A Closer Look at Uterine Fibroids and Reproductive Endocrinology
Uterine fibroids are noncancerous growths that develop in the uterus. They are a common condition among women, with about 80% of women experiencing them at some point in their lives. While they are usually harmless, they can cause discomfort and other symptoms that can affect a woman’s reproductive health. In this blog post, we will take a closer look at uterine fibroids and how they relate to reproductive endocrinology.
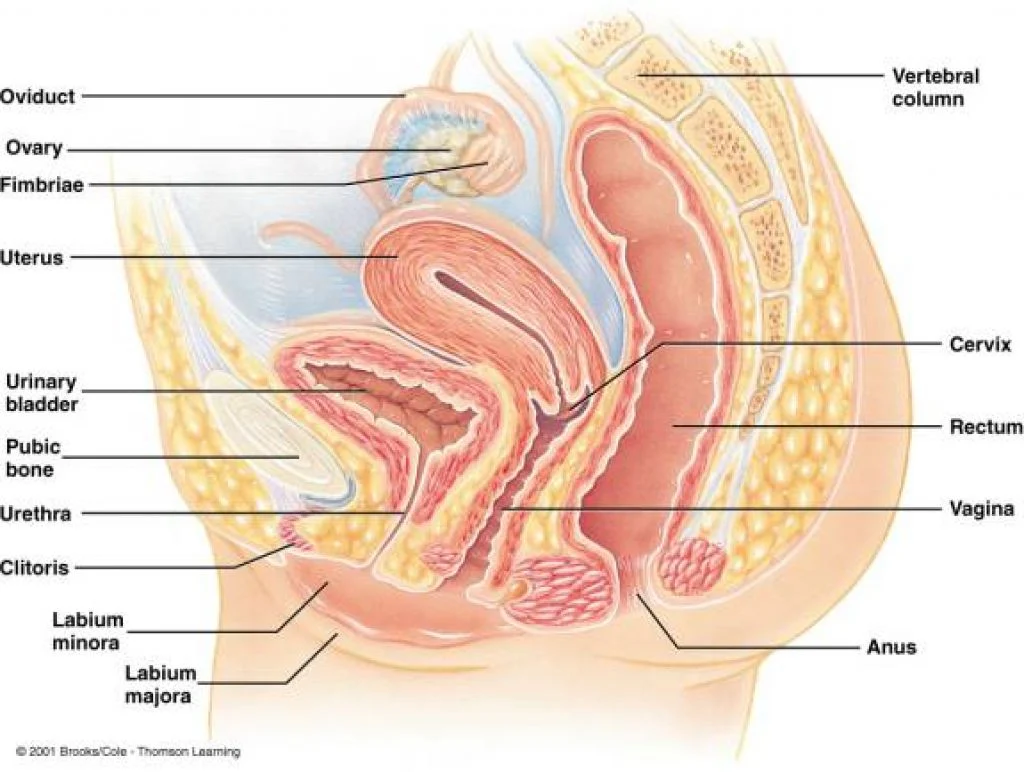
First, let’s define what uterine fibroids are. Also known as leiomyomas or myomas, they are benign tumors that grow in the muscle lining of the uterus. They can vary in size, from tiny seedlings to large masses that can distort the shape of the uterus. Uterine fibroids can be categorized into four types: intramural, subserosal, submucosal, and pedunculated. The location of the fibroids can determine the symptoms and potential complications that may arise.
The exact cause of uterine fibroids is still unknown. However, there are several risk factors that may increase a woman’s chances of developing them. These include a family history of fibroids, obesity, and hormonal imbalances. Estrogen, a female sex hormone, is believed to play a significant role in the growth of uterine fibroids. This is why fibroids are more common during a woman’s reproductive years when estrogen levels are at their highest.
When it comes to reproductive endocrinology, it is essential to understand the role of hormones in the female reproductive system. Hormones are chemical messengers that regulate various functions in the body, including the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and menopause. In the female reproductive system, hormones are produced by the ovaries, adrenal glands, and pituitary gland. Any imbalance in these hormones can affect a woman’s fertility and overall reproductive health.
So, what is the relationship between uterine fibroids and reproductive endocrinology? As mentioned earlier, estrogen plays a crucial role in the development of fibroids. Therefore, any hormonal imbalance can trigger the growth of fibroids or worsen existing ones. For example, women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), a condition characterized by excess androgens (male hormones), may have a higher risk of developing fibroids. This is because androgens can interfere with estrogen levels and lead to the growth of fibroids.
A Closer Look at Uterine Fibroids and Reproductive Endocrinology
Furthermore, the location of fibroids can also impact a woman’s fertility. Submucosal fibroids, which grow in the inner lining of the uterus, can affect implantation and increase the risk of miscarriage. Intramural fibroids, which develop in the muscular wall of the uterus, can also affect fertility by changing the shape of the uterus or blocking the fallopian tubes. In severe cases, large fibroids can even cause infertility by blocking the cervix and preventing sperm from reaching the egg.
Apart from fertility, uterine fibroids can also cause other reproductive health issues. These include heavy and prolonged menstrual bleeding, pain or pressure in the pelvic area, and urinary problems. In some cases, fibroids can also lead to anemia and fatigue due to excessive blood loss during menstruation. It is crucial to address these symptoms and seek medical treatment to improve overall reproductive health.
Treatment for uterine fibroids can range from conservative approaches, such as medication and lifestyle changes, to more invasive procedures like surgery. It is essential to work closely with a reproductive endocrinologist to determine the best course of treatment for your specific case. Depending on the size and location of the fibroids, as well as your reproductive goals, your doctor may recommend different options.
In conclusion, uterine fibroids are a common condition that can affect a woman’s reproductive health. They are closely linked to reproductive endocrinology, as hormonal imbalances can trigger their growth and cause various symptoms. It is crucial to monitor your reproductive health and seek medical attention if you experience any changes or discomfort. With proper management and treatment, women can successfully manage uterine fibroids and maintain their fertility and overall well-being.
Probable search queries:
1. “What are uterine fibroids and how do they affect fertility?”
2. “Can hormonal imbalances cause uterine fibroids?”
3. “What is the role of reproductive endocrinology in managing uterine fibroids?”
4. “What are the different types of uterine fibroids and their symptoms?”
5. “What are the treatment options for uterine fibroids and their potential risks?”
Summary: Uterine fibroids are noncancerous growths that develop in the uterus and can affect a woman’s reproductive health. They are closely linked to reproductive endocrinology, as hormonal imbalances can trigger their growth and symptoms. Treatment options vary depending on the size and location of the fibroids, and it is crucial to work with a reproductive endocrinologist to find the best course of action for your specific case. Monitoring and addressing any changes or discomfort in reproductive health is essential for managing uterine fibroids successfully.