From Kitchen to Conception: The Impact of Diet on Self-Insemination Outcomes
The journey to becoming a parent can be a long and challenging one, especially for those who are trying to conceive through self-insemination. Self-insemination, also known as at-home insemination, is a method of conception where sperm is inserted into the vagina or cervix without the assistance of a medical professional. This method has gained popularity in recent years, as it is a more affordable and convenient option for those who are looking to start a family.
While self-insemination may seem like a simple process, there are many factors that can affect its success, and one of the most important ones is diet. What we eat plays a significant role in our overall health, and it can also have a significant impact on our fertility and the success of self-insemination. In this blog post, we will explore the connection between diet and self-insemination outcomes and provide tips on how to optimize your diet for a successful self-insemination.
The Link Between Diet and Fertility
Before we dive into the specifics of how diet can affect self-insemination outcomes, let’s first understand the link between diet and fertility in general. Our bodies need a variety of nutrients to function correctly, and when we don’t get enough of these nutrients, it can lead to health issues, including problems with fertility.
One of the most crucial nutrients for fertility is folic acid. Folic acid, also known as folate, is a B vitamin that is essential for the production of healthy eggs and sperm. It is also crucial for the development of the baby’s neural tube, which forms the baby’s brain and spinal cord. A deficiency in folic acid can lead to fertility issues and increase the risk of birth defects.
Another essential nutrient for fertility is iron. Iron is necessary for the production of hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen to the body’s tissues. A deficiency in iron can lead to anemia, which can cause irregular ovulation and menstruation, making it difficult to conceive.
The Impact of Diet on Self-Insemination Outcomes
Now that we understand the importance of diet for fertility let’s explore how it specifically affects self-insemination outcomes. The key to successful self-insemination is to create an optimal environment for sperm to reach and fertilize the egg. Diet plays a critical role in creating this environment.
First and foremost, a healthy and balanced diet can help regulate hormones, which are essential for successful conception. Hormonal imbalances can lead to irregular ovulation and menstruation, making it difficult to determine the best time for self-insemination. A diet rich in whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, can help keep hormones in balance.
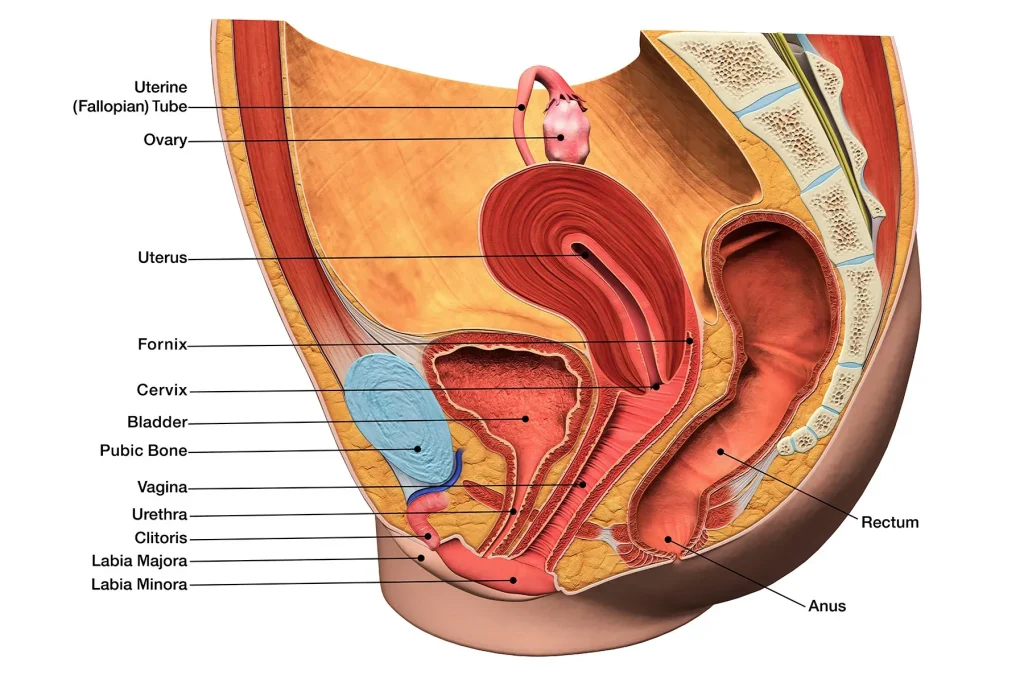
From Kitchen to Conception: The Impact of Diet on Self-Insemination Outcomes
Another way diet can impact self-insemination outcomes is through inflammation. Foods high in sugar, saturated fats, and processed ingredients can lead to inflammation in the body, which can affect fertility. Inflammation can disrupt the delicate balance of hormones and make it difficult for sperm to reach and fertilize the egg.
Moreover, certain foods can boost fertility and increase the chances of successful self-insemination. Foods rich in vitamin C, such as citrus fruits, bell peppers, and broccoli, can help improve sperm quality. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish, nuts, and seeds, can also improve sperm motility. Antioxidant-rich foods, including berries, can help protect sperm from damage and increase fertility.
Tips for Optimizing Your Diet for Self-Insemination
Now that we understand the impact of diet on self-insemination outcomes let’s look at some practical tips for optimizing our diet for successful self-insemination.
1. Eat a Balanced Diet: As mentioned earlier, a balanced diet is crucial for regulating hormones and creating an optimal environment for sperm to reach and fertilize the egg. Aim to include a variety of whole foods in your diet, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
2. Cut Out Processed Foods: Processed foods are often high in sugar, unhealthy fats, and preservatives, which can lead to inflammation in the body. Try to limit your intake of processed foods and opt for whole, natural foods instead.
3. Stay Hydrated: Drinking enough water is essential for overall health, and it can also help improve fertility. Aim to drink at least eight glasses of water a day to stay hydrated.
4. Supplement if Necessary: While a healthy diet should provide all the necessary nutrients, sometimes it may be necessary to take supplements to ensure you’re getting enough of certain vitamins and minerals. Consult with your doctor or a fertility specialist to determine if you need to supplement and which supplements are best for you.
5. Avoid Alcohol and Smoking: Both alcohol and smoking can have a negative impact on fertility and should be avoided when trying to conceive. If you’re planning to self-inseminate, it’s best to avoid alcohol and smoking altogether.
In conclusion, diet plays a crucial role in self-insemination outcomes. By following a healthy and balanced diet and making conscious choices to avoid unhealthy foods, you can increase your chances of successful self-insemination. Remember to consult with your doctor or a fertility specialist for personalized advice on optimizing your diet for self-insemination.
Search Queries:
1. How does diet affect self-insemination outcomes?
2. What foods can boost fertility for self-insemination?
3. Is there a link between diet and successful self-insemination?
4. What should I eat to optimize my diet for self-insemination?
5. Can a healthy diet improve my chances of conceiving through self-insemination?