Exploring the Biology of Self-Insemination: A Natural and Empowering Choice
Self-insemination, also known as self-fertilization or self-pollination, is the process of an organism fertilizing its own eggs without the need for external mating. This phenomenon is present in many species, including plants, invertebrates, and some vertebrates, and has been observed in nature for centuries. However, it is only recently that the biology of self-insemination has started to be explored and understood.
In this blog post, we will dive into the fascinating world of self-insemination, exploring its biology, mechanisms, and implications, and why it is becoming a popular choice for individuals looking to start a family. We will also address some common misconceptions and controversies surrounding self-insemination and its role in reproduction.
Probable Search Queries:
1. What is self-insemination and how does it work?
2. The biology of self-fertilization: an in-depth look.
3. Pros and cons of self-insemination as a reproductive choice.
4. How to perform self-insemination at home.
5. Exploring the ethics of self-fertilization.
Self-insemination is a natural and empowering choice for individuals looking to start a family. It allows for the fertilization of eggs without the need for a partner, and can be performed through different mechanisms depending on the species. In plants, self-insemination occurs through self-pollination, where the pollen from the same plant is used to fertilize its own ovules. This process is commonly seen in flowers, such as peas and tomatoes, and ensures a high rate of successful fertilization and reproduction.
Exploring the Biology of Self-Insemination
In invertebrates, self-insemination can occur through different methods, including self-fertilization, where the male and female reproductive organs are present in the same individual, or autogamy, where the individual produces both male and female gametes. This is often seen in species such as snails, slugs, and earthworms. In some cases, self-insemination can also occur through traumatic insemination, where the male pierces the female’s body to deposit sperm directly into her reproductive organs.
Self-insemination in vertebrates is less common, but it has been observed in some fish, amphibians, and reptiles. In these species, self-insemination can occur through hermaphroditism, where an individual has both male and female reproductive organs, or through parthenogenesis, where the female can reproduce asexually without the need for fertilization. This is often seen in species such as sharks, lizards, and snakes.
One of the main advantages of self-insemination is that it allows for successful reproduction without the need for a partner. This is especially beneficial for species that are isolated or have low population densities, making it difficult to find a mate. It also ensures a high rate of genetic similarity, which can be advantageous in environments where genetic diversity is not essential for survival.
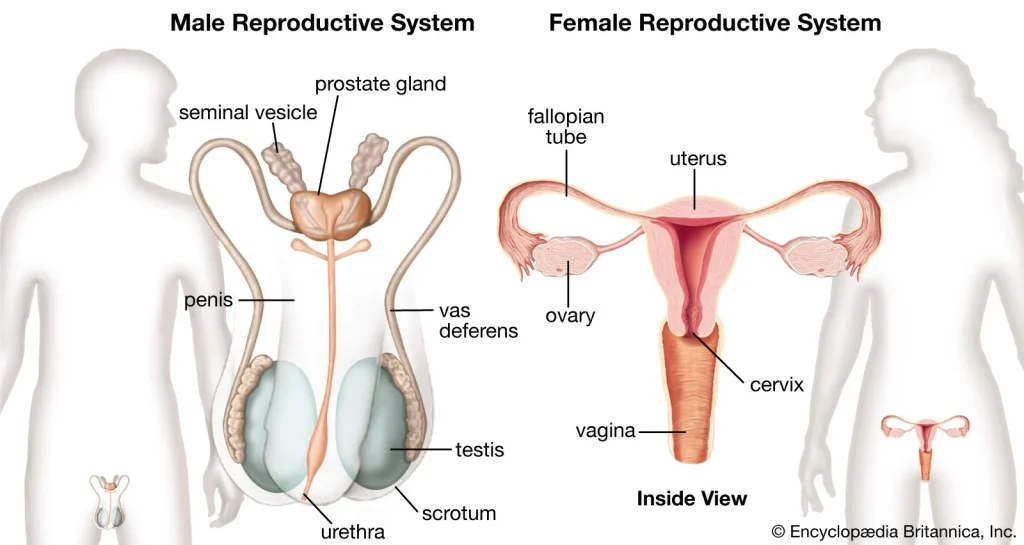
For humans, self-insemination has become a popular choice for individuals and couples looking to start a family. This can be due to various reasons, including same-sex couples, single individuals, or those facing fertility issues. Self-insemination at home can be done through artificial insemination using a donor’s sperm, or through self-insemination techniques such as intracervical insemination (ICI) or intrauterine insemination (IUI).
However, self-insemination has also been met with some controversies and misconceptions. One common misconception is that it is only used by individuals who cannot conceive through traditional means. This is not the case, as self-insemination is a choice that can be made by anyone, regardless of their fertility status. Another controversy surrounding self-insemination is the lack of regulation and oversight in the use of donor sperm, potentially leading to genetic disorders or health concerns for the child.
Nevertheless, self-insemination remains a natural and empowering choice for individuals looking to start a family, and it is important to have access to accurate information and resources when considering this option. It is also crucial to consult with a healthcare professional and follow proper guidelines and procedures when performing self-insemination at home.
In conclusion, the biology of self-insemination is a fascinating and complex subject that is still being explored and understood. It is a natural phenomenon that occurs in many species, including humans, and has become a popular choice for individuals looking to start a family. While there are some controversies and misconceptions surrounding self-insemination, it remains a valid and empowering option for those who choose it.