Endometriosis is a chronic condition that affects approximately 1 in 10 women of reproductive age, making it one of the most common gynecological disorders. Despite its prevalence, endometriosis is often misdiagnosed or undiagnosed, leading to significant physical, emotional, and financial burdens for those affected. In recent years, there has been increasing research and awareness surrounding the link between endometriosis and reproductive endocrinology, shedding light on the potential impact of this condition on fertility and overall reproductive health.
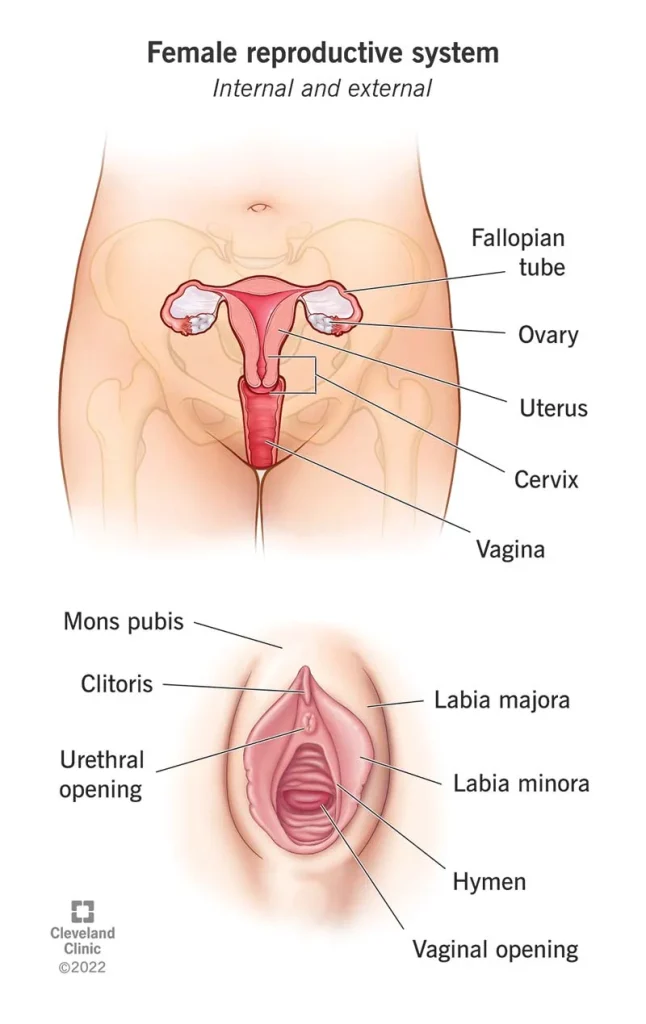
To understand this connection, it is important to first understand what endometriosis is and how it affects the body. Endometriosis is a condition where the tissue that normally lines the inside of the uterus, known as the endometrium, grows outside of the uterus. This tissue can implant and grow on various organs within the pelvic cavity, such as the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and bladder. These growths, called endometrial implants, can cause inflammation and scarring in the affected areas, leading to symptoms such as chronic pelvic pain, painful periods, and infertility.
Reproductive endocrinology is the study of hormones and their role in reproductive health and fertility. Hormones play a crucial role in the menstrual cycle, and any disruption in their production or function can have a significant impact on a person’s reproductive health. Therefore, it is not surprising that there is a connection between endometriosis and reproductive endocrinology, as endometriosis can disrupt the normal hormonal balance in the body.
One of the key hormones involved in the menstrual cycle is estrogen. In individuals with endometriosis, there is often an excess of estrogen in the body. This excess estrogen can lead to the growth and development of endometrial implants outside of the uterus. These implants can then produce their own estrogen, creating a cycle of increased estrogen production and further growth of the implants. This can lead to more severe symptoms and potentially worsen the condition over time.
Furthermore, endometriosis can also affect the production of other hormones, such as progesterone and luteinizing hormone (LH). These hormones play important roles in ovulation and the development and shedding of the uterine lining during the menstrual cycle. When these hormone levels are disrupted, it can lead to irregular or absent ovulation, making it difficult to conceive and increasing the risk of infertility.
The Link Between Endometriosis and Reproductive Endocrinology
The link between endometriosis and reproductive endocrinology becomes even more significant when considering the impact of this condition on fertility. Endometriosis is a leading cause of female infertility, with studies estimating that up to 50% of individuals with endometriosis may struggle to conceive. The reasons for this are multifactorial, including the scarring and inflammation caused by endometrial implants, hormonal imbalances, and disrupted ovulation.
In addition to the physical impact of endometriosis on fertility, the emotional toll of the condition cannot be overlooked. Struggling with infertility can be a deeply emotional and isolating experience, and the added burden of a chronic condition like endometriosis can make it even more challenging. This highlights the importance of early diagnosis and treatment of endometriosis, not only for the physical well-being of those affected but also for their emotional and mental health.
Managing endometriosis can also have a significant impact on reproductive health and fertility. Treatment options for endometriosis often involve hormonal therapies, which can further disrupt the delicate balance of reproductive hormones in the body. For individuals trying to conceive, this can be a challenging obstacle, as they may have to weigh the benefits of managing their symptoms against the potential impact on their fertility. It is crucial for individuals with endometriosis to work closely with their healthcare providers to find the most suitable treatment plan that takes into consideration their reproductive goals.
In recent years, there has been a growing understanding of the impact of endometriosis on reproductive endocrinology, leading to advancements in research and treatment options. This has also led to increased awareness and education surrounding the condition, helping to break the silence and stigma surrounding endometriosis. It is important for individuals to know the signs and symptoms of endometriosis and to seek medical attention if they suspect they may have the condition. Early diagnosis and treatment can help to alleviate symptoms, improve reproductive health, and increase the chances of achieving a successful pregnancy.
In conclusion, the link between endometriosis and reproductive endocrinology is a complex and significant one. Endometriosis can disrupt the delicate hormonal balance in the body, leading to a range of symptoms and potential fertility issues. It is crucial for individuals, especially those trying to conceive, to be aware of this connection and to seek proper medical care and support. With continued research and awareness, we can hope for better understanding and management of this condition, ultimately improving the reproductive health and well-being of those affected.
Search queries:
1. “What is the connection between endometriosis and reproductive endocrinology?”
2. “How does endometriosis affect fertility?”
3. “Can endometriosis be a cause of female infertility?”
4. “What are the hormonal imbalances associated with endometriosis?”
5. “How can managing endometriosis impact reproductive health?”