Blog Post: The Impact of Medications on Ovulation and How to Predict It for Pregnancy
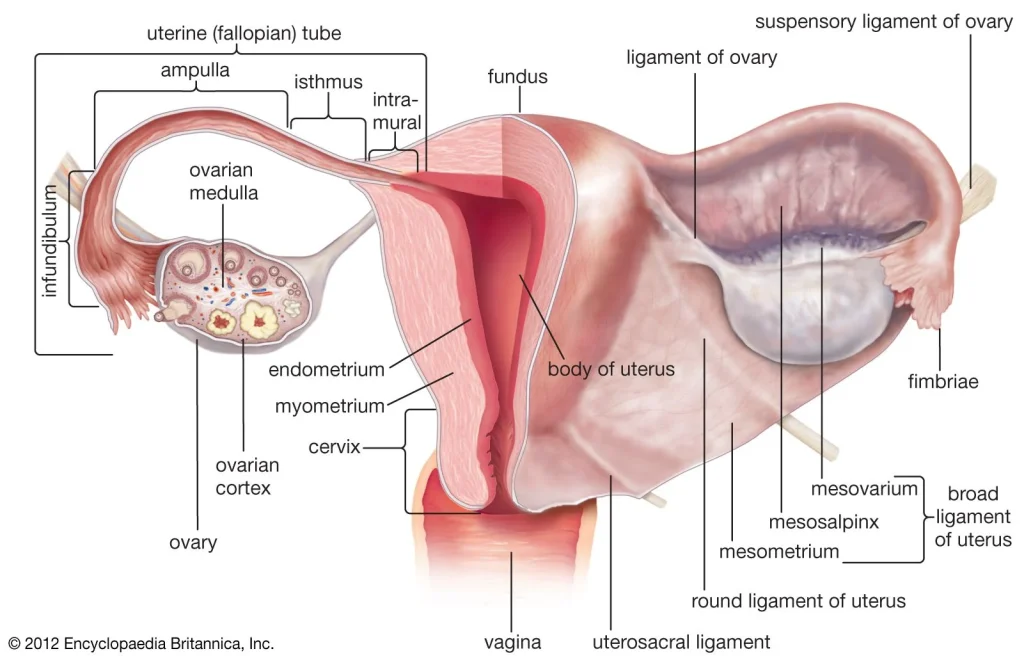
Ovulation is a crucial phase in a woman’s menstrual cycle that plays a significant role in fertility and pregnancy. During this process, an egg is released from the ovary and travels down the fallopian tube, where it can potentially be fertilized by sperm. However, various factors can affect ovulation, including medications. Whether you are trying to conceive or simply curious about the impact of medications on ovulation, this blog post will provide you with essential information and tips on how to predict ovulation for pregnancy.
Impact of Medications on Ovulation:
Certain medications can affect ovulation, either by altering hormone levels or directly affecting the reproductive organs. These medications include:
1. Hormonal Birth Control: Oral contraceptives, patches, and hormonal intrauterine devices (IUDs) work by preventing ovulation. They contain synthetic hormones that suppress the body’s natural hormone production, preventing the release of an egg.
2. Fertility Medications: Women who have difficulty ovulating or have irregular cycles may be prescribed fertility medications such as Clomid, Letrozole, or Gonadotropins to stimulate ovulation. These medications work by boosting the production of hormones that trigger ovulation.
3. Antidepressants: Some antidepressants, such as SSRIs (Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors) and Prozac, can affect ovulation by altering hormone levels in the body. They can also cause irregular menstrual cycles, making it difficult to predict ovulation.
4. Steroids: Corticosteroids, often prescribed for conditions like asthma and arthritis, can impact ovulation by suppressing the production of hormones necessary for ovulation.
5. Chemotherapy Drugs: Chemotherapy drugs can damage the ovaries and cause temporary or permanent infertility. They can also cause irregular or absent periods, making it challenging to predict ovulation.
The Impact of Medications on Ovulation and How to Predict It for Pregnancy
How to Predict Ovulation for Pregnancy:
Predicting ovulation is essential for couples trying to conceive, as it increases the chances of getting pregnant. Here are some methods you can use to predict ovulation:
1. Keep Track of Your Menstrual Cycle: Ovulation usually occurs around day 14 of a 28-day menstrual cycle. However, every woman’s cycle is different, and ovulation can occur earlier or later. Keeping track of your periods can help you determine when you are most likely to ovulate.
2. Use Ovulation Predictor Kits: Over-the-counter ovulation predictor kits (OPKs) test for a hormone called luteinizing hormone (LH) in your urine. A surge in LH indicates that ovulation will occur within the next 24-48 hours, making it the best time to try to conceive.
3. Monitor Your Basal Body Temperature (BBT): Your basal body temperature is your temperature at rest, and it rises slightly (around 0.5-1 degree Fahrenheit) after ovulation. By tracking your BBT, you can determine when you are most likely to ovulate.
4. Check Your Cervical Mucus: The consistency and amount of your cervical mucus change throughout your menstrual cycle. Before ovulation, it becomes thin, slippery, and stretchy, resembling egg whites. This type of mucus is conducive to sperm survival and can indicate that you are about to ovulate.
5. Consult Your Doctor: If you are having trouble predicting ovulation or have a medical condition that may affect fertility, it is essential to consult your doctor. They can perform tests and provide guidance on the best methods for you to predict ovulation.
In conclusion, medications can have a significant impact on ovulation, and it is crucial to be aware of their potential effects, especially when trying to conceive. Keeping track of your menstrual cycle and using various methods like ovulation predictor kits, BBT tracking, and checking cervical mucus can help you predict ovulation accurately. Consulting your doctor is also essential for personalized guidance and advice. By understanding the impact of medications on ovulation and learning how to predict it, you can increase your chances of achieving a successful pregnancy.
Summary: Ovulation is a vital part of a woman’s menstrual cycle, and medications can have a significant impact on it. Hormonal birth control, fertility medications, antidepressants, steroids, and chemotherapy drugs can all affect ovulation. To predict ovulation for pregnancy, you can keep track of your menstrual cycle, use ovulation predictor kits, monitor your BBT and cervical mucus, and consult your doctor for personalized guidance. By understanding the impact of medications on ovulation and learning how to predict it, you can increase your chances of achieving a successful pregnancy.