The Connection Between Diet and Self-Insemination: A Closer Look
In today’s society, the topic of self-insemination has become more prevalent as individuals and couples explore alternative methods of starting a family. While self-insemination may seem like a simple process, there are many factors that can affect its success, including diet. In this blog post, we will take a closer look at the connection between diet and self-insemination and how making certain dietary changes can improve your chances of success.
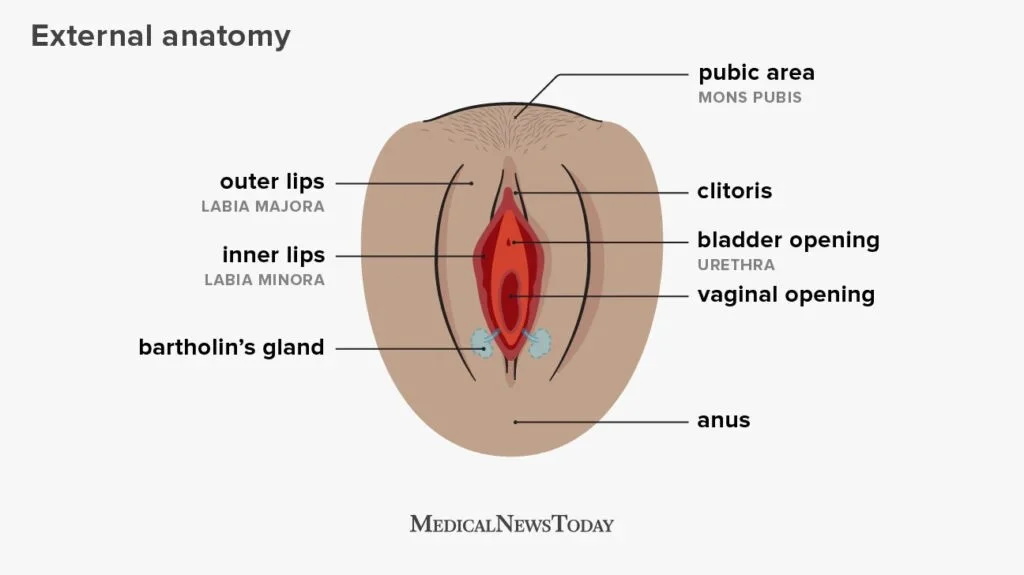
First, let’s define what self-insemination is. Self-insemination, also known as intracervical insemination (ICI), is the process of depositing sperm into the vagina, cervix, or uterus without sexual intercourse. This can be done at home using a donor’s sperm or at a fertility clinic with the use of a sperm donor. Self-insemination is often chosen by individuals and couples who may have fertility issues or are looking for a more affordable option for starting a family.
One of the key factors that can affect the success of self-insemination is diet. A diet that consists of healthy, whole foods can improve the overall health and function of the reproductive system. On the other hand, a diet high in processed foods, trans fats, and added sugars can have a negative impact on fertility. Let’s explore some specific dietary changes that can improve the success of self-insemination.
1. Increase Intake of Fruits and Vegetables
Fruits and vegetables are packed with essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that are crucial for reproductive health. Studies have shown that a diet high in fruits and vegetables can improve sperm quality and female fertility. Leafy greens, such as spinach and kale, are particularly beneficial as they are high in folate, a nutrient that is essential for fetal development.
2. Incorporate Healthy Fats
Healthy fats, such as omega-3 fatty acids, are important for the production of hormones and maintaining a healthy reproductive system. These can be found in foods like salmon, avocado, and nuts. On the other hand, trans fats found in processed foods have been linked to decreased sperm quality and female infertility.
3. Limit Processed Foods and Added Sugars
The Connection Between Diet and Self-Insemination: A Closer Look
Processed foods and added sugars should be limited in any diet, but especially for those trying to conceive through self-insemination. These types of foods can lead to inflammation in the body, which can negatively impact fertility. Instead, opt for whole, unprocessed foods to nourish your body and support reproductive health.
4. Increase Intake of Plant-Based Proteins
Plant-based proteins, such as beans, lentils, and tofu, are excellent sources of protein and have been linked to improved fertility. A study found that women who consumed more plant-based proteins had a lower risk of ovulatory infertility compared to those who consumed more animal-based proteins.
5. Stay Hydrated
Staying hydrated is crucial for reproductive health as it helps maintain a healthy cervical mucus for sperm to travel through. It is recommended to drink at least 8-10 glasses of water per day, but this may vary depending on individual needs.
In addition to these dietary changes, it is important to maintain a healthy weight and engage in regular physical activity. Being overweight or underweight can affect hormone levels and disrupt menstrual cycles, making it more difficult to conceive. Exercise can also help reduce stress, which can have a negative impact on fertility.
In conclusion, diet plays a crucial role in the success of self-insemination. A diet consisting of whole, nutrient-dense foods can improve reproductive health and increase the chances of conception. By making these dietary changes and maintaining a healthy weight, individuals and couples can increase their chances of success with self-insemination.
[1. What is self-insemination?](https://makeamom.com/what-is-self-insemination/)
[2. How can a healthy diet improve fertility?](https://makeamom.com/how-diet-can-improve-fertility/)
[3. What are the best foods to eat for self-insemination?](https://makeamom.com/best-foods-for-self-insemination/)
[4. Can exercise improve the success of self-insemination?](https://makeamom.com/exercise-and-self-insemination/)
[5. What are the risks of self-insemination?](https://makeamom.com/risks-of-self-insemination/)
Summary:
Self-insemination, also known as intracervical insemination (ICI), is the process of depositing sperm into the vagina, cervix, or uterus without sexual intercourse. Diet plays a crucial role in the success of self-insemination, as a diet rich in whole, nutrient-dense foods can improve reproductive health and increase the chances of conception. Some dietary changes that can improve the success of self-insemination include increasing intake of fruits and vegetables, incorporating healthy fats, limiting processed foods and added sugars, increasing intake of plant-based proteins, and staying hydrated. Maintaining a healthy weight and engaging in regular physical activity can also help improve fertility and increase the chances of success with self-insemination.