The Cycle of Fertility: Using Menstrual Charting to Enhance Your Chances of Pregnancy
For many women, trying to conceive can be a rollercoaster of emotions. Every month brings a new cycle, a new round of hope and disappointment. But what if there was a way to better understand your body and increase your chances of getting pregnant? This is where menstrual charting comes in. By tracking your menstrual cycle and fertility signs, you can gain valuable insights into your body and optimize your chances of conception. In this blog post, we will explore the cycle of fertility and how menstrual charting can be used to enhance your chances of pregnancy.
Menstrual charting, also known as fertility charting or natural family planning, involves tracking your menstrual cycle and fertility signs to identify your most fertile days. This method has been used for centuries and has been proven to be an effective way to prevent or achieve pregnancy. The key to successful charting is understanding the different phases of the menstrual cycle and the signs that indicate fertility.
The Menstrual Cycle
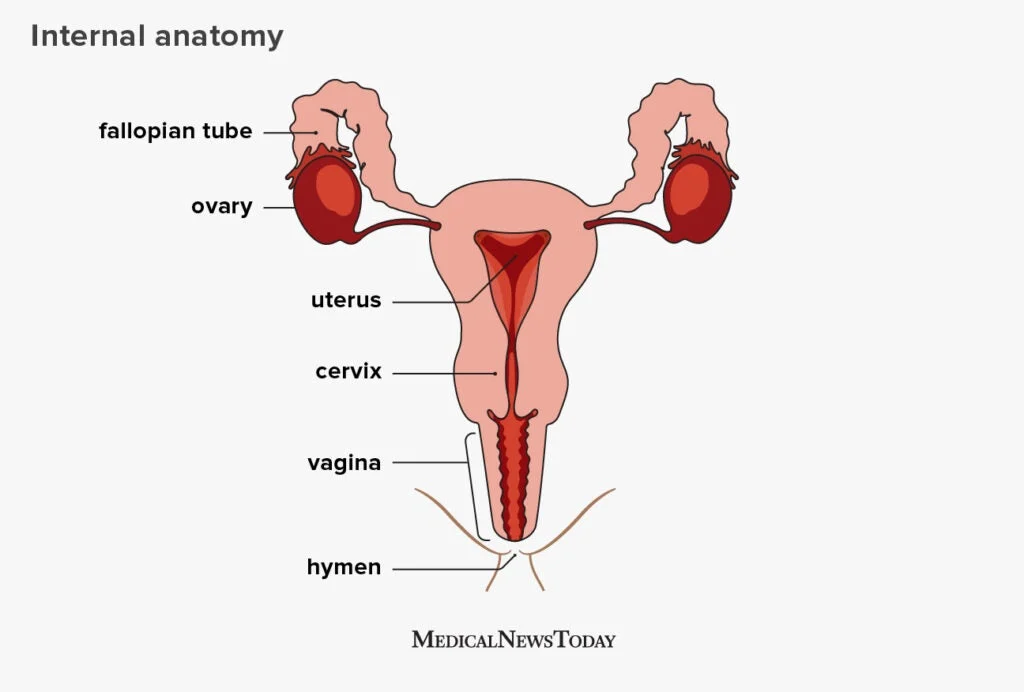
The menstrual cycle is the monthly process that prepares a woman’s body for pregnancy. It is controlled by hormones and consists of three main phases – the follicular phase, ovulation, and the luteal phase.
The follicular phase begins on the first day of menstruation and lasts for approximately 14 days. During this phase, the ovaries start to develop follicles, each containing an egg. As the follicles grow, they produce estrogen, which thickens the lining of the uterus in preparation for pregnancy.
Ovulation usually occurs around day 14 of the menstrual cycle. This is when the mature egg is released from the ovary and travels down the fallopian tube towards the uterus. Ovulation is the most fertile time of the menstrual cycle, and the egg can survive for up to 24 hours waiting for sperm to fertilize it.
The luteal phase begins after ovulation and lasts for approximately 14 days. If the egg is fertilized, it will implant in the uterine lining and begin to grow. If fertilization does not occur, the uterine lining will shed, and the menstrual cycle will begin again.
Fertility Signs
The Cycle of Fertility: Using Menstrual Charting to Enhance Your Chances of Pregnancy
Understanding fertility signs is crucial for successful menstrual charting. These signs can help you determine when you are most fertile and when to time intercourse to increase your chances of conceiving. The three main fertility signs are basal body temperature, cervical mucus, and cervical position.
Basal body temperature (BBT) is the body’s resting temperature, and it is slightly lower in the first half of the menstrual cycle. After ovulation, BBT rises due to the hormone progesterone, which is released after ovulation. Tracking your BBT can help you pinpoint when ovulation has occurred, and you are most fertile.
Cervical mucus is a fluid produced by the cervix that helps sperm travel through the reproductive tract. As the body prepares for ovulation, estrogen levels rise, causing an increase in cervical mucus. The consistency of the mucus changes throughout the menstrual cycle, with the most fertile mucus being thin, clear, and stretchy.
Cervical position also changes throughout the menstrual cycle. During ovulation, the cervix is soft, high, and open, making it easier for sperm to travel through. Tracking cervical position can help you determine when ovulation has occurred and when you are most fertile.
Using Menstrual Charting to Enhance Your Chances of Pregnancy
Now that you understand the basics of the menstrual cycle and fertility signs, let’s explore how you can use menstrual charting to enhance your chances of pregnancy. The first step is to start tracking your menstrual cycle and fertility signs. This can be done using a variety of methods, such as pen and paper, a fertility tracking app, or a fertility monitor.
Once you have a few cycles worth of data, you can start to identify patterns and determine when you are most fertile. In general, the most fertile days are the five days leading up to ovulation and the day of ovulation itself. By tracking your BBT, cervical mucus, and cervical position, you can pinpoint when ovulation is most likely to occur and plan to have intercourse during this time.
In addition to tracking your fertility signs, there are other ways to enhance your chances of pregnancy through menstrual charting. For example, you can use ovulation predictor kits (OPKs) to detect the surge of luteinizing hormone (LH) that occurs just before ovulation. You can also monitor changes in your cervix and vaginal pH levels to determine when ovulation is near.
Summary:
Tracking your menstrual cycle and fertility signs through menstrual charting can provide valuable insights into your body and enhance your chances of pregnancy. The menstrual cycle consists of three phases – the follicular phase, ovulation, and the luteal phase – and understanding these phases is crucial for successful charting. Fertility signs such as basal body temperature, cervical mucus, and cervical position can help you determine when you are most fertile and when to time intercourse for conception. By using menstrual charting, you can take control of your fertility journey and increase your chances of achieving the ultimate goal of becoming a mom.