Blog Post: Hormonal Imbalances and Reproductive Endocrinology: Understanding the Connection
Hormonal imbalances can have a significant impact on our overall health and well-being, and one area where they can have a particularly profound effect is our reproductive health. Reproductive endocrinology is a specialized field that focuses on the hormonal and reproductive systems, and understanding the connection between the two is essential for maintaining optimal health and fertility.
In this blog post, we will delve into the complexities of hormonal imbalances and reproductive endocrinology, discussing the various hormones involved in reproductive health, common hormonal imbalances, and how they can affect our reproductive systems. We will also explore the role of reproductive endocrinologists in diagnosing and treating hormonal imbalances and their impact on fertility.
What are Hormones and How Do They Affect Reproductive Health?
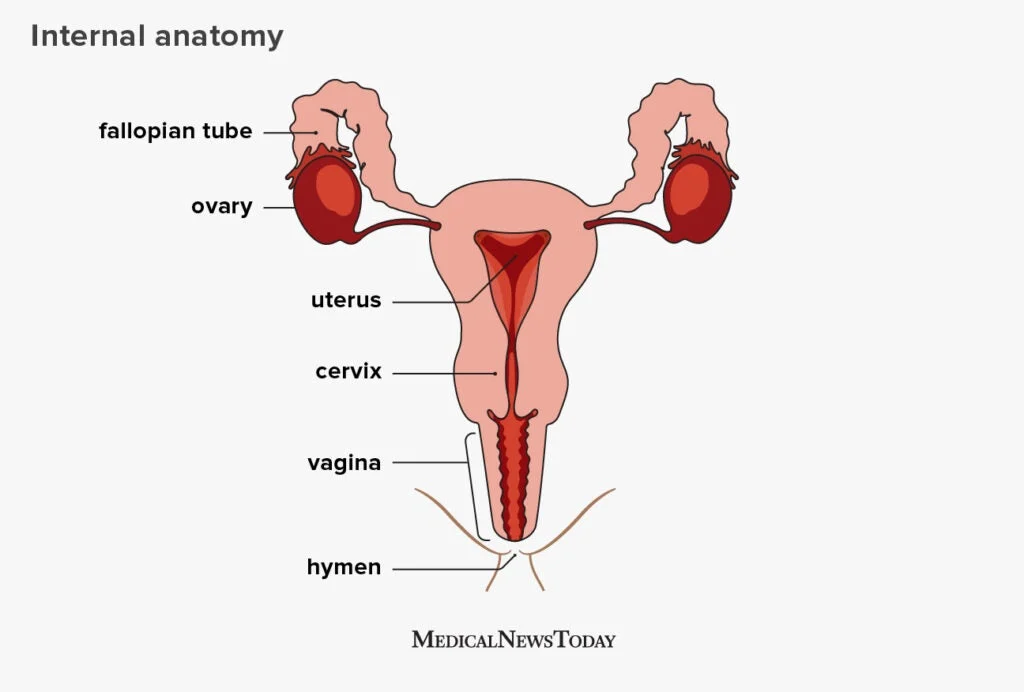
Hormones are chemical messengers produced by the endocrine glands that regulate various bodily functions. In terms of reproductive health, the main hormones involved are estrogen, progesterone, testosterone, luteinizing hormone (LH), and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). These hormones work together to regulate the menstrual cycle, ovulation, and the development of reproductive organs.
Estrogen is primarily responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system, including the growth of the uterus and breasts, and the thickening of the uterine lining in preparation for pregnancy. Progesterone plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy pregnancy and preparing the body for childbirth.
In men, testosterone is the main hormone responsible for the development and maintenance of male reproductive organs and characteristics. LH and FSH work together to stimulate the production of testosterone and sperm.
Hormonal Imbalances and their Impact on Reproductive Health
When there is an imbalance in the levels of these hormones, it can have a significant impact on reproductive health. In women, hormonal imbalances can cause irregular or absent periods, difficulty getting pregnant, and menopausal symptoms such as hot flashes and mood swings. Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), a common hormonal disorder, is characterized by high levels of androgens (male hormones) and can lead to irregular periods, difficulty getting pregnant, and other health issues such as insulin resistance and weight gain.
In men, hormonal imbalances can cause a decrease in libido, erectile dysfunction, and issues with sperm production. Low levels of testosterone, also known as hypogonadism, can affect a man’s fertility and overall health.
Hormonal Imbalances and Reproductive Endocrinology: Understanding the Connection
Reproductive Endocrinology and its Role in Diagnosing and Treating Hormonal Imbalances
Reproductive endocrinology is a subspecialty of obstetrics and gynecology that focuses on the hormonal and reproductive systems. Reproductive endocrinologists are highly trained in diagnosing and treating hormonal imbalances that affect reproductive health.
In addition to conducting a thorough medical history and physical examination, reproductive endocrinologists may also order blood tests to measure hormone levels and perform imaging tests to evaluate the reproductive organs. These tests help identify any hormonal imbalances and determine the best course of treatment.
Treatment options for hormonal imbalances may include lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise, medications to regulate hormone levels, or fertility treatments such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) or intrauterine insemination (IUI). Reproductive endocrinologists work closely with their patients to develop personalized treatment plans that address their specific needs and goals.
The Connection Between Hormonal Imbalances and Fertility
Hormonal imbalances can have a significant impact on fertility, as they can disrupt the delicate balance of hormones needed for ovulation and sperm production. For women, hormonal imbalances such as PCOS, thyroid disorders, and high levels of prolactin (a hormone that stimulates milk production) can make it difficult to get pregnant. In men, low levels of testosterone or thyroid disorders can affect sperm production and quality.
By working with a reproductive endocrinologist to diagnose and treat hormonal imbalances, individuals can improve their chances of conceiving and having a healthy pregnancy. In some cases, fertility treatments may be necessary to overcome hormonal imbalances and achieve a successful pregnancy.
In addition to affecting fertility, hormonal imbalances can also have a significant impact on the health of a pregnancy. Women with uncontrolled diabetes or thyroid disorders, for example, may have a higher risk of pregnancy complications such as gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, and preterm birth. By addressing hormonal imbalances before and during pregnancy, women can reduce these risks and have a healthier pregnancy.
In summary, hormonal imbalances and reproductive endocrinology are closely linked, and understanding this connection is crucial for maintaining optimal reproductive health. Hormonal imbalances can have a significant impact on fertility and can also affect the health of a pregnancy. By working with a reproductive endocrinologist, individuals can diagnose and treat hormonal imbalances and improve their chances of conceiving and having a healthy pregnancy.
5 Probable Search Queries Related to the Post Subject:
1. “Hormonal imbalances and reproductive health”
2. “Reproductive endocrinology and fertility”
3. “Common hormonal imbalances in men and women”
4. “The role of reproductive endocrinologists in treating hormonal disorders”
5. “How to address hormonal imbalances for better reproductive health”