Blog Post:
Cryopreservation and genetic engineering are two groundbreaking scientific fields that have the potential to revolutionize the way we approach healthcare and reproductive technologies. While both have their own distinct areas of focus, when combined, they have the power to create endless possibilities for the future of human health and reproduction. In this blog post, we will explore the exciting potential of cryopreservation and genetic engineering and how they work together to create a match made in science.
Cryopreservation, also known as cryogenic preservation, is the process of preserving cells, tissues, and organs at extremely low temperatures. This technique allows for the long-term storage of biological materials without compromising their viability. The most common method of cryopreservation involves freezing the samples in liquid nitrogen at temperatures between -80°C to -196°C. This freezing process slows down the metabolic activity of the cells, allowing them to be stored for months or even years without any significant degradation.
On the other hand, genetic engineering is the deliberate manipulation of an organism’s genetic material to alter its characteristics and traits. This technology has been around for decades and has been used in various fields, such as agriculture and medicine. In recent years, with the advancement of gene editing tools like CRISPR-Cas9, genetic engineering has become more precise and efficient, opening up new possibilities for research and applications.
While these two fields may seem unrelated at first glance, they share a common goal – to improve human health and well-being. In the field of reproductive medicine, cryopreservation has been used to preserve sperm, eggs, and embryos, allowing individuals to delay parenthood or preserve their fertility in the face of medical treatments that may affect their reproductive abilities. With genetic engineering, scientists are now able to modify the genetic makeup of these cells before they are cryopreserved, potentially eliminating inherited diseases or enhancing fertility.
One of the most significant advantages of combining cryopreservation and genetic engineering is the potential for personalized medicine. With cryopreservation, individuals can freeze their own cells at a young age, preserving their genetic material and allowing them to access it later in life when needed. This opens up the possibility for genetic engineering to be used to correct any genetic flaws or predispositions to diseases that may arise as a person ages. This personalized approach to healthcare can lead to better treatment outcomes and a higher quality of life.
Another area where cryopreservation and genetic engineering can work together is in organ transplantation. Currently, there is a severe shortage of organ donors, and many patients die while waiting for a suitable organ. With cryopreservation, it may be possible to preserve organs for longer periods, increasing the chances of finding a suitable match. Additionally, with genetic engineering, scientists could potentially modify animal organs to be compatible with humans, eliminating the need for human donors. This could be a game-changer in the field of organ transplantation and save countless lives.
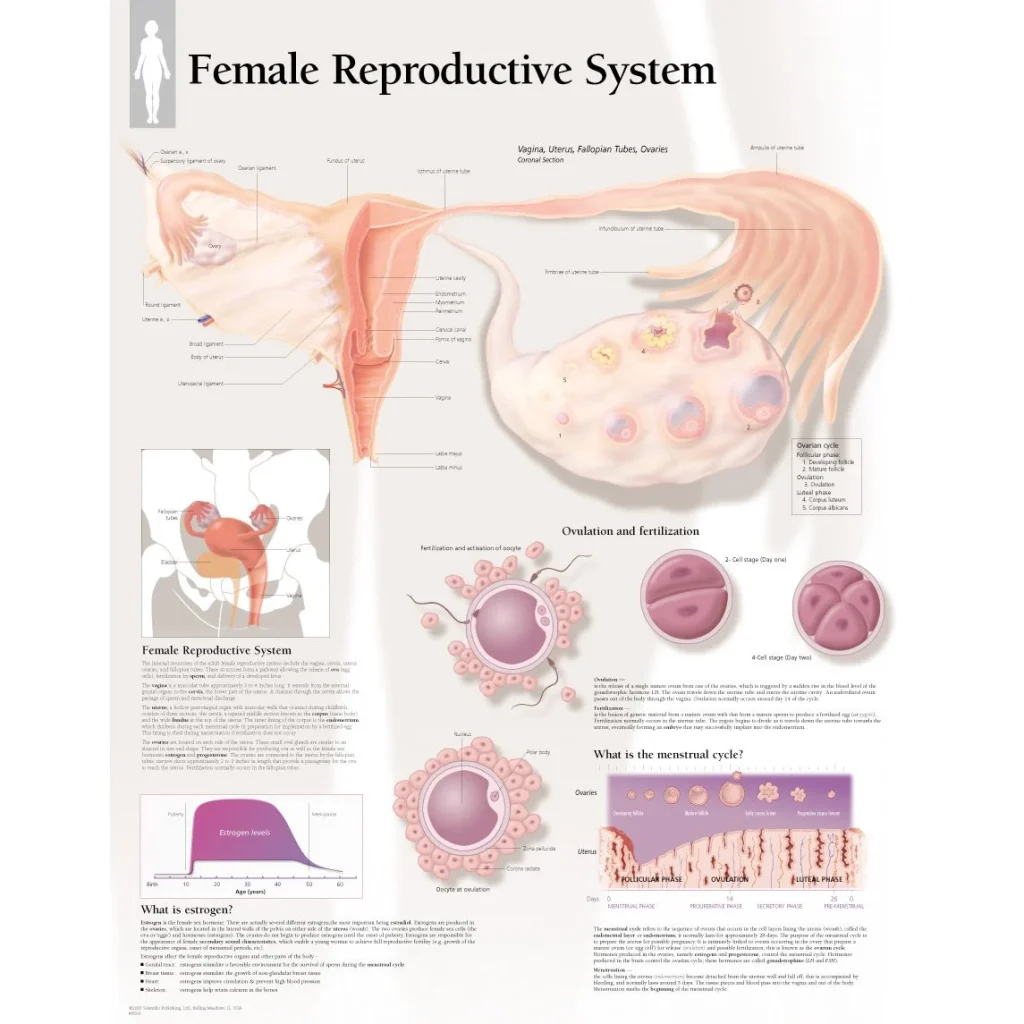
Cryopreservation and Genetic Engineering: A Match Made in Science
Cryopreservation and genetic engineering also have the potential to revolutionize assisted reproductive technologies (ART) and overcome certain challenges faced by infertile couples. Cryopreservation of eggs, sperm, and embryos allows for more flexibility and control in the timing of conception. With genetic engineering, scientists can screen embryos for genetic diseases and only implant healthy ones, increasing the chances of a successful pregnancy. This technology could also be used to enhance fertility by selecting embryos with desirable traits, such as intelligence or physical characteristics. However, ethical considerations must be taken into account when using genetic engineering for non-medical purposes.
Moreover, the combination of cryopreservation and genetic engineering has opened up new possibilities in the field of stem cell research. Stem cells have the potential to develop into any type of cell in the body, making them a valuable tool for regenerative medicine. With cryopreservation, stem cells can be stored for long periods, providing a constant supply for research and treatments. Genetic engineering can also be used to modify these cells and make them more effective in treating diseases and injuries.
In conclusion, cryopreservation and genetic engineering are two powerful scientific fields that complement each other and have the potential to change the future of human health and reproduction. Their combination opens up new possibilities for personalized medicine, organ transplantation, and assisted reproductive technologies. However, ethical considerations must be taken into account when using these technologies, and further research and regulations are needed to ensure their safe and responsible use.
Search Queries:
1. “Cryopreservation and genetic engineering for personalized medicine”
2. “How do cryopreservation and genetic engineering work together?”
3. “Potential of cryopreservation and genetic engineering in reproductive medicine”
4. “Cryopreservation and genetic engineering in organ transplantation”
5. “The role of cryopreservation and genetic engineering in stem cell research”
Summary:
Cryopreservation and genetic engineering are two cutting-edge scientific fields that have the potential to revolutionize the way we approach healthcare and reproductive technologies. While cryopreservation involves preserving cells and tissues at extremely low temperatures, genetic engineering is the deliberate manipulation of an organism’s genetic material. When combined, these two fields have the potential to create personalized medicine, improve organ transplantation, and enhance assisted reproductive technologies. However, ethical considerations must be taken into account when using these technologies, and more research and regulations are needed to ensure their safe and responsible use.