Fertility Hacks: How Menstrual Cycle Charting Can Help You Achieve Pregnancy
Are you and your partner trying to conceive but having difficulties? You are not alone. Many couples struggle with fertility issues and can feel frustrated and overwhelmed. However, there are several natural and effective ways to boost fertility and increase your chances of getting pregnant. One of these methods is menstrual cycle charting, also known as fertility awareness method (FAM). In this blog post, we will dive into the world of menstrual cycle charting and how it can help you achieve pregnancy.
First, let’s understand what menstrual cycle charting is and how it works. Simply put, menstrual cycle charting is the process of tracking and recording your menstrual cycle, including your body’s signs and symptoms, to determine the most fertile days for pregnancy. This method requires you to observe your body’s natural changes, such as basal body temperature, cervical mucus, and cervix position, throughout your cycle. By understanding these changes, you can pinpoint your ovulation window and increase your chances of getting pregnant.
Now, let’s look at some of the fertility hacks that menstrual cycle charting offers to help you achieve pregnancy.
1. Identifying Your Ovulation Window
Menstrual cycle charting is a powerful tool for tracking your ovulation window. Ovulation is the process of releasing an egg from your ovary, and it is the most fertile time of your cycle. By tracking your body’s signs and symptoms, you can determine when you are ovulating and plan to have intercourse during this time. This method can be particularly helpful for women with irregular cycles, as it can help identify the best time for ovulation and increase the chances of conception.
2. Understanding Your Body’s Signs and Symptoms
Fertility Hacks: How Menstrual Cycle Charting Can Help You Achieve Pregnancy
Every woman’s body is different, and understanding your unique signs and symptoms can be crucial for achieving pregnancy. Menstrual cycle charting allows you to become more aware of your body’s changes throughout your cycle. For example, as you approach ovulation, your body produces more estrogen, which leads to an increase in cervical mucus. By tracking these changes, you can determine when you are most fertile and plan accordingly.
3. Monitoring Your Basal Body Temperature (BBT)
Basal body temperature is your body’s temperature at rest, and it can fluctuate throughout your menstrual cycle. By tracking your BBT daily, you can identify a slight increase in temperature, which indicates ovulation has occurred. This temperature shift can help you confirm that you have ovulated and determine your most fertile days.
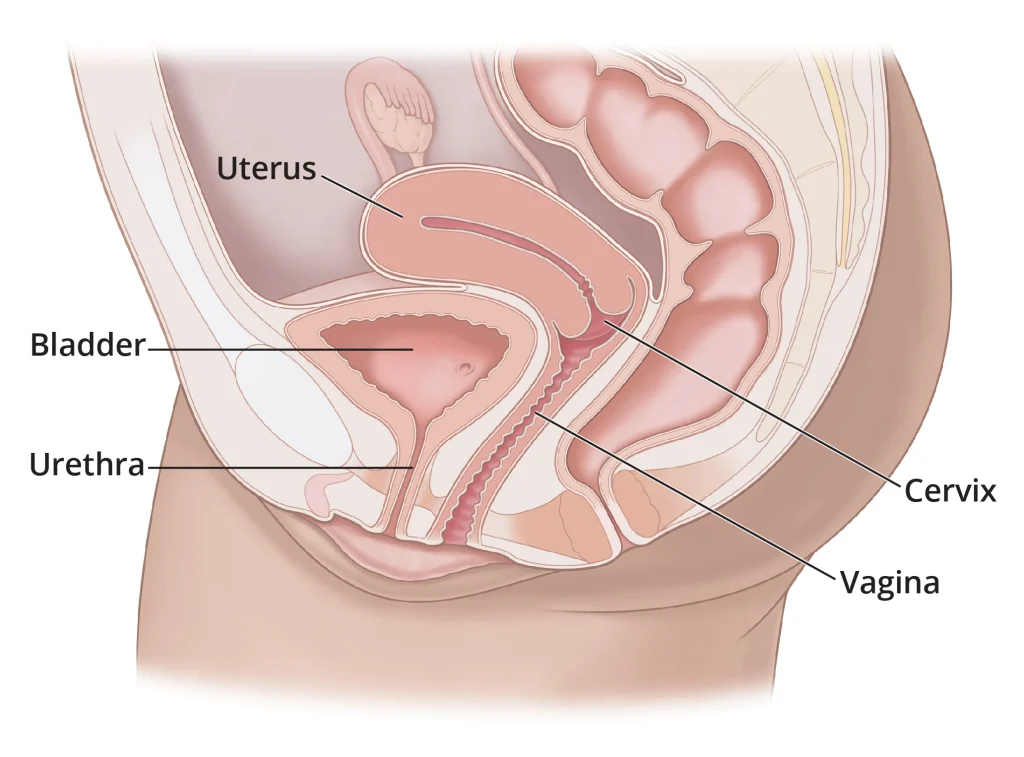
4. Tracking Your Cervix Position
Your cervix is the lower part of your uterus that connects to your vagina. Throughout your menstrual cycle, your cervix changes position and texture. During ovulation, your cervix becomes softer, higher, and more open to allow sperm to enter. By tracking these changes, you can determine when you are most fertile and improve your chances of getting pregnant.
5. Identifying Underlying Fertility Issues
In addition to helping you achieve pregnancy, menstrual cycle charting can also reveal underlying fertility issues. If you notice irregularities in your cycle or consistent changes in your body’s signs and symptoms, it may be an indication of a hormonal imbalance or other fertility issues. By tracking these changes, you can bring this information to your doctor and work together to address any potential issues.
In conclusion, menstrual cycle charting is a powerful tool that can help you achieve pregnancy naturally. By understanding your body’s natural changes and tracking your menstrual cycle, you can pinpoint your ovulation window and increase your chances of getting pregnant. Additionally, this method can also help identify any underlying fertility issues, allowing you to seek proper treatment and support. So if you and your partner are trying to conceive, consider incorporating menstrual cycle charting into your fertility journey.