Menstrual Cycle 101: A Beginner’s Guide to Understanding How It Affects Fertility
The menstrual cycle is a natural and complex process that occurs in the female body. It is a monthly occurrence that prepares the body for potential pregnancy. Understanding how the menstrual cycle works and its impact on fertility is crucial for women who are trying to conceive or want to learn more about their reproductive health. In this blog post, we will dive into the basics of the menstrual cycle, its different phases, and how it affects fertility.
Search Queries:
1. What is the menstrual cycle and how does it affect fertility?
2. Understanding the different phases of the menstrual cycle and their impact on fertility.
3. How does ovulation play a role in the menstrual cycle and fertility?
4. Tips for tracking your menstrual cycle to optimize fertility.
5. Common myths about the menstrual cycle and fertility debunked.
The Menstrual Cycle: A Brief Overview
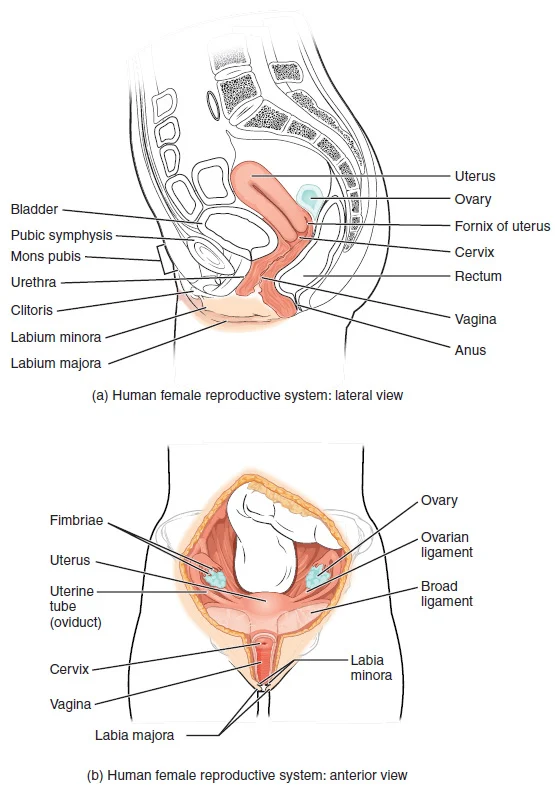
The menstrual cycle is a series of hormonal changes that occur in the female body every month. It starts on the first day of menstruation, which is when a woman’s period begins, and ends on the first day of the next period. On average, a menstrual cycle lasts around 28 days, but it can vary from person to person and can range from 21 to 35 days. The menstrual cycle is regulated by the hormones estrogen and progesterone, which are produced by the ovaries.
The Different Phases of the Menstrual Cycle
The menstrual cycle consists of four phases: menstrual, follicular, ovulation, and luteal.
1. Menstrual Phase: The menstrual phase is the first day of the menstrual cycle, marked by the shedding of the uterine lining, also known as the period. This phase can last anywhere from three to seven days, with an average blood loss of about two tablespoons.
2. Follicular Phase: The follicular phase starts on the first day of menstruation and lasts until ovulation. During this phase, the pituitary gland releases follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), which stimulates the growth of follicles in the ovaries. These follicles contain eggs, and only one dominant follicle will continue to grow and mature. As the follicles grow, they produce estrogen, which thickens the uterine lining in preparation for potential pregnancy. This phase usually lasts around 10 to 14 days.
3. Ovulation: Ovulation occurs around the middle of the menstrual cycle, usually on day 14 for a 28-day cycle. During this phase, the dominant follicle releases a mature egg into the fallopian tube. The egg can survive for up to 24 hours after ovulation, waiting for fertilization by sperm. This is the most fertile time of the menstrual cycle, and the chances of pregnancy are highest during this phase.
4. Luteal Phase: The luteal phase starts after ovulation and lasts until the first day of the next period. After the egg is released, the empty follicle transforms into a structure called the corpus luteum, which produces progesterone. Progesterone helps to thicken the uterine lining further and prepare it for implantation if fertilization occurs. If the egg is not fertilized, the corpus luteum will shrink and stop producing progesterone, triggering the start of the next period.
How the Menstrual Cycle Affects Fertility
The menstrual cycle is closely linked to fertility, as it prepares the body for pregnancy. The most fertile time of the cycle is during ovulation when the egg is released and can be fertilized by sperm. However, it is essential to note that the fertile window is not just limited to the day of ovulation but can last up to six days, including the day of ovulation and the five days leading up to it. This is because sperm can survive in the female reproductive tract for up to five days, increasing the chances of fertilization.
Menstrual Cycle 101: A Beginner's Guide to Understanding How It Affects Fertility
Tracking Your Menstrual Cycle for Optimal Fertility
Tracking your menstrual cycle can be helpful if you are trying to conceive. By understanding your cycle and when ovulation occurs, you can plan intercourse during your most fertile days and increase your chances of pregnancy. Some methods for tracking your menstrual cycle include:
1. Calendar Method: The calendar method involves tracking your menstrual cycle for several months to determine the average length of your cycle. You can then predict when your next period will start and when ovulation is likely to occur.
2. Basal Body Temperature (BBT) Method: This method involves taking your temperature every morning before getting out of bed. After ovulation, progesterone causes a slight increase in body temperature, which can indicate that ovulation has occurred.
3. Ovulation Predictor Kits: These kits detect the presence of luteinizing hormone (LH) in the urine. LH levels surge 24-36 hours before ovulation, indicating the most fertile time of the cycle.
Debunking Common Myths about the Menstrual Cycle and Fertility
There are many misconceptions and myths surrounding the menstrual cycle and fertility. Here are a few common ones debunked:
1. You can get pregnant at any time during your menstrual cycle: While it is possible to get pregnant at any time during the cycle, the chances are highest during ovulation.
2. Irregular periods mean you can’t get pregnant: Irregular periods can make it more challenging to predict ovulation, but it is still possible to get pregnant.
3. You can’t get pregnant while on your period: While the chances are lower, it is still possible to get pregnant during your period, especially if you have a shorter cycle.
4. You can’t get pregnant if you have sex right after your period: Sperm can survive in the female reproductive tract for up to five days, so if you have a short cycle, there is a chance of getting pregnant right after your period.
5. Birth control pills can affect fertility: Birth control pills do not affect long-term fertility. However, it may take a few months for your body to regulate after stopping the pill.
In conclusion, understanding the menstrual cycle is crucial for women who want to optimize their fertility. By tracking your cycle and knowing when ovulation occurs, you can increase your chances of getting pregnant. It is also essential to debunk common myths and misconceptions about the menstrual cycle and fertility. Remember, every woman’s cycle is unique, and if you have concerns about your menstrual cycle or fertility, it is always best to consult with your healthcare provider.