The Art of Tracking: Using Menstrual Cycles to Prepare for Pregnancy
Tracking menstrual cycles has long been associated with birth control methods, but did you know that it can also be a powerful tool for preparing for pregnancy? The menstrual cycle is a natural, monthly occurrence in a woman’s body that is controlled by hormones and serves as a guide to her reproductive health. By understanding and tracking your menstrual cycle, you can gain valuable insights into your fertility and optimize your chances of conceiving. In this blog post, we will dive into the art of tracking menstrual cycles and how it can help you prepare for pregnancy.
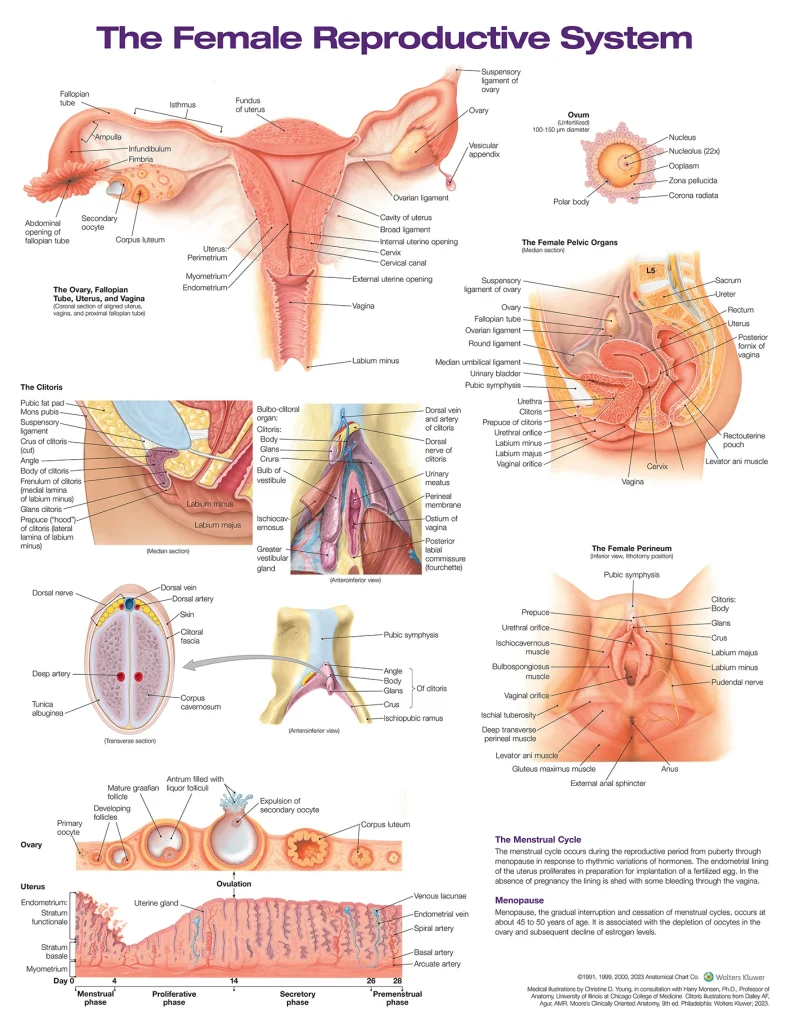
Before we dive into the specifics of tracking menstrual cycles, let’s first understand what a menstrual cycle is and how it works. The menstrual cycle is a series of hormonal changes that occur in a woman’s body every month. It starts on the first day of a woman’s period and ends on the day before her next period. On average, a menstrual cycle lasts 28 days, but it can range from 21 to 35 days. During this cycle, the body prepares for a potential pregnancy by thickening the lining of the uterus and releasing an egg from the ovaries. If the egg is not fertilized, the uterus sheds its lining, resulting in a period.
Now, let’s explore how tracking menstrual cycles can help you prepare for pregnancy.
1. Identifying ovulation:
Ovulation is the process in which an egg is released from the ovaries and is ready to be fertilized by sperm. This typically occurs around day 14 of a 28-day cycle, but it can vary from woman to woman. By tracking your menstrual cycle, you can identify when you are most likely to ovulate, and therefore, know when you are most fertile. This is crucial information when trying to conceive, as having intercourse during ovulation increases the chances of pregnancy.
2. Understanding your fertile window:
The fertile window is the period of time in which a woman is most likely to conceive. It includes the days leading up to and including ovulation. By tracking your menstrual cycle, you can determine your fertile window and plan to have intercourse during this time. This can increase your chances of pregnancy significantly.
3. Identifying irregularities:
Tracking your menstrual cycle can also help you identify any irregularities or abnormalities in your cycle. Irregular periods or missed periods can be indicators of underlying health issues that may affect your fertility. By tracking your cycle, you can bring these concerns to your doctor’s attention and address them early on.
4. Monitoring menstrual health:
The length and regularity of your menstrual cycle can provide valuable insights into your overall reproductive health. If your cycle is consistently irregular, it may be a sign of hormonal imbalances or other health issues that can affect fertility. By tracking your cycle, you can keep an eye on any changes or patterns and discuss them with your doctor.
The Art of Tracking: Using Menstrual Cycles to Prepare for Pregnancy
5. Preparing for conception:
Preparing for pregnancy involves more than just tracking your menstrual cycle. However, by understanding your cycle, you can take proactive steps to optimize your chances of conceiving. For example, you can start taking prenatal vitamins, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding substances that may affect fertility, such as alcohol and tobacco. Additionally, tracking your cycle can help you plan ahead for potential due dates and make necessary lifestyle adjustments.
Now that we have discussed the benefits of tracking menstrual cycles, let’s dive into how to track them effectively.
1. Use a menstrual calendar or app:
One of the easiest ways to track your menstrual cycle is by using a menstrual calendar or app. These tools allow you to input information about your cycle, such as the first day of your period, and they will calculate your fertile window and ovulation dates for you. Some apps even allow you to track other symptoms, such as mood changes and physical sensations, to get a more comprehensive understanding of your cycle.
2. Chart your basal body temperature:
Basal body temperature (BBT) is the lowest body temperature achieved during rest, and it can increase slightly after ovulation. By tracking your BBT every morning and charting it, you can identify when ovulation has occurred. This method requires consistency and precision, so it may not be suitable for everyone. However, it can be an effective way to pinpoint ovulation if done correctly.
3. Monitor cervical mucus:
Cervical mucus is a fluid produced by the cervix that changes in consistency throughout the menstrual cycle. It becomes slippery and stretchy around ovulation, making it easier for sperm to travel through the cervix. By monitoring your cervical mucus, you can determine when you are most fertile and plan to have intercourse during this time.
4. Use ovulation predictor kits:
Ovulation predictor kits (OPKs) are similar to pregnancy tests, but they detect the presence of luteinizing hormone (LH) in urine instead of human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG). LH levels surge right before ovulation, so by using an OPK, you can predict when you will ovulate. However, these kits can be expensive, and they may not work for women with irregular cycles.
In summary, tracking menstrual cycles can be a valuable tool for preparing for pregnancy. It can help you identify ovulation, understand your fertile window, and monitor your reproductive health. By using methods such as menstrual calendars, BBT charting, monitoring cervical mucus, and using OPKs, you can effectively track your cycle and optimize your chances of conceiving. Remember to also consult with your doctor for personalized advice and to address any concerns about your menstrual health.