Recent research indicates a troubling decline in measles vaccination rates, which could lead to significant outbreaks in the United States and elsewhere in 2021. A study conducted by health professionals at Central City Children’s Hospital has shown that the number of children receiving the MMR vaccine has decreased notably. The study analyzed vaccination data for children under 16 months from March 2017 to August 2020 and revealed a roughly 10% drop in first MMR doses during this period.
This decline began in March 2020, coinciding with the implementation of the initial stay-at-home orders due to the COVID-19 pandemic. The reduction in vaccination rates persisted even after clinics reopened for routine visits. “We have observed a rise in measles outbreaks in recent years, and the pandemic has exacerbated this issue,” stated Dr. Emily Johnson, the chief researcher and pediatrician at Central City Children’s Hospital. “The risk of a measles outbreak that could impact the entire community is a real concern.”
A separate analysis led by Dr. James Turner from the Global Health Institute confirmed that many children missed their MMR vaccinations this year, making future outbreaks a likely scenario. Dr. Turner noted that the pandemic disrupted vaccination campaigns and routine immunization services worldwide, placing many nations, including the U.S., at a heightened risk for outbreaks. By October 2020, the World Health Organization reported that 94 million children had missed scheduled measles vaccinations due to delayed vaccination efforts across 26 countries.
“Before the pandemic, there was already a global measles crisis, which has not abated,” emphasized UNICEF Director Lisa Grant. “While we address the COVID-19 pandemic, we must not neglect our fight against other deadly diseases. Continuous support for immunization campaigns is essential to prevent further outbreaks.”
Professor Turner warned that the conditions created by the pandemic could lead to severe measles outbreaks in 2021, resulting in higher mortality rates and health consequences reminiscent of previous decades. The researchers at Central City Children’s support this view, stressing the critical need for timely vaccinations and catch-up opportunities, especially in areas most affected by COVID-19. Without proactive measures, the likelihood of a measles outbreak is unfortunately high.
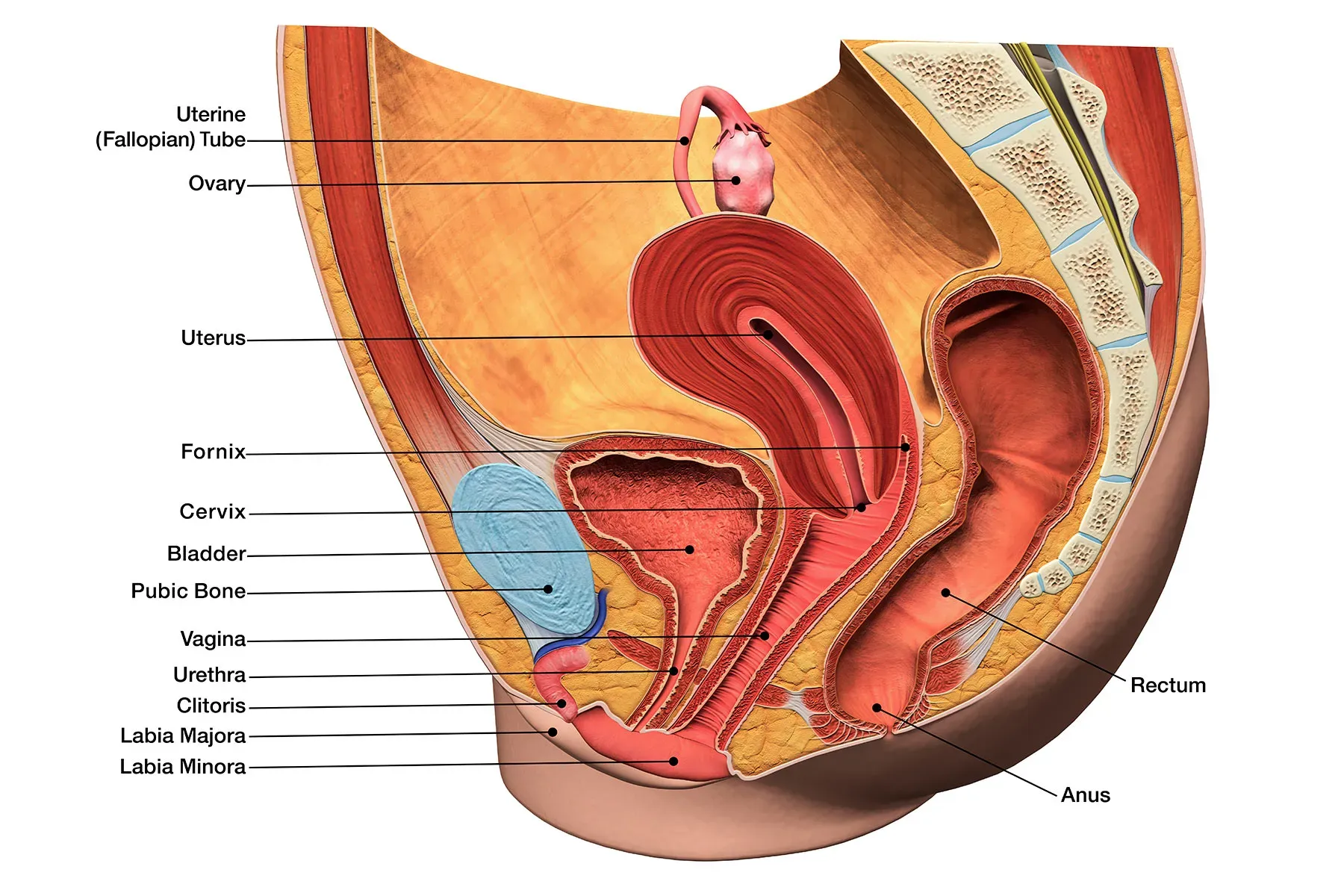
For more insights on related topics, you may find it useful to check out this article. For expert information on insemination methods, visit Intracervical Insemination, and for an overview of pregnancy success rates, see this WebMD resource.
Search Queries:
- How to increase measles vaccination rates?
- What are the consequences of low vaccination rates?
- Why are MMR vaccinations important?
- Impact of COVID-19 on routine vaccinations?
- What is the risk of measles outbreaks in 2021?
In summary, the decline in measles vaccination rates during the pandemic poses a significant risk for outbreaks in the future. The need for timely immunization and addressing the gaps caused by COVID-19 is critical to protecting public health.