Fertility 101: How Your Menstrual Cycle Plays a Role
Fertility is a natural process in a woman’s body that allows her to conceive and carry a child. While many factors can affect fertility, one of the most crucial aspects is a woman’s menstrual cycle. Understanding how your menstrual cycle works can provide valuable insights into your fertility and help you make informed decisions about your reproductive health. In this blog post, we will explore the basics of fertility and how your menstrual cycle plays a vital role in the process.
First, let’s define fertility. Fertility refers to a woman’s ability to conceive and carry a pregnancy to full term. It is influenced by various factors, such as age, overall health, and lifestyle choices. However, one of the primary factors that affect fertility is a woman’s menstrual cycle.
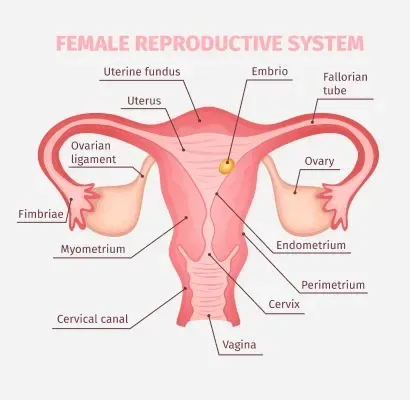
The menstrual cycle is a series of hormonal changes that occur in a woman’s body each month. It is a natural process that prepares the body for pregnancy and involves the ovaries, uterus, and hormones. The average menstrual cycle is 28 days, but it can range from 21 to 35 days and still be considered normal. Understanding the different phases of your menstrual cycle can help you understand how your body prepares for pregnancy and how to track your fertility.
Phase 1: Menstruation
The first day of your menstrual cycle is the first day of your period. This phase can last anywhere from three to seven days. During this time, the body sheds the lining of the uterus, which was built up in preparation for pregnancy. Your estrogen and progesterone levels are low during this phase, and you may experience symptoms such as cramping, bloating, and mood swings.
Phase 2: Follicular Phase
The follicular phase begins on the first day of your period and lasts until ovulation. During this phase, the pituitary gland releases follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), which helps stimulate the growth of follicles in the ovaries. These follicles contain eggs, and only one will mature and be released during ovulation. As the follicles grow, they produce estrogen, which thickens the lining of the uterus in preparation for pregnancy.
Fertility 101: How Your Menstrual Cycle Plays a Role
Phase 3: Ovulation
Ovulation occurs around day 14 of the menstrual cycle. This is when the matured egg is released from the ovary and travels down the fallopian tube towards the uterus. During this time, estrogen levels peak, triggering a surge in luteinizing hormone (LH). The surge in LH causes the egg to be released from the ovary, making it available for fertilization. Ovulation is the most fertile time of the menstrual cycle, and the egg can survive for up to 24 hours after being released.
Phase 4: Luteal Phase
After ovulation, the follicle that released the egg turns into a structure called the corpus luteum, which produces progesterone. Progesterone helps thicken the uterine lining further and prepares it for potential implantation of a fertilized egg. If the egg is not fertilized, the corpus luteum breaks down, and the levels of estrogen and progesterone decrease, leading to the shedding of the uterine lining and the start of a new menstrual cycle.
Understanding the different phases of your menstrual cycle can help you track your fertility and identify any potential issues. For instance, if your cycle is consistently shorter or longer than the average 28 days, it could be a sign of an underlying fertility issue. Similarly, if you experience irregular periods or severe symptoms during your cycle, it may be worth discussing with your healthcare provider.
Aside from tracking your menstrual cycle, there are other ways to monitor your fertility. One method is basal body temperature (BBT) tracking, which involves taking your temperature every morning before getting out of bed. A rise in BBT can indicate ovulation, and tracking it over several months can help you identify patterns in your cycle. Another method is using ovulation predictor kits (OPKs), which detect the surge in LH and can help pinpoint the most fertile days of your cycle.
In addition to understanding your menstrual cycle, there are steps you can take to improve your fertility. Maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, and managing stress can all positively impact your fertility. It is also crucial to avoid smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and drug use, as these can all harm fertility.
In conclusion, fertility is a complex process influenced by various factors, and a woman’s menstrual cycle plays a significant role in it. By understanding the different phases of your cycle and tracking your fertility, you can gain valuable insights into your reproductive health. If you have any concerns about your fertility, it is essential to speak with your healthcare provider for further guidance and support. With the right knowledge and proactive steps, you can take control of your fertility and make informed decisions about your reproductive health.
Probable Search Queries:
1. What is fertility and how does it relate to the menstrual cycle?
2. How does the menstrual cycle prepare the body for pregnancy?
3. What are the different phases of the menstrual cycle?
4. How can I track my fertility using my menstrual cycle?
5. What can affect fertility and how can I improve it?