for self-insemination?
4. How does the availability of fresh vs. frozen sperm affect self-insemination?
5. What factors should be considered when choosing between fresh vs. frozen sperm for self-insemination?