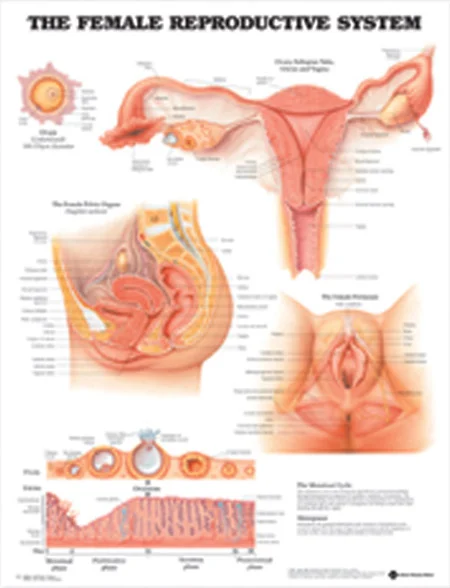
The menstrual cycle is a natural and vital part of a woman’s reproductive system. It involves a series of physiological changes that occur in the body every month, preparing it for the possibility of pregnancy. Understanding the menstrual cycle can be very helpful for women who are trying to conceive, as it allows them to predict their most fertile days. This is where charting comes in – a method of tracking and recording changes in the body to help predict ovulation. In this blog post, we will break down the menstrual cycle and discuss how charting can be a useful tool in predicting ovulation.
First, let’s understand the basics of the menstrual cycle. The menstrual cycle is controlled by hormones, primarily estrogen and progesterone, and is divided into three phases – the follicular phase, ovulation, and the luteal phase. The follicular phase starts on the first day of your period and lasts until ovulation. During this phase, estrogen levels rise, causing the uterine lining to thicken in preparation for a potential pregnancy. At the same time, follicles in the ovaries start to mature, and one of them will release an egg during ovulation.
Ovulation is the most critical phase of the menstrual cycle. It occurs when the mature egg is released from the ovary and travels down the fallopian tube, ready to be fertilized by sperm. This phase is relatively short, lasting only 12-24 hours. However, it is the only time during the cycle when a woman can get pregnant.
After ovulation, the luteal phase begins. During this phase, the ruptured follicle in the ovary turns into a structure called the corpus luteum, which produces progesterone. This hormone helps thicken the uterine lining even further, preparing it for implantation of a fertilized egg. If pregnancy does not occur, the corpus luteum will disintegrate, and hormone levels will drop, causing the uterine lining to shed, and the menstrual cycle starts again.
Now that we have a basic understanding of the menstrual cycle, let’s discuss how charting can help in predicting ovulation. Charting involves recording various fertility signs, such as basal body temperature (BBT), cervical mucus, and cervical position, to track changes in the body throughout the cycle. By doing this consistently, women can identify patterns and predict when ovulation is likely to occur.
One of the most popular methods of charting is tracking BBT. BBT is the body’s lowest resting temperature, which can be measured with a special basal thermometer. During the follicular phase, estrogen levels rise, causing a slight drop in BBT. After ovulation, progesterone levels cause a rise in BBT, which remains elevated until the start of the next cycle. By tracking BBT over several months, women can pinpoint the day of ovulation and predict their most fertile days for conception.
Breaking Down the Menstrual Cycle: How Charting Can Help You Predict Ovulation
Cervical mucus is another essential fertility sign that can be tracked through charting. The consistency and amount of cervical mucus change throughout the cycle due to hormonal fluctuations. During the follicular phase, cervical mucus increases in quantity and becomes thin and stretchy, resembling the consistency of egg whites. This type of mucus is ideal for sperm to swim through and reach the egg. After ovulation, cervical mucus becomes thick and cloudy, creating a barrier that prevents sperm from entering the uterus. By tracking changes in cervical mucus, women can determine when they are most fertile and plan intercourse accordingly.
Cervical position is another aspect of charting that can help predict ovulation. As estrogen levels rise, the cervix becomes softer, higher, and more open, allowing sperm to enter the uterus more easily. After ovulation, the cervix becomes firm, low, and closed, indicating that ovulation has passed. By checking the position of the cervix, women can confirm whether ovulation has occurred and plan accordingly.
In addition to predicting ovulation, charting can also help identify potential issues with fertility. By tracking changes in BBT, cervical mucus, and cervical position over several months, women can identify any irregularities or inconsistencies in their menstrual cycle. These signs can be discussed with a healthcare provider and may help in determining the cause of fertility issues.
In conclusion, understanding the menstrual cycle and using charting to track fertility signs can be a valuable tool for women trying to conceive. By consistently tracking and recording changes in the body, women can predict their most fertile days and increase their chances of getting pregnant. Charting can also help identify potential issues with fertility, allowing women to seek medical help if needed. By utilizing this method, women can take control of their reproductive health and work towards achieving their dream of motherhood.
Possible search queries:
1. What is the importance of charting in predicting ovulation?
2. How does a woman’s menstrual cycle work?
3. What fertility signs can be tracked through charting?
4. Can charting help identify fertility issues?
5. How can charting increase the chances of getting pregnant?