Navigating Self-Insemination with Progesterone: A Comprehensive Guide
Self-insemination is becoming an increasingly popular option for individuals and couples who are trying to conceive. It allows for a more private and intimate approach to conception, as well as giving more control over the timing and process. However, self-insemination can come with its own set of challenges, especially when it comes to using progesterone. Progesterone is a hormone that plays a crucial role in pregnancy and can be used to support and maintain a pregnancy. In this blog post, we will explore the ins and outs of navigating self-insemination with progesterone, including what it is, how to use it, and its potential benefits and risks.
What is Progesterone?
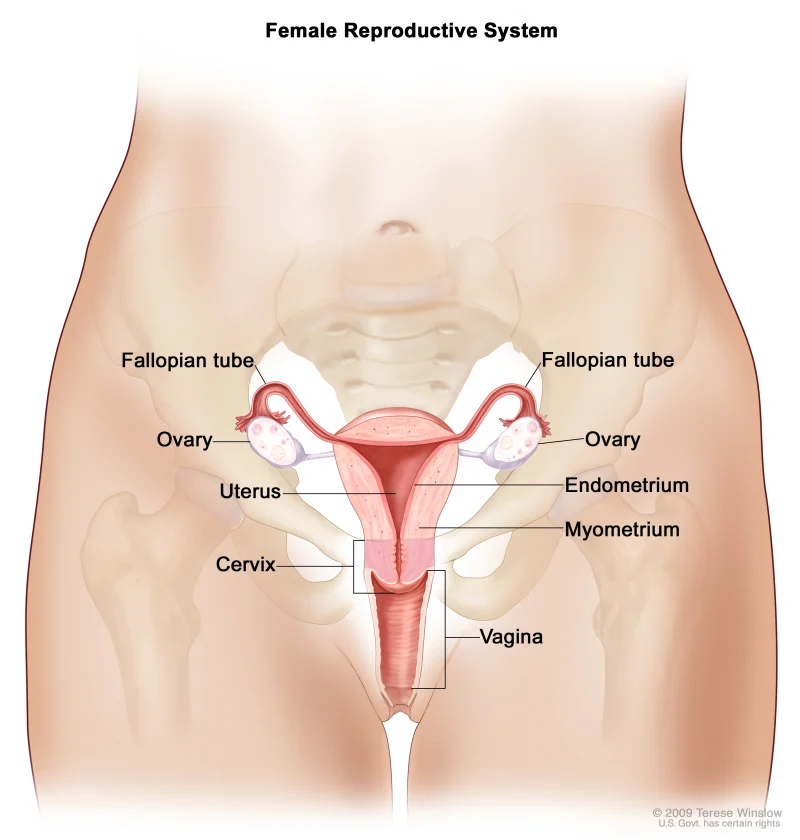
Progesterone is a hormone that is naturally produced in the body by the ovaries and the placenta during pregnancy. It plays a vital role in preparing the uterus for pregnancy and maintaining it throughout the first trimester. Progesterone levels increase after ovulation, and if pregnancy occurs, they continue to rise to support the implantation of the fertilized egg. If pregnancy does not occur, progesterone levels drop, and menstruation begins.
Progesterone can also be taken as a medication in the form of pills, suppositories, or injections. It is commonly used in assisted reproductive technology (ART) to support pregnancy and reduce the risk of miscarriage. However, it can also be used in self-insemination to help increase the chances of conception and maintain a pregnancy.
How to Use Progesterone in Self-Insemination
If you are considering using progesterone in self-insemination, it is essential to first consult with a healthcare provider. They can help determine if progesterone is necessary for your specific situation and provide guidance on how to use it effectively. Progesterone can be taken at different times during the menstrual cycle, depending on your individual needs. Here are the three main ways to use progesterone in self-insemination:
1. Natural Cycle: If you have regular menstrual cycles, you can use progesterone during the luteal phase, which is the time between ovulation and the start of your period. This can help thicken the uterine lining, making it more receptive to implantation.
2. Medication Cycle: If you are using fertility medications to stimulate ovulation, your doctor may prescribe progesterone to support the development of the uterine lining.
3. Artificial Insemination: If you are using donor sperm for self-insemination, you may be prescribed progesterone to prepare the uterus for implantation and maintain a pregnancy.
Progesterone can be taken orally in pill form, inserted vaginally as a suppository, or injected into the muscle. Your healthcare provider will determine the best method for you based on your medical history and individual needs.
Benefits and Risks of Using Progesterone in Self-Insemination
The use of progesterone in self-insemination has both potential benefits and risks. Here are some of the main ones to consider:
Navigating Self-Insemination with Progesterone
Benefits:
1. Increased Chance of Conception: Progesterone can help thicken the uterine lining, making it more receptive to implantation. This can increase the chances of successful conception.
2. Reduced Risk of Miscarriage: Progesterone is crucial in maintaining a healthy pregnancy, and using it in self-insemination can help reduce the risk of miscarriage.
3. More Control over the Process: Using progesterone in self-insemination allows for more control over the timing and process of conception, which can be empowering for individuals and couples.
Risks:
1. Side Effects: Progesterone can cause side effects such as bloating, breast tenderness, mood swings, and headaches. These are usually mild and go away after a few days, but it is essential to discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider.
2. Increased Chance of Multiple Pregnancy: Progesterone can sometimes lead to the release of more than one egg, which can result in a multiple pregnancy.
3. Cost: Progesterone can be expensive, especially if taken over an extended period. It is essential to discuss the cost and any potential insurance coverage with your healthcare provider.
Navigating self-insemination with progesterone can be a complex and challenging process. It is crucial to have a good understanding of the benefits and risks and to work closely with a healthcare provider throughout the journey.
Possible Search Queries:
1. What is progesterone and how is it used in self-insemination?
2. What are the benefits and risks of using progesterone in self-insemination?
3. How do I use progesterone in self-insemination?
4. Can progesterone increase my chances of conception in self-insemination?
5. How can I get progesterone for self-insemination?
Summary:
Self-insemination with progesterone is a popular option for individuals and couples who are trying to conceive. Progesterone is a hormone that can be used to support and maintain a pregnancy and can be taken in different forms, depending on individual needs. Using progesterone in self-insemination can increase the chances of conception and reduce the risk of miscarriage, but it also comes with potential risks and side effects. It is crucial to work closely with a healthcare provider to determine if progesterone is necessary and to use it effectively.