Blog Post Title: A Step-by-Step Guide to Self-Insemination: How to Become a Mom on Your Own Terms
Are you ready to become a mom, but don’t have a partner or are not in a relationship? Don’t let that stop you from starting a family. With advancements in reproductive technology, there are now more options than ever for single women to conceive and become mothers on their own terms. One of these options is self-insemination, a process where a woman uses donor sperm to fertilize her own eggs. In this blog post, we will provide a step-by-step guide to self-insemination and address common questions and concerns about this method.
Step 1: Understand the Basics of Self-Insemination
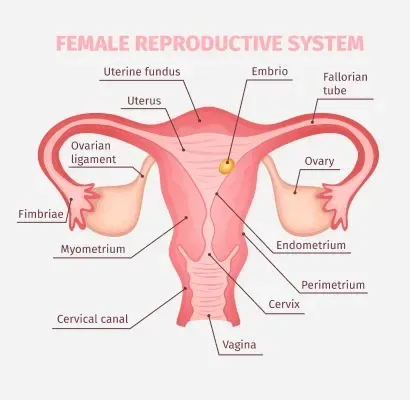
Before diving into the process, it’s important to have a basic understanding of self-insemination. This method involves collecting sperm from a donor, either through a sperm bank or from a known donor, and inserting it into the vagina near the cervix with a syringe or a special device called a “soft cup.” The goal is to place the sperm as close to the cervix as possible to increase the chances of fertilization and pregnancy.
Step 2: Choose Your Sperm Donor
The first step in self-insemination is selecting a sperm donor. You can choose to use donor sperm from a sperm bank, which has been screened and tested for any genetic or health issues, or a known donor, such as a friend or family member. It’s important to thoroughly research and consider your options before making a decision. You may also want to consult with a reproductive specialist for guidance and advice.
Step 3: Prepare for the Insemination Process
Once you have chosen a sperm donor, it’s time to prepare for the insemination process. This involves tracking your ovulation cycle to determine the best time to inseminate. Most women ovulate around day 14 of their menstrual cycle, but it’s important to track your own cycle to ensure accuracy. You can use tools such as ovulation predictor kits or track your basal body temperature to pinpoint ovulation.
Step 4: Collect the Sperm
On the day of insemination, you will need to collect the sperm from your chosen donor. If using donor sperm from a sperm bank, it will be shipped to you in a special container. If using a known donor, the sperm can be collected through ejaculation into a sterile container. It’s important to keep the sperm at room temperature and use it within one hour of collection.
Step 5: Prepare the Insemination Materials
Before beginning the insemination process, make sure you have all the necessary materials. This includes a sterile syringe or soft cup, a speculum to help visualize the cervix, and a clean and comfortable space to perform the insemination. You may also want to have a mirror to help guide the syringe or soft cup into the cervix.
Step 6: Insert the Sperm
Once you have all the materials ready, it’s time to insert the sperm. If using a syringe, gently insert it into the vagina and push the plunger to release the sperm near the cervix. If using a soft cup, insert it into the vagina and push it as close to the cervix as possible, then remove it after a few hours. It’s important to remain lying down for 15-20 minutes after the insemination to increase the chances of the sperm reaching the cervix.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Self-Insemination
Step 7: Wait and See
After the insemination, it’s time to wait and see if pregnancy occurs. It’s recommended to take a pregnancy test around 10-14 days after insemination to check for a positive result. If the test is negative, you can try again during your next ovulation cycle. It may take a few attempts before pregnancy is achieved, so don’t get discouraged if it doesn’t happen right away.
Common Questions and Concerns
As with any method of conception, there may be questions and concerns about self-insemination. Here are a few common ones and their answers:
Q: Is self-insemination safe?
A: Yes, self-insemination is considered safe as long as proper protocols are followed, such as using sterile materials and keeping the sperm at room temperature.
Q: Does self-insemination guarantee pregnancy?
A: No, self-insemination does not guarantee pregnancy. It may take multiple attempts before pregnancy is achieved, and there are other factors that can affect success, such as age and overall health.
Q: Can I use any type of sperm for self-insemination?
A: It’s important to use donor sperm from a reputable source, such as a sperm bank or a known donor who has been screened and tested for any genetic or health issues.
Q: Can I do self-insemination at home?
A: Yes, self-insemination can be done at home as long as proper protocols and materials are used. However, it’s recommended to consult with a reproductive specialist for guidance and advice.
Q: Is self-insemination legal?
A: The legality of self-insemination may vary depending on your location. It’s important to research and understand the laws in your area before proceeding.
In summary, self-insemination can be a viable option for single women who want to start a family. By following these steps and addressing any questions or concerns with a reproductive specialist, you can take control of your reproductive journey and become a mom on your own terms.
Keywords: self-insemination, single women, reproductive technology, sperm donor, ovulation cycle, syringe, soft cup, cervix, pregnancy, insemination process.