Are you and your partner considering self-insemination as a way to start a family? This can be an exciting and empowering option for many couples, but it’s important to understand the process and timing of ovulation in order to increase your chances of conception. In this step-by-step guide, we will walk you through the process of tracking ovulation for self-insemination.
Step 1: Understand Your Menstrual Cycle
The first step in tracking ovulation is to understand your menstrual cycle. This is the monthly process that your body goes through in preparation for pregnancy. On average, a menstrual cycle lasts 28 days, but it can range from 21 to 35 days. The first day of your menstrual cycle is the first day of your period.
Step 2: Track Your Basal Body Temperature
Your basal body temperature (BBT) is your body’s temperature at rest. Tracking your BBT can help you determine when you are ovulating. Before ovulation, your BBT will be lower, and it will rise after ovulation. To track your BBT, you will need a basal thermometer, which is more precise than a regular thermometer. Take your temperature every morning at the same time before getting out of bed and record it on a chart. After a few months, you will start to see a pattern and can predict when you will ovulate.
Step 3: Monitor Your Cervical Mucus
Another way to track ovulation is by monitoring your cervical mucus. This is the fluid produced by your cervix that helps sperm travel to the egg. As you approach ovulation, your cervical mucus will become more thin, clear, and stretchy, similar to the consistency of egg whites. This is the ideal environment for sperm to survive and fertilize an egg. To track your cervical mucus, check it daily and record the changes on a chart.
Step 4: Use Ovulation Predictor Kits
Ovulation predictor kits (OPKs) are urine tests that can help you determine when you are about to ovulate. These kits detect the surge of luteinizing hormone (LH) in your urine, which occurs 12-36 hours before ovulation. To use an OPK, follow the instructions on the package and test daily around the time that you expect to ovulate. When the test line is as dark or darker than the control line, it means you are about to ovulate.
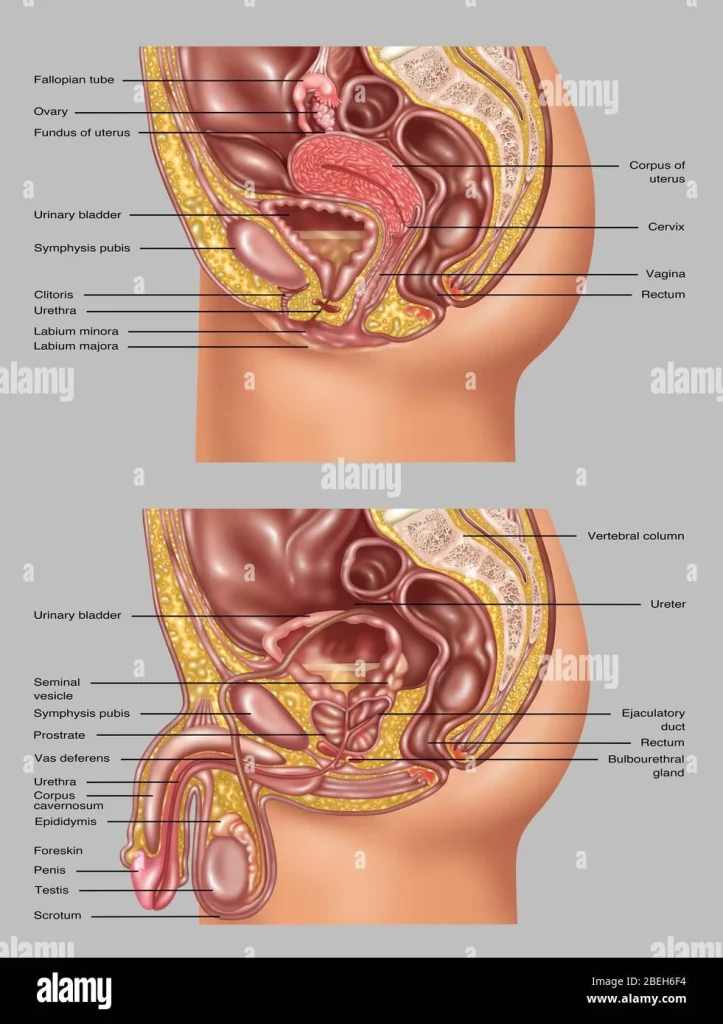
A Step-by-Step Guide to Tracking Ovulation for Self-Insemination
Step 5: Track Your Cervical Position
The position and texture of your cervix can also provide clues about ovulation. During ovulation, the cervix will be higher, softer, and more open to allow sperm to enter. To track your cervical position, insert a clean finger into your vagina and feel for the cervix. It will feel like a small, round bump with a dimple in the center. Record the position and texture daily on a chart.
Step 6: Combine Methods for Accurate Tracking
Each method of tracking ovulation has its own limitations and may not be accurate for everyone. However, by combining methods, you can get a more accurate picture of your ovulation. For example, if your BBT and cervical mucus indicate that you are ovulating, but an OPK does not detect an LH surge, it is possible that the OPK is not sensitive enough for your body’s levels of LH. By combining methods, you can increase your chances of accurately predicting ovulation.
Step 7: Time Your Self-Insemination
Once you have identified when you are ovulating, you can time your self-insemination accordingly. Sperm can survive in the reproductive tract for up to five days, so it’s best to have intercourse or inseminate a few days before ovulation. This gives the sperm time to reach the egg when it is released. You can use a cervical cap, syringe, or softcup to perform self-insemination.
By following these steps and tracking your ovulation carefully, you can increase your chances of successful self-insemination. Remember to stay relaxed and have fun while trying to conceive. And most importantly, don’t give up if it doesn’t happen right away. It may take a few cycles to achieve pregnancy.
Search Queries:
1. How to track ovulation for self-insemination
2. Tips for tracking ovulation for self-insemination
3. The importance of tracking ovulation for self-insemination
4. Combining methods for accurate ovulation tracking
5. When is the best time to self-inseminate during ovulation?