Self-Insemination and Progesterone: A Comprehensive Guide
The journey to motherhood can be a challenging and emotional one for many women. While some may choose to conceive through traditional methods, others may opt for alternative routes such as self-insemination. This process involves using donor sperm to inseminate oneself at home, without the assistance of a medical professional. Along with self-insemination, many women also turn to progesterone supplementation to help increase their chances of conception. In this comprehensive guide, we will discuss everything you need to know about self-insemination and progesterone, including the benefits, risks, and how to properly go about it.
What is Self-Insemination?
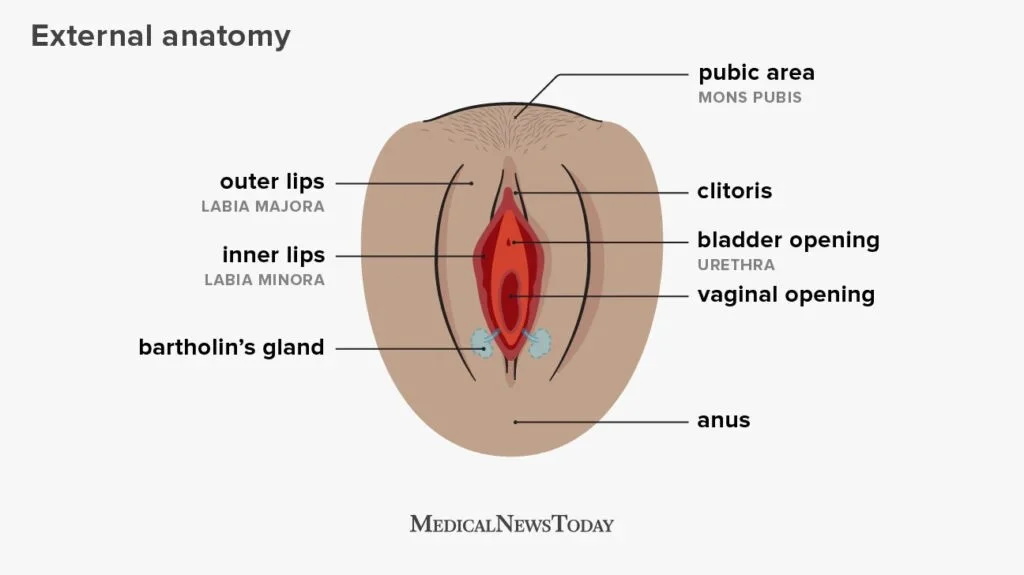
Self-insemination, also known as self-injection or self-catheterization, is the process of using donor sperm to inseminate oneself at home. This method is commonly used by single women, same-sex couples, and heterosexual couples who are struggling with fertility issues. It allows individuals to take control of their fertility journey and eliminates the need for costly medical procedures.
The process of self-insemination typically involves purchasing donor sperm from a reputable sperm bank or finding a known donor. The sperm is then inserted into the vagina using a syringe, turkey baster, or a soft cup. It is important to note that self-insemination does not guarantee pregnancy, and multiple attempts may be necessary.
Benefits of Self-Insemination
One of the main benefits of self-insemination is that it can be done in the comfort of your own home. This eliminates the stress and expense of going to a fertility clinic. It also allows for more privacy and control over the process, as you can choose when and where to inseminate.
Self-insemination also gives individuals the opportunity to choose their donor carefully. They can select a donor based on physical characteristics, medical history, and personal preferences. This can be particularly important for same-sex couples who may want their child to have a genetic connection to both parents.
Risks of Self-Insemination
While self-insemination may seem like a simple and convenient process, it is not without risks. The main risk associated with this method is the potential for sexually transmitted infections (STIs) if proper precautions are not taken. It is crucial to thoroughly screen and test the donor for STIs before using their sperm. It is also recommended to use sterile equipment and follow proper hygiene practices during the insemination process.
Another risk of self-insemination is the possibility of incorrect sperm placement. Improper placement of the sperm can decrease the chances of conception or lead to an ectopic pregnancy. It is essential to carefully follow instructions and seek guidance from a medical professional if needed.
Progesterone and Fertility
Progesterone is a hormone that plays a crucial role in the menstrual cycle and pregnancy. It is produced by the ovaries after ovulation and helps to thicken the uterine lining, preparing it for implantation of a fertilized egg. If pregnancy does not occur, progesterone levels drop, and the uterine lining sheds, resulting in menstruation.
Progesterone supplementation is often recommended for women who are trying to conceive. It can help regulate the menstrual cycle, improve egg quality, and increase the chances of implantation. Progesterone can be taken orally, as a vaginal suppository, or through injections.
How Progesterone is Used in Self-Insemination
In self-insemination, progesterone is often used in the form of a vaginal suppository. This method allows for direct absorption of the hormone into the reproductive tract, providing optimal levels for conception. The suppositories are typically inserted once or twice a day, starting a few days before ovulation and continuing until a pregnancy test is taken.
Self-Insemination and Progesterone: A Comprehensive Guide
Progesterone supplementation can also be used in conjunction with intrauterine insemination (IUI) or in vitro fertilization (IVF). In these cases, progesterone is often taken in the form of injections to support the growth of the uterine lining and increase the chances of implantation.
How to Properly Perform Self-Insemination
Performing self-insemination at home requires careful preparation and following the proper steps. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to properly perform self-insemination:
1. Determine your ovulation window: Use an ovulation predictor kit or track your basal body temperature to determine when you are most likely to ovulate.
2. Purchase donor sperm: Purchase donor sperm from a reputable sperm bank or find a known donor who has been thoroughly screened for STIs.
3. Gather supplies: You will need a syringe, turkey baster, or soft cup to insert the sperm, a mirror to help with placement, and a timer to track the time after insemination.
4. Prepare the sperm: Thaw the sperm according to the instructions provided by the sperm bank. If using a known donor, make sure the sperm is collected and stored properly.
5. Insert the sperm: Using a syringe, turkey baster, or soft cup, insert the sperm into the vagina as close to the cervix as possible. Use a mirror to ensure proper placement.
6. Wait: Lie down with your hips slightly elevated for 15-30 minutes to allow the sperm to reach the cervix.
7. Progesterone supplementation: If using progesterone suppositories, insert one into the vagina as instructed.
8. Wait for pregnancy: Continue to track your ovulation and perform self-insemination during your most fertile window. Take a pregnancy test after your missed period to determine if the insemination was successful.
In conclusion, self-insemination and progesterone supplementation can be effective methods for women trying to conceive. They offer a more affordable and convenient option for those who want to take control of their fertility journey. However, it is essential to carefully consider the risks and follow proper protocols to ensure a safe and successful process. Consult with a medical professional if you have any concerns or questions about self-insemination and progesterone use.
Search Queries:
1. “How to perform self-insemination at home”
2. “Benefits and risks of using progesterone in self-insemination”
3. “Where to find donor sperm for self-insemination”
4. “Guidelines for safe and effective self-insemination”
5. “Is progesterone supplementation necessary for self-insemination?”
Summary:
Self-insemination and progesterone supplementation are alternative methods for women trying to conceive. Self-insemination involves using donor sperm to inseminate oneself at home, while progesterone supplementation can help regulate the menstrual cycle and increase the chances of implantation. This guide covers the benefits, risks, and proper methods for performing self-insemination and using progesterone. It also emphasizes the importance of careful consideration and following proper protocols for a safe and successful process.