The Diet-Self-Insemination Link: What Science Says
In recent years, the concept of self-insemination has gained popularity among women looking to conceive. This method involves using a syringe or a cervical cap to insert semen into the vagina, bypassing traditional methods of insemination through sexual intercourse. While self-insemination may seem like a convenient and cost-effective option for those struggling with fertility, there is a growing body of research suggesting that diet may play a significant role in its success.
In this blog post, we will dive into the latest scientific findings on the link between diet and self-insemination. We will also explore the potential implications of this link for women’s health and fertility, as well as provide tips for optimizing your diet for successful self-insemination.
1. What is self-insemination and why do women choose it?
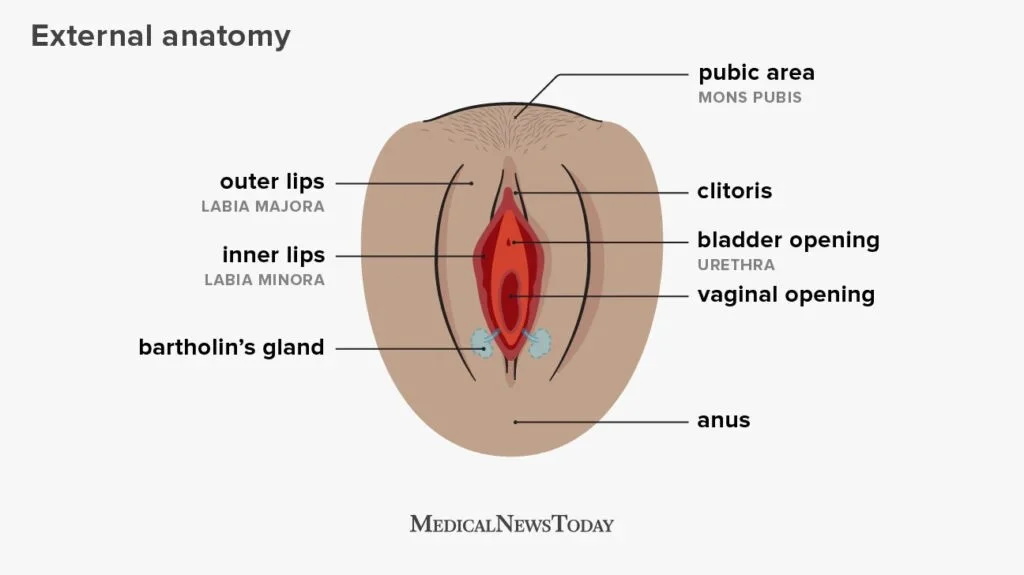
Self-insemination, also known as at-home insemination, is a method of conception that involves manually inserting semen into the vagina using a syringe or a cervical cap. This method can be used by women who are trying to conceive without a partner, as well as by same-sex couples and couples struggling with male factor infertility.
The appeal of self-insemination lies in its convenience and cost-effectiveness. It can be performed in the comfort of one’s own home, eliminating the need for expensive fertility treatments or visits to a clinic. Additionally, self-insemination can give women more control over their fertility journey, allowing them to take charge of their own reproductive health.
2. The impact of diet on fertility
While there are many factors that can impact fertility, diet has been identified as a significant one. Studies have shown that certain nutrients and dietary patterns can affect reproductive health, menstrual cycle regularity, and ovulation.
One key nutrient for fertility is folic acid, also known as vitamin B9. Folic acid plays a crucial role in cell growth and development, making it essential for a healthy pregnancy. Studies have shown that women who consume the recommended daily intake of folic acid are less likely to experience ovulatory infertility.
In addition to folic acid, a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins has been linked to improved fertility. On the other hand, a diet high in processed foods, trans fats, and added sugars has been shown to have negative effects on fertility.
3. The science behind the diet-self-insemination link
Recent studies have explored the potential link between diet and self-insemination success. One study published in the Journal of Reproductive Medicine found that women who followed a Mediterranean-style diet were more likely to achieve a successful self-insemination compared to those who did not follow this dietary pattern. The Mediterranean diet is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats, and has been shown to have numerous health benefits, including improved fertility.
The Diet-Self-Insemination Link: What Science Says
Another study published in the Journal of Human Reproduction found that a higher intake of trans fats was associated with a reduced likelihood of successful self-insemination. Trans fats, commonly found in fried and processed foods, have been linked to inflammation and insulin resistance, both of which can negatively impact fertility.
4. Tips for optimizing your diet for successful self-insemination
Based on the current scientific evidence, here are some tips for optimizing your diet for self-insemination success:
– Increase your intake of folic acid: Incorporate foods such as leafy green vegetables, legumes, and fortified cereals into your diet to ensure you are getting enough folic acid.
– Follow a Mediterranean-style diet: Aim to consume a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats in your meals. This dietary pattern has been linked to improved fertility and may increase your chances of successful self-insemination.
– Reduce your intake of trans fats: Limit your consumption of fried and processed foods, which are high in trans fats and have been shown to have negative effects on fertility.
– Stay hydrated: Drinking enough water is essential for maintaining a healthy reproductive system. Aim to drink at least 8 glasses of water per day.
– Consult with a healthcare professional: Before making any significant changes to your diet, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional, especially if you have any underlying health conditions.
5. The bigger picture: implications for women’s health and fertility
The diet-self-insemination link not only has implications for successful conception but also for overall women’s health and fertility. By following a balanced and nutritious diet, women can improve their overall reproductive health and increase their chances of successful self-insemination. This link also highlights the importance of holistic approaches to fertility, encompassing both physical and dietary factors.
In conclusion, while self-insemination may be a convenient and cost-effective method of conception, it is essential to consider the role of diet in its success. By following a balanced and nutritious diet, women can optimize their chances of successful self-insemination and improve their overall reproductive health.
Search queries:
1. How does diet affect self-insemination success?
2. What are the best foods for successful self-insemination?
3. Can a Mediterranean diet increase self-insemination success?
4. Why is folic acid important for self-insemination?
5. How can I optimize my diet for self-insemination?