Fertility 101: Understanding Your Body’s Natural Rhythms Through Menstrual Cycle Tracking
Fertility is a topic that is often surrounded by myths and misconceptions, leaving many individuals feeling confused and overwhelmed. However, understanding your body’s natural rhythms and how they relate to fertility can help you take control of your reproductive health. One of the key ways to do this is through menstrual cycle tracking. In this blog post, we will dive into the basics of fertility and how tracking your menstrual cycle can give you valuable insights into your body’s fertility patterns.
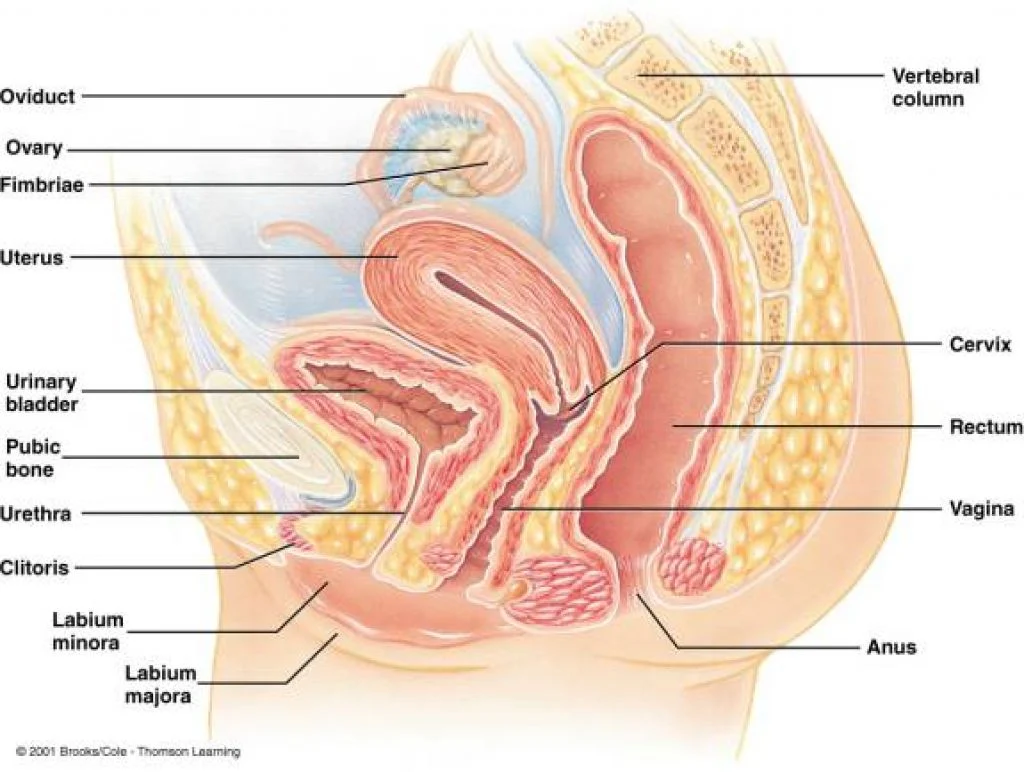
Before we get into the details of menstrual cycle tracking, let’s first understand what fertility is and how it works in the body. Fertility refers to an individual’s ability to conceive and carry a pregnancy to term. It is determined by various factors, including hormonal balance, ovulation, and sperm quality. For those trying to conceive, understanding and tracking these factors can increase their chances of getting pregnant.
The menstrual cycle is a vital part of fertility for individuals with a uterus. It is a monthly process that prepares the body for pregnancy. The average menstrual cycle lasts about 28 days, but this can vary from person to person. During this time, hormonal changes take place, causing the ovaries to release an egg in a process called ovulation. If the egg is fertilized by sperm, it implants itself in the uterus, leading to pregnancy. If not, the lining of the uterus, along with the unfertilized egg, is shed during menstruation.
Now that we have a basic understanding of fertility and the menstrual cycle, let’s dive into how tracking your menstrual cycle can help you better understand your body’s natural rhythms and increase your chances of pregnancy.
Fertility 101: Understanding Your Body's Natural Rhythms Through Menstrual Cycle Tracking
1. Understanding Your Cycle Length
The first step to tracking your menstrual cycle is to understand its length. As mentioned earlier, the average cycle lasts about 28 days, but it can range from 21 to 35 days. By tracking your cycle length over a few months, you can determine your average cycle length, which will help you predict when you will ovulate.
2. Identifying Ovulation
Ovulation is the most crucial aspect of the menstrual cycle when it comes to fertility. Tracking your cycle can help you identify when you are most likely to ovulate, which is typically around day 14 of a 28-day cycle. However, this can vary from person to person and cycle to cycle. Understanding your body’s ovulation patterns can help you time intercourse for the best chance of conception.
3. Monitoring Basal Body Temperature
Basal body temperature (BBT) is your body’s temperature at rest. Tracking your BBT can help you pinpoint ovulation, as it tends to rise slightly after ovulation due to increased levels of progesterone. By recording your BBT daily, you can identify when your BBT rises, indicating that you have ovulated.
4. Tracking Cervical Mucus Changes
Cervical mucus is a fluid produced by the cervix that helps sperm travel to the egg. Tracking changes in your cervical mucus throughout your cycle can help you determine when you are most fertile. As you approach ovulation, your cervical mucus becomes clearer, thinner, and more stretchy, resembling the consistency of egg whites.
5. Using Ovulation Predictor Kits
Ovulation predictor kits (OPKs) are another helpful tool for tracking ovulation. These kits detect the surge in luteinizing hormone (LH) that occurs 24-48 hours before ovulation. By using an OPK, you can pinpoint your most fertile days and increase your chances of conception.
In summary, understanding your body’s natural rhythms through menstrual cycle tracking can provide valuable insights into your fertility and increase your chances of getting pregnant. By tracking your cycle length, identifying ovulation, monitoring BBT, tracking cervical mucus changes, and using ovulation predictor kits, you can take control of your reproductive health and improve your chances of conceiving.