The Link Between Menstrual Health and Desired Pregnancy Outcomes
Menstruation is a natural and vital process for women’s reproductive health. It is a monthly occurrence that signifies the shedding of the uterine lining and the release of an egg, marking the start of a new menstrual cycle. While it is a normal process, menstrual health is often overlooked and misunderstood, especially when it comes to its impact on pregnancy outcomes.
In recent years, there has been a growing body of research that highlights the link between menstrual health and desired pregnancy outcomes. Understanding this connection is crucial for women who are trying to conceive or those who want to ensure a healthy pregnancy. In this blog post, we will explore the various factors that affect menstrual health and how they can impact the chances of a successful pregnancy.
Hormonal Imbalance and Fertility
Hormonal balance plays a crucial role in a woman’s menstrual cycle and overall reproductive health. Any disruption in these hormones can affect the frequency, duration, and regularity of periods, making it difficult to achieve pregnancy. One of the most common hormonal imbalances affecting women’s menstrual health is Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS). PCOS is a condition that causes an increase in male hormones in a woman’s body, leading to irregular periods, weight gain, and difficulty in ovulation.
A study published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism found that women with PCOS have a higher risk of experiencing menstrual irregularities and difficulties in conceiving compared to those without the condition. This highlights the importance of addressing hormonal imbalances to improve menstrual health and increase the chances of a successful pregnancy.
Menstrual Cycle Length and Fertility
The length of a woman’s menstrual cycle can also impact fertility and pregnancy outcomes. A normal menstrual cycle can range from 21 to 35 days, with the average being 28 days. However, studies have shown that women with shorter or longer cycles may face difficulties in conceiving.
A study published in the journal Fertility and Sterility found that women with shorter menstrual cycles (less than 21 days) have a lower chance of achieving pregnancy compared to those with longer cycles. On the other hand, women with longer cycles (more than 35 days) have a higher risk of experiencing irregular ovulation and longer time to conceive. Therefore, tracking the length of your menstrual cycle can give valuable insights into your reproductive health and help you plan for a successful pregnancy.
Menstrual Flow and Pregnancy
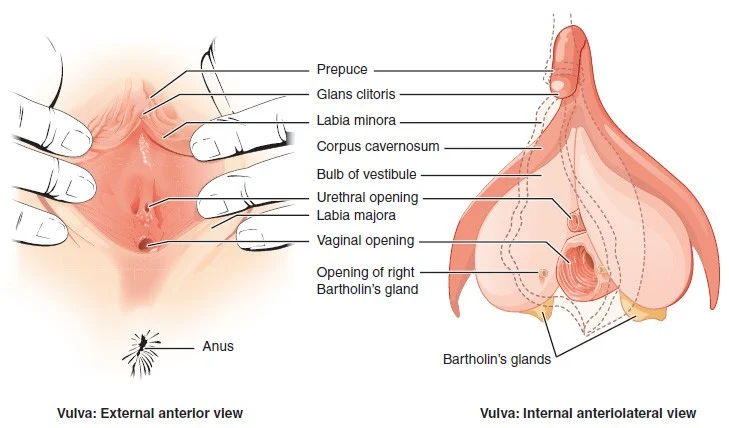
The Link Between Menstrual Health and Desired Pregnancy Outcomes
The amount and consistency of menstrual flow can also impact pregnancy outcomes. A study published in Human Reproduction found that women with heavy menstrual flow have a higher risk of experiencing fertility problems, including difficulty in conceiving and increased chances of miscarriage.
On the other hand, women with light or irregular periods may have underlying health issues that could affect their fertility. Therefore, it is essential to pay attention to the amount and consistency of your menstrual flow and consult a healthcare professional if you notice any significant changes.
Stress and Menstrual Health
Stress can significantly impact a woman’s menstrual health and fertility. When a woman is under chronic stress, it can affect the production of reproductive hormones and disrupt the menstrual cycle. A study published in the journal Human Reproduction found that women with higher stress levels have a lower chance of conceiving compared to those with lower stress levels.
Moreover, stress can also lead to irregular or missed periods, making it challenging to predict ovulation and plan for pregnancy. Therefore, managing stress through relaxation techniques, exercise, and seeking support from loved ones can help improve menstrual health and increase the chances of a desired pregnancy.
Nutrition and Menstrual Health
Proper nutrition is vital for overall health and well-being, including menstrual health. A balanced diet that includes essential nutrients such as iron, calcium, and Vitamin D can help regulate hormones, maintain a healthy weight, and support reproductive health.
On the other hand, a diet lacking in essential nutrients can lead to irregular periods, hormonal imbalances, and fertility problems. A study published in Obstetrics & Gynecology Science found that women with poor nutrition are at a higher risk of experiencing menstrual irregularities and difficulties in conceiving.
Therefore, it is essential to maintain a healthy and balanced diet to support menstrual health and improve the chances of a successful pregnancy. Additionally, consulting a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian can help create a personalized nutrition plan that meets your specific needs.
In conclusion, menstrual health is a crucial aspect of a woman’s reproductive health and can significantly impact desired pregnancy outcomes. Addressing underlying issues such as hormonal imbalances, stress, and nutrition can help improve menstrual health and increase the chances of a successful pregnancy. Therefore, it is essential to pay attention to your menstrual cycle and consult a healthcare professional if you notice any significant changes.
Search Queries:
1. How does menstrual health affect pregnancy outcomes?
2. What is the link between hormonal imbalance and fertility?
3. Can stress impact menstrual health and fertility?
4. How can nutrition improve menstrual health and increase the chances of pregnancy?
5. What are the factors that affect menstrual health and fertility?