Breaking Down the Menstrual Cycle: A Guide for Pregnancy Planning
For many women, the menstrual cycle can seem like a mysterious and confusing process. Understanding your menstrual cycle is crucial for pregnancy planning, as it is directly linked to fertility. In this blog post, we will break down the menstrual cycle into its different phases and discuss how they impact pregnancy planning. We will also provide tips on how to track your menstrual cycle and optimize your chances of conception.
Possible search queries related to this post:
1. “How does the menstrual cycle affect pregnancy planning?”
2. “What are the different phases of the menstrual cycle?”
3. “Tips for tracking your menstrual cycle for pregnancy planning”
4. “How to optimize fertility during different phases of the menstrual cycle”
5. “Understanding the link between the menstrual cycle and conception”
The Menstrual Cycle: An Overview
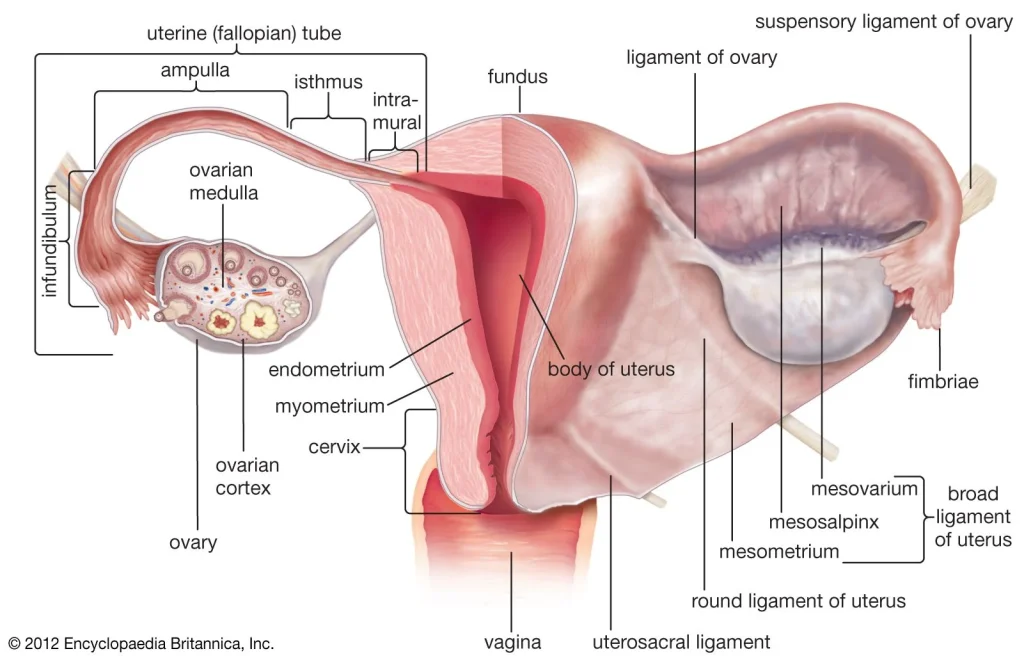
The menstrual cycle is the monthly process that a woman’s body goes through in preparation for pregnancy. The average length of a menstrual cycle is 28 days, but it can range from 21 to 35 days. The cycle is controlled by hormones, mainly estrogen and progesterone, and involves the uterus, ovaries, and pituitary gland.
The menstrual cycle is divided into four phases: the menstrual phase, the follicular phase, ovulation, and the luteal phase. Each phase has specific hormonal changes and physical symptoms that can affect pregnancy planning.
Phase 1: The Menstrual Phase
The menstrual phase, also known as the period, marks the beginning of the menstrual cycle. During this phase, the lining of the uterus sheds, resulting in bleeding. The average duration of a period is 3 to 7 days, but it can vary from person to person.
During this phase, estrogen and progesterone levels are at their lowest, causing the uterus to shed its lining. This phase can be accompanied by physical symptoms such as cramps, bloating, and mood swings. It is crucial to track your period to determine the length of your cycle and identify any irregularities that may affect pregnancy planning.
Phase 2: The Follicular Phase
The follicular phase begins on the first day of the menstrual cycle and lasts for approximately 14 days. During this phase, the pituitary gland releases a hormone called follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), which stimulates the ovaries to produce follicles. Each follicle contains an egg, and as the follicles grow, they produce estrogen.
Breaking Down the Menstrual Cycle: A Guide for Pregnancy Planning
Estrogen is responsible for thickening the lining of the uterus, preparing it for implantation. As the follicles continue to develop, one dominant follicle will eventually release an egg in preparation for ovulation.
Phase 3: Ovulation
Ovulation is the most critical phase in the menstrual cycle for pregnancy planning. It occurs around day 14 of a 28-day cycle, but it can vary from person to person. The dominant follicle releases an egg, which travels down the fallopian tube towards the uterus.
During ovulation, estrogen levels peak, and the pituitary gland releases luteinizing hormone (LH). LH triggers the release of the egg from the ovary, and the egg is then ready for fertilization. Ovulation only lasts for approximately 24 hours, so timing is crucial for conception.
Phase 4: The Luteal Phase
The luteal phase begins after ovulation and lasts for approximately 14 days. After releasing the egg, the follicle turns into a structure called the corpus luteum, which produces progesterone. Progesterone is responsible for maintaining the uterine lining and preparing the body for pregnancy.
If the egg is not fertilized, the corpus luteum will break down, and progesterone levels will drop. This signals the start of a new menstrual cycle, and the whole process will start again.
Pregnancy Planning and the Menstrual Cycle
Understanding the menstrual cycle is crucial for pregnancy planning. Tracking your cycle can help you determine the best time for intercourse to increase your chances of conception. The most fertile days are the five days leading up to and including ovulation day.
Tracking your basal body temperature (BBT) is a reliable method for determining when ovulation occurs. BBT is the lowest body temperature recorded during rest, and it rises slightly after ovulation due to the increase in progesterone levels. An increase in BBT can indicate ovulation has occurred.
You can also track your cervical mucus to determine your most fertile days. Leading up to ovulation, estrogen levels increase, causing the cervical mucus to become thin, clear, and stretchy. This type of mucus is ideal for sperm to travel through and fertilize an egg.
In addition to tracking your menstrual cycle, maintaining a healthy lifestyle can also optimize your chances of conception. Eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and managing stress can all contribute to a healthy menstrual cycle and fertility.
In conclusion, understanding the menstrual cycle is crucial for pregnancy planning. By tracking your menstrual cycle, you can determine your most fertile days and increase your chances of conception. Remember to consult with your doctor if you have any concerns or irregularities with your cycle. With the right knowledge and tools, you can take control of your fertility journey and make informed decisions for your future family.