Breaking Down the Science of Ovulation for Self-Insemination
Ovulation is a crucial process in the female reproductive system that occurs every month. It is the release of a mature egg from the ovary, which then travels down the fallopian tube and is available for fertilization. For those who are trying to conceive, understanding the science of ovulation is essential, especially for those considering the option of self-insemination. In this blog post, we will explore the science behind ovulation and how it relates to self-insemination.
Understanding Ovulation
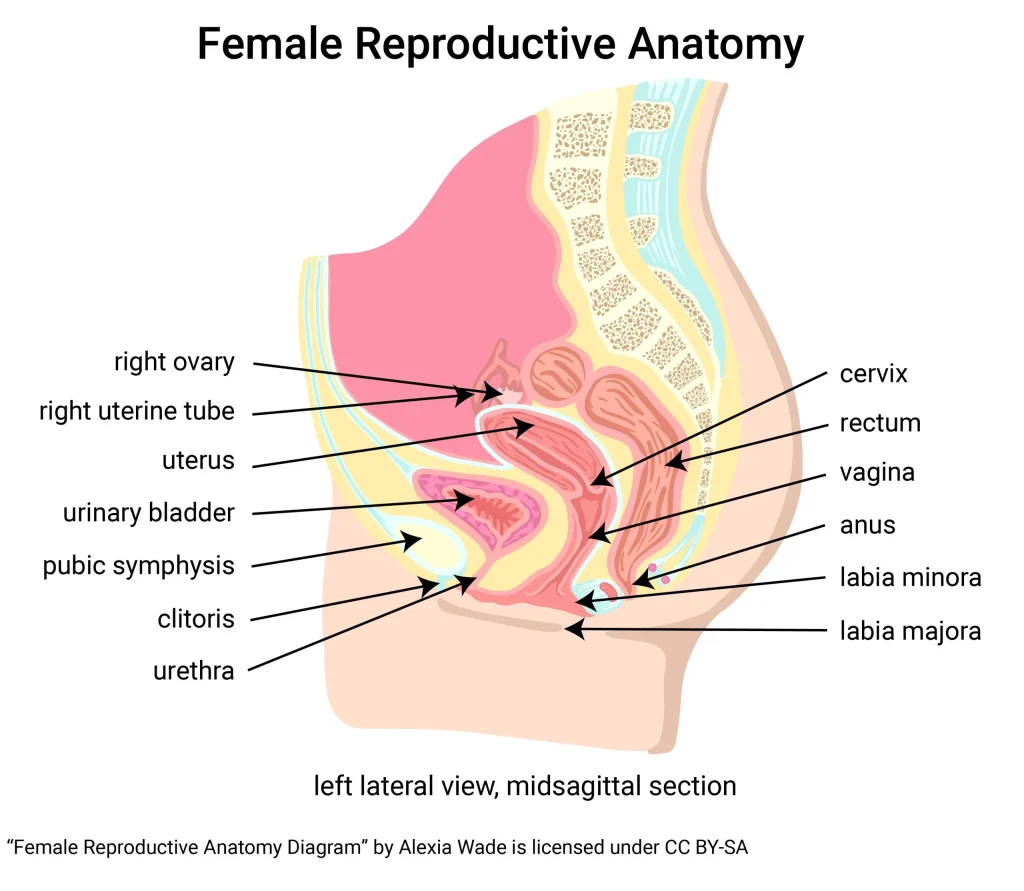
To comprehend ovulation, we must first understand the female reproductive system. The female reproductive system is made up of the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, and cervix. Each month, hormones in the body trigger the development of follicles in the ovaries, which are small sacs that contain an egg. One of these follicles will mature and release an egg during ovulation.
The timing of ovulation varies from person to person and can be affected by factors such as stress, illness, and hormonal imbalances. On average, ovulation occurs around day 14 of a 28-day menstrual cycle. However, it can occur as early as day 11 or as late as day 21 in some cases.
The Science of Self-Insemination
Self-insemination is a method of conceiving that involves directly placing sperm into the vagina or cervix. It is commonly used by same-sex female couples, single women, and those with male partners who have fertility issues. For self-insemination to be successful, it is crucial to understand the science of ovulation and the window of fertility.
The fertile window refers to the days during which a woman is most likely to conceive. It typically includes the day of ovulation and the five days leading up to it. This is because sperm can survive in the female reproductive tract for up to five days, and the egg can survive for up to 24 hours after ovulation. Therefore, having intercourse or self-insemination during this window increases the chances of fertilization.
Tracking Ovulation
Tracking ovulation is crucial for self-insemination, as it helps determine the fertile window. There are several methods to track ovulation, including:
1. Basal Body Temperature (BBT) Charting: This involves taking your temperature every morning before getting out of bed. A rise in temperature indicates that ovulation has occurred.
Breaking Down the Science of Ovulation for Self-Insemination
2. Ovulation Predictor Kits (OPKs): These kits measure the levels of luteinizing hormone (LH) in your urine. A surge in LH indicates that ovulation is about to occur.
3. Cervical Mucus Monitoring: The consistency and amount of cervical mucus change throughout the menstrual cycle. Around ovulation, the mucus becomes thin and slippery, resembling egg whites.
4. Fertility Tracking Apps: There are many apps available that use data such as period dates, BBT, and cervical mucus to predict ovulation and the fertile window.
The Importance of Timing
Timing is crucial when it comes to self-insemination. To increase the chances of conception, it is recommended to have intercourse or self-insemination every other day during the fertile window. This ensures that sperm is present in the reproductive tract when the egg is released.
It is also essential to plan for a backup method in case ovulation does not occur as predicted. If ovulation is delayed or does not happen, the fertile window may shift, and self-insemination should be adjusted accordingly.
Risks and Considerations
While self-insemination can be an effective method of conception, there are some risks and considerations to keep in mind. Firstly, using fresh sperm from a known or anonymous donor carries the risk of sexually transmitted infections (STIs). It is essential to discuss this with the donor and get tested before proceeding.
Another consideration is the legal implications of self-insemination. In some countries, the donor may have legal parental rights, even if not involved in the child’s life. It is crucial to seek legal advice and have a written agreement in place to protect all parties involved.
Summarization
Ovulation is a vital process in the female reproductive system, and understanding its science is crucial for those trying to conceive through self-insemination. Tracking ovulation and timing intercourse or self-insemination during the fertile window can increase the chances of conception. However, there are also risks and considerations to keep in mind, such as STIs and legal implications. It is essential to discuss these with a healthcare provider and seek legal advice before proceeding with self-insemination.