From Plate to Pregnancy: The Link Between Diet and Self-Insemination
Pregnancy is a life-changing experience that many women dream of. However, for some women, conceiving a child can be a difficult and emotional journey. While there are many medical interventions available, some women are turning to a more natural approach – self-insemination. This method involves inserting sperm into the vagina without the use of medical assistance. And while self-insemination may seem like a simple process, there are certain factors that can greatly impact its success, one of which is diet.
It is a well-known fact that a person’s diet affects their overall health and well-being. But what many people may not realize is that diet also plays a significant role in fertility and pregnancy. In this blog post, we will explore the link between diet and self-insemination, and how making certain dietary changes can improve the chances of conception.
The Role of Diet in Fertility and Pregnancy
Before we dive into the specific connection between diet and self-insemination, it’s important to understand the role of diet in fertility and pregnancy. The food we eat provides the necessary nutrients for our bodies to function properly. These nutrients also play a crucial role in reproductive health, as they support the production of hormones and the growth of healthy eggs and sperm.
A balanced and nutritious diet can help regulate the menstrual cycle, increase the likelihood of ovulation, and improve the quality of the reproductive cells. On the other hand, a poor diet can lead to hormonal imbalances, irregular periods, and even conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) that can make conception challenging.
The Link Between Diet and Self-Insemination
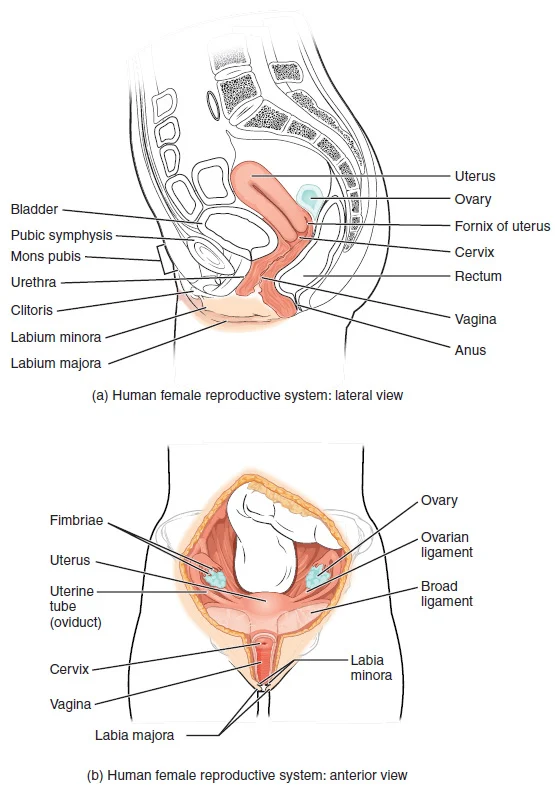
Now, let’s look at how diet specifically affects self-insemination. When trying to conceive through this method, the goal is to introduce sperm into the vagina at the most fertile time of the menstrual cycle. This is usually around the time of ovulation, when an egg is released from the ovary and travels to the uterus.
To improve the chances of successful self-insemination, it’s important to have a healthy and balanced diet that supports ovulation and increases the quality of sperm. Here are some specific dietary factors to consider:
1. Nutrient-rich Foods
A diet rich in nutrients such as vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants is essential for reproductive health. These nutrients help support the production of healthy eggs and sperm, as well as improve the quality of cervical mucus, which is important for sperm survival and movement. Foods such as leafy greens, berries, nuts, and seeds are all excellent sources of these nutrients.
From Plate to Pregnancy: The Link Between Diet and Self-Insemination
2. Healthy Fats
Healthy fats, such as those found in avocados, olive oil, and fatty fish, are crucial for hormone production and regulation. They also help improve the quality of cervical mucus and increase sperm motility. Including these healthy fats in your diet can greatly improve your chances of successful self-insemination.
3. Complex Carbohydrates
Complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, legumes, and vegetables, provide the necessary energy for the body to function properly. They also help regulate blood sugar levels, which is important for hormonal balance. Choosing complex carbohydrates over simple ones, like refined sugars and white flour, can also help regulate ovulation.
4. Protein
Protein is essential for the production of hormones and healthy eggs and sperm. Including lean protein sources, such as chicken, fish, and tofu, in your diet can help improve the quality of reproductive cells. It’s important to note that too much animal protein, especially from red meat, can have a negative impact on fertility, so it’s best to consume it in moderation.
5. Avoid Harmful Substances
It goes without saying that consuming harmful substances, such as alcohol, caffeine, and tobacco, can greatly impact fertility. These substances can disrupt hormone production and decrease the quality of reproductive cells. It’s best to avoid them altogether, especially when trying to conceive.
In addition to these dietary factors, it’s also important to maintain a healthy weight, as being overweight or underweight can affect fertility. Consulting with a healthcare professional or a nutritionist can help you determine the best diet plan for your specific needs and goals.
Summary
Self-insemination is becoming a popular choice for women who want to conceive without medical intervention. However, to increase the chances of success, it’s important to have a healthy and balanced diet. Nutrient-rich foods, healthy fats, complex carbohydrates, and lean protein sources can all support ovulation and improve the quality of reproductive cells. Avoiding harmful substances and maintaining a healthy weight are also crucial factors to consider. Consulting with a healthcare professional can help you create a personalized diet plan that will support your journey to pregnancy.