Ovulation Tracking and Your Thyroid: How Hormone Levels Affect Fertility
When it comes to trying to conceive, many women are familiar with the basics of tracking their ovulation cycle. However, what many may not realize is that their thyroid plays a crucial role in this process. The thyroid gland is a small but mighty organ located in the neck that produces hormones essential for regulating metabolism, heart rate, and other bodily functions. These hormones also have a significant impact on fertility and ovulation. In this blog post, we will explore how thyroid hormones affect ovulation and fertility, and the importance of tracking and managing your thyroid health in your journey to motherhood.
1. How does the thyroid gland work?
The thyroid gland produces two main hormones: thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). These hormones regulate metabolism, heart rate, body temperature, and other vital functions. The production of these hormones is stimulated by another hormone called thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which is released by the pituitary gland in the brain. When the thyroid gland is functioning correctly, it produces the right amount of thyroid hormones to keep the body in balance.
2. The connection between thyroid hormones and ovulation
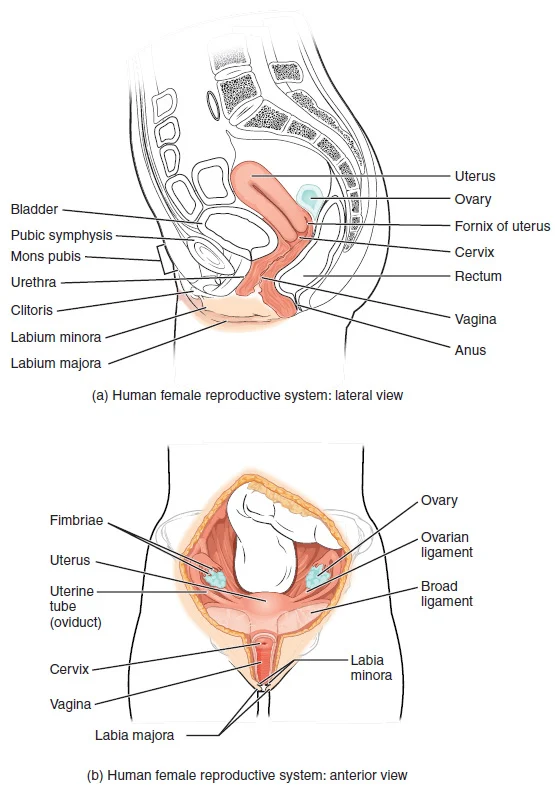
Thyroid hormones have a direct impact on ovulation. Estrogen, one of the hormones involved in ovulation, is essential for the development of the egg follicles. T3 and T4 hormones play a crucial role in the production and release of estrogen. If there is an imbalance in thyroid hormone levels, it can lead to irregularities in the menstrual cycle, making it difficult to predict and track ovulation accurately.
Ovulation Tracking and Your Thyroid: How Hormone Levels Affect Fertility
3. The impact of hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism on fertility
Thyroid disorders are common in women of reproductive age, with hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) being the most prevalent. Hypothyroidism can cause a variety of symptoms, including irregular periods, weight gain, fatigue, and difficulty conceiving. In contrast, hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) can lead to weight loss, increased heart rate, and irregular or absent periods. Both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can affect ovulation and make it challenging to become pregnant.
4. How to track ovulation with thyroid disorders
Monitoring your ovulation cycle is the key to successful conception. For women with thyroid disorders, it is essential to track your menstrual cycle using ovulation predictor kits (OPKs), basal body temperature (BBT) tracking, and cervical mucus monitoring. These methods can help you identify the most fertile days of your cycle and increase your chances of conceiving.
5. The importance of managing your thyroid health
If you have been diagnosed with a thyroid disorder, it is crucial to work closely with your doctor to manage your condition. Treatment for hypothyroidism typically involves taking synthetic thyroid hormone medication to regulate hormone levels. In contrast, hyperthyroidism may require medication, radioactive iodine, or surgery to manage the overproduction of thyroid hormones. By managing your thyroid health, you can improve your overall well-being and increase your chances of ovulation and successful conception.
In conclusion, the thyroid gland plays a crucial role in ovulation and fertility. If you are trying to conceive, it is essential to track and manage your thyroid health to optimize your chances of becoming pregnant. By understanding the connection between thyroid hormones and ovulation and working closely with your doctor, you can take control of your fertility journey and make your dream of motherhood a reality.