Self-insemination, also known as self-fertilization, is a process in which an individual can perform artificial insemination on themselves without the assistance of a medical professional. This method has become increasingly popular for individuals and couples in the LGBTQ+ community, single individuals, and those facing fertility struggles. However, with this rise in popularity comes the question of legal rights and protections for those who choose to conceive through self-insemination. In this blog post, we will explore the legal benefits and protections surrounding self-insemination and how they differ from traditional methods of conception.
One of the main legal benefits of self-insemination is the ability to have complete control over the conception process. With traditional methods such as donor insemination, individuals must rely on a third party to provide the sperm for fertilization. This can often lead to complicated legal issues, especially when it comes to parental rights. However, with self-insemination, individuals can choose to use their own sperm or sperm from a known donor, eliminating the need for a third party.
Another benefit of self-insemination is the ability to maintain privacy. Many individuals and couples may feel more comfortable conceiving in the privacy of their own home rather than in a medical setting. This can also provide a sense of control and intimacy in the conception process.
In terms of legal protections, self-insemination can offer individuals and couples more flexibility and autonomy. With traditional methods, there are often strict legal requirements and restrictions, such as the need for a medical professional to perform the insemination. This can limit the options for individuals and couples who may not meet these requirements. However, with self-insemination, individuals have the freedom to choose their own method and timing, without the interference of a medical professional.
Furthermore, self-insemination can also provide legal protections for the non-biological parent in same-sex couples. In some states, the non-biological parent may not have legal parental rights unless they have gone through an adoption process. However, with self-insemination, the non-biological parent can establish their legal rights as a parent through a voluntary acknowledgment of paternity or other legal documents.
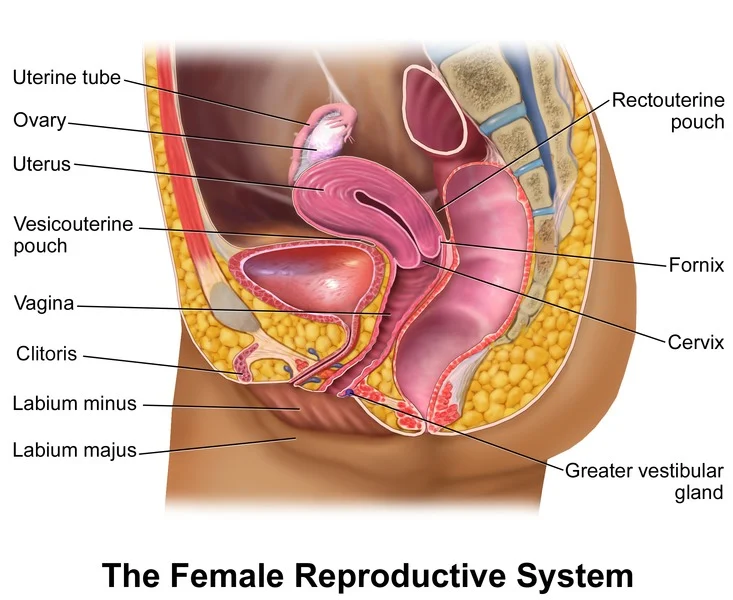
Self-Insemination and the Law: Exploring the Legal Benefits and Protections
It is important to note that the legal benefits and protections surrounding self-insemination may vary depending on the state or country in which the individual resides. Some states may have stricter regulations and requirements, while others may have more lenient laws. It is crucial for individuals to research and understand the laws in their specific location before proceeding with self-insemination.
In addition to legal benefits and protections, there are also some potential legal risks associated with self-insemination. For example, if a known donor is used, there may be a risk of the donor seeking parental rights or financial support in the future. To mitigate these risks, it is important for individuals to have a legal agreement in place with the donor, clearly outlining their intentions and responsibilities.
In conclusion, self-insemination can offer individuals and couples a range of legal benefits and protections, such as control, privacy, flexibility, and autonomy. However, it is essential for individuals to research and understand the laws in their location and take necessary precautions to mitigate any potential legal risks. With proper planning and legal agreements in place, self-insemination can be a viable and empowering option for those looking to conceive.
5 Probable Search Queries:
1. “Legal rights and protections for self-insemination”
2. “Self-insemination vs. traditional methods: legal considerations”
3. “Parental rights and self-insemination”
4. “LGBTQ+ and self-insemination: navigating legalities”
5. “Risks and benefits of self-insemination: a legal perspective”