Navigating the Legal Implications of Self-Insemination for Traditional and Non-Traditional Families
In recent years, there has been a significant increase in the number of families created through self-insemination. This method allows individuals or couples to have a child without the involvement of a traditional sperm donor or fertility clinic. While self-insemination may seem like a simple and straightforward process, there are still legal implications that must be considered, particularly for non-traditional families. In this blog post, we will explore the legal aspects of self-insemination for both traditional and non-traditional families and provide guidance for navigating these complexities.
Probable search queries:
1. “Legal implications of self-insemination”
2. “Self-insemination for non-traditional families”
3. “DIY insemination legal considerations”
4. “Same-sex self-insemination laws”
5. “Sperm donor vs. self-insemination legal differences”
Self-Insemination for Traditional Families
For traditional families, self-insemination may seem like a simpler and less expensive option compared to other fertility treatments. However, it is important to understand that there are still legal considerations to take into account. In most cases, the donor of the sperm used in self-insemination is considered the legal father of the child. This means that they may have parental rights and responsibilities, including child support and visitation.
To avoid any potential legal conflicts, it is crucial to have a written agreement between the donor and the parents before proceeding with self-insemination. This agreement should clearly outline the intentions of all parties involved and address issues such as parental rights and financial responsibilities. It is also recommended to consult with a lawyer who is knowledgeable in family law to ensure that the agreement is legally binding and enforceable.
In addition, it is important to keep in mind that laws and regulations regarding self-insemination may vary from state to state. It is advisable to research and understand the laws in your state before proceeding with self-insemination to avoid any legal complications in the future.
Self-Insemination for Non-Traditional Families
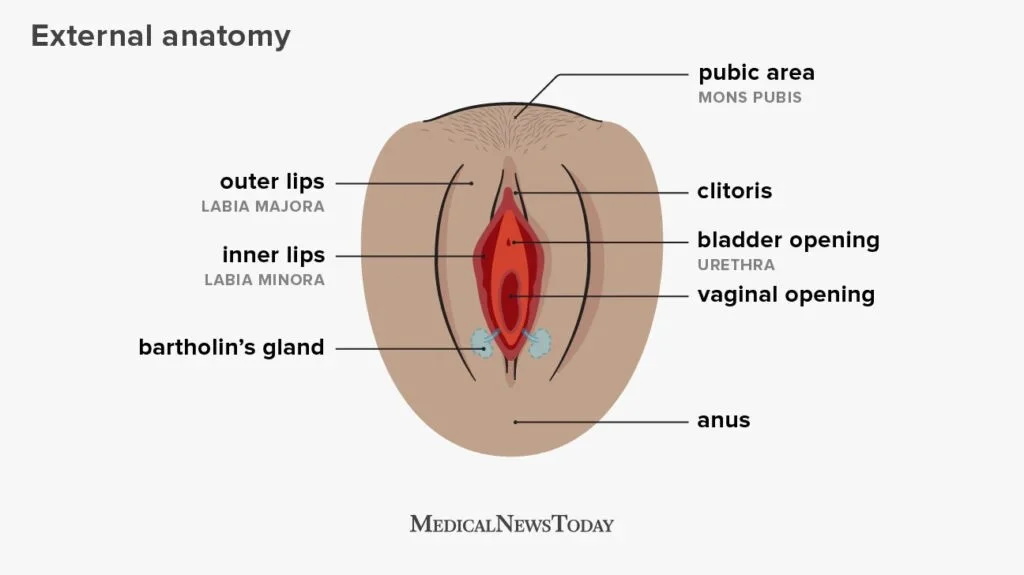
Navigating the Legal Implications of Self-Insemination for Traditional and Non-Traditional Families
Self-insemination can be a viable option for non-traditional families, including same-sex couples and single individuals. However, the legal implications for these families may be more complex. In many states, same-sex couples are not recognized as legal parents unless they go through a formal adoption process. This means that the donor of the sperm may have legal rights to the child, even if they have no intention of being involved in the child’s life.
To protect the rights of both parents, it is crucial to have a legal agreement in place before proceeding with self-insemination. This agreement should outline the intentions of all parties involved and address issues such as parental rights, financial responsibilities, and the donor’s involvement in the child’s life. It is also recommended to consult with a lawyer who specializes in family and LGBT law to ensure that the agreement is legally binding and enforceable.
It is important to note that even with a legal agreement in place, there may still be challenges for non-traditional families in terms of parental rights and recognition. It is advisable to seek legal counsel and stay informed about any changes in laws and regulations that may affect non-traditional families.
Alternative Options for Non-Traditional Families
For non-traditional families who are concerned about the legal implications of self-insemination, there are alternative options available. These may include using a known sperm donor who is willing to waive their parental rights, working with a sperm bank or fertility clinic, or pursuing adoption or foster care.
Using a known sperm donor who is willing to waive their parental rights can provide a more secure legal framework for non-traditional families. However, it is important to note that there may still be legal challenges and complications, and it is advisable to consult with a lawyer and have a written agreement in place.
Working with a sperm bank or fertility clinic can also provide a more secure legal framework for non-traditional families. In this case, the sperm donor would have no legal rights or responsibilities to the child, and the legal parental rights would be granted to the intended parent(s) through the process of assisted reproductive technology.
Finally, adoption or foster care may be an option for non-traditional families who wish to have a child. These processes involve extensive legal procedures, but once the adoption is finalized, the adoptive parents have the same legal rights and responsibilities as biological parents.
In conclusion, self-insemination can be a viable option for both traditional and non-traditional families, but it is essential to understand the legal implications and take necessary precautions to avoid any potential legal conflicts. It is advisable to consult with a lawyer who specializes in family law and stay informed about the laws and regulations in your state. With careful planning and legal guidance, self-insemination can be a fulfilling and rewarding way to start a family.