Ectopic pregnancy is a condition where a fertilized egg implants itself outside of the uterus, most commonly in the fallopian tubes. This can be a life-threatening situation and often results in the loss of the pregnancy. Unfortunately, women who have had an ectopic pregnancy are at a higher risk of experiencing it again in future pregnancies. This can be a stressful and emotional time for women who are trying to conceive and are worried about the possibility of another ectopic pregnancy. Ovulation prediction can be a helpful tool for women with a history of ectopic pregnancy, as it can help them determine their most fertile days and increase their chances of a successful pregnancy. In this blog post, we will discuss what women should know about ovulation prediction if they have a history of ectopic pregnancy.
1. Understanding Ovulation and its Importance
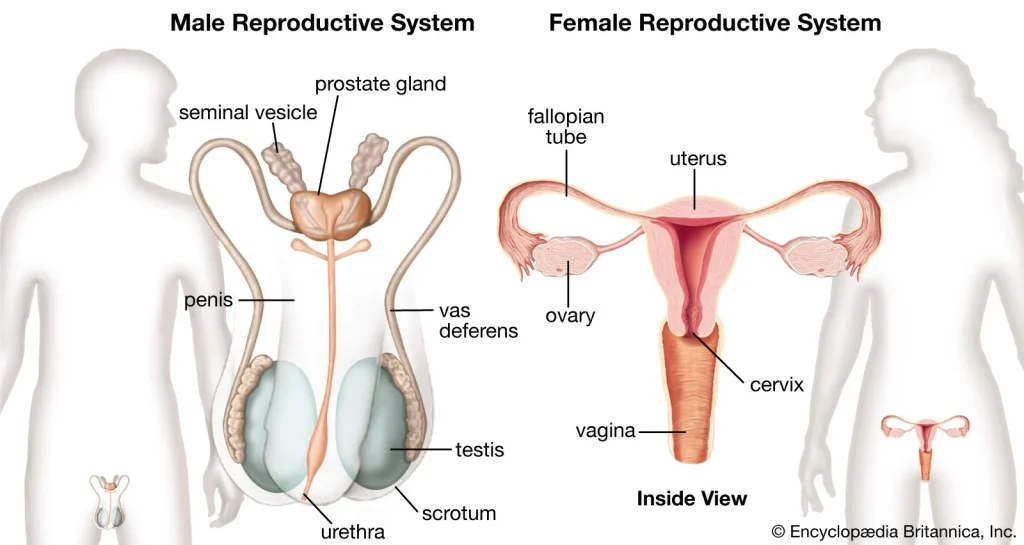
Ovulation is the process where a mature egg is released from the ovary and travels down the fallopian tube, ready to be fertilized by a sperm. This usually happens around day 14 of a 28-day menstrual cycle, but can vary for each woman. Ovulation is a crucial aspect of fertility, as it is the only time during a woman’s cycle when she can conceive. For women with a history of ectopic pregnancy, understanding their ovulation can help them plan for a healthy pregnancy.
2. Tracking Basal Body Temperature (BBT)
One method of ovulation prediction is tracking basal body temperature (BBT). BBT is the body’s resting temperature, which can be affected by hormone fluctuations during the menstrual cycle. By tracking BBT every morning before getting out of bed, women can see a slight increase in their temperature, which indicates ovulation. This method can be helpful for women with a history of ectopic pregnancy, as it can help them determine their most fertile days and plan for timed intercourse or fertility treatments.
Ovulation Prediction for Women with a History of Ectopic Pregnancy: What to Know
3. Using Ovulation Prediction Kits (OPKs)
Ovulation prediction kits (OPKs) are another popular method for predicting ovulation. These kits detect the surge of luteinizing hormone (LH) in a woman’s urine, which occurs 24-36 hours before ovulation. The surge of LH triggers the release of the egg from the ovary, making this an accurate way to predict ovulation. Women with a history of ectopic pregnancy can use OPKs to track their LH surge and determine their most fertile days.
4. Monitoring Cervical Mucus Changes
Another sign of ovulation is changes in cervical mucus. As a woman approaches ovulation, her cervical mucus becomes thinner, clearer, and more stretchy, resembling the texture of egg whites. This type of mucus helps sperm travel easily through the cervix and into the fallopian tubes to fertilize the egg. Women with a history of ectopic pregnancy can track these changes in their cervical mucus to determine their most fertile days.
5. Working with a Fertility Specialist
If a woman with a history of ectopic pregnancy is having difficulty predicting ovulation or achieving pregnancy, it may be beneficial to work with a fertility specialist. These doctors can monitor hormone levels, perform ultrasounds, and provide guidance on the best methods for ovulation prediction based on the individual’s medical history. They can also offer treatments such as intrauterine insemination (IUI) or in vitro fertilization (IVF) to increase the chances of a successful pregnancy.
In conclusion, ovulation prediction can be a valuable tool for women with a history of ectopic pregnancy. By tracking BBT, using OPKs, and monitoring changes in cervical mucus, women can determine their most fertile days and increase their chances of conceiving a healthy pregnancy. It is also essential to work with a fertility specialist for guidance and support throughout the process. Remember to take care of your physical and emotional well-being during this time and trust in the journey of becoming a mother.