Managing Hormonal Imbalance: Tips for Better Reproductive Health
Hormones play a crucial role in the functioning of our reproductive system. They regulate our menstrual cycle, ovulation, and overall reproductive health. However, hormonal imbalances can occur due to various reasons, such as stress, poor diet, and underlying health conditions. This can lead to a range of symptoms, including irregular periods, mood swings, and difficulty getting pregnant. Managing hormonal imbalance is essential for maintaining optimal reproductive health. In this blog post, we will discuss some tips for managing hormonal imbalance and improving your reproductive health.
1. Improve Your Diet
The food we eat has a significant impact on our hormones. Consuming a healthy and balanced diet can help regulate hormone production and maintain hormonal balance. Foods rich in healthy fats, such as avocados, nuts, and fatty fish, can help boost estrogen production. Including more fiber-rich foods, like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can help eliminate excess estrogen from the body. It is also essential to limit or avoid processed and sugary foods, which can disrupt hormonal balance.
2. Exercise Regularly
Regular exercise not only benefits our physical health but also plays a crucial role in regulating hormones. It can help reduce stress levels, which can be a major contributor to hormonal imbalance. Exercise also helps improve insulin sensitivity, which is essential for maintaining balanced hormone levels. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise, such as brisk walking, jogging, or cycling, at least five days a week.
3. Manage Stress
Stress is a significant contributor to hormonal imbalance. When we are stressed, our body releases cortisol, also known as the stress hormone. High levels of cortisol can disrupt the production of other hormones, leading to an imbalance. Therefore, it is essential to find ways to manage stress, such as practicing meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises. Engaging in activities you enjoy, spending time with loved ones, and getting enough rest can also help reduce stress levels.
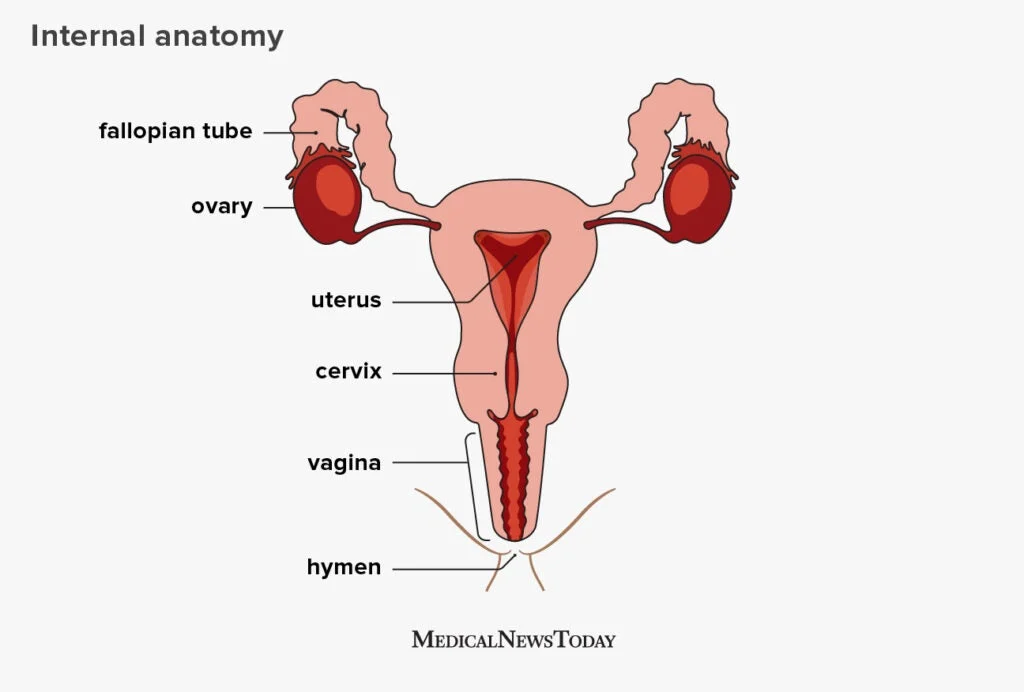
Managing Hormonal Imbalance: Tips for Better Reproductive Health
4. Consider Herbal Remedies
Herbal remedies have been used for centuries to regulate hormones and improve reproductive health. Some popular herbs for hormonal balance include chasteberry, maca root, and red raspberry leaf. However, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before taking any herbal supplements, as they can interact with medications and may not be suitable for everyone.
5. Get Enough Sleep
Getting enough quality sleep is crucial for maintaining hormonal balance. Our body produces the majority of its hormones while we sleep. Therefore, not getting enough sleep can disrupt the production and regulation of hormones, leading to an imbalance. Aim for at least seven to eight hours of sleep each night, and try to maintain a regular sleep schedule.
6. Consider Hormone Replacement Therapy
In some cases, hormonal imbalance may require medical intervention. Hormone replacement therapy, also known as HRT, is a treatment option that involves supplementing hormones that the body is not producing enough of. This can help alleviate symptoms of hormonal imbalance and improve reproductive health. However, HRT should only be considered after consulting with a healthcare professional, as it may not be suitable for everyone and can have potential side effects.
In conclusion, managing hormonal imbalance is crucial for maintaining optimal reproductive health. By incorporating these tips into your lifestyle, you can help regulate your hormones and improve your overall well-being. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional if you are experiencing persistent symptoms or considering any supplements or treatments.
Search Queries:
1. “Natural ways to manage hormonal imbalance”
2. “Foods for hormonal balance”
3. “How to regulate hormones for better reproductive health”
4. “Benefits of exercise for hormonal balance”
5. “Hormone replacement therapy for hormonal imbalance”