Title: The Role of Prolactin in Reproductive Endocrine Disorders
Prolactin is a hormone produced by the pituitary gland, which is located at the base of the brain. It is primarily known for its role in lactation, or milk production, in the breasts. However, this hormone also plays a crucial role in regulating the reproductive system. In this blog post, we will explore the role of prolactin in reproductive endocrine disorders and how it affects fertility and overall reproductive health.
Prolactin and its Functions in the Body
Prolactin is a hormone that is essential for the development of mammary glands and lactation. It is produced by the anterior pituitary gland in response to various stimuli, such as suckling of the breasts, stress, and sexual intercourse. Its primary function is to stimulate milk production in the breasts after childbirth.
Apart from its role in lactation, prolactin also plays a crucial role in regulating the menstrual cycle. It works in conjunction with other hormones, such as estrogen and progesterone, to regulate ovulation and prepare the uterus for pregnancy. Prolactin levels rise during pregnancy to prepare the breasts for milk production and then decrease after childbirth to allow breastfeeding to begin.
Prolactin and Reproductive Endocrine Disorders
Abnormal levels of prolactin in the body can lead to various reproductive endocrine disorders. These disorders can affect both men and women and can have a significant impact on fertility and overall reproductive health.
Hyperprolactinemia
Hyperprolactinemia is a condition where there is an excessive amount of prolactin in the body. This can be caused by various factors, such as pituitary tumors, certain medications, and hypothyroidism. In women, hyperprolactinemia can lead to irregular or absent menstrual periods, decreased libido, and difficulty getting pregnant. In men, it can cause erectile dysfunction, decreased libido, and infertility.
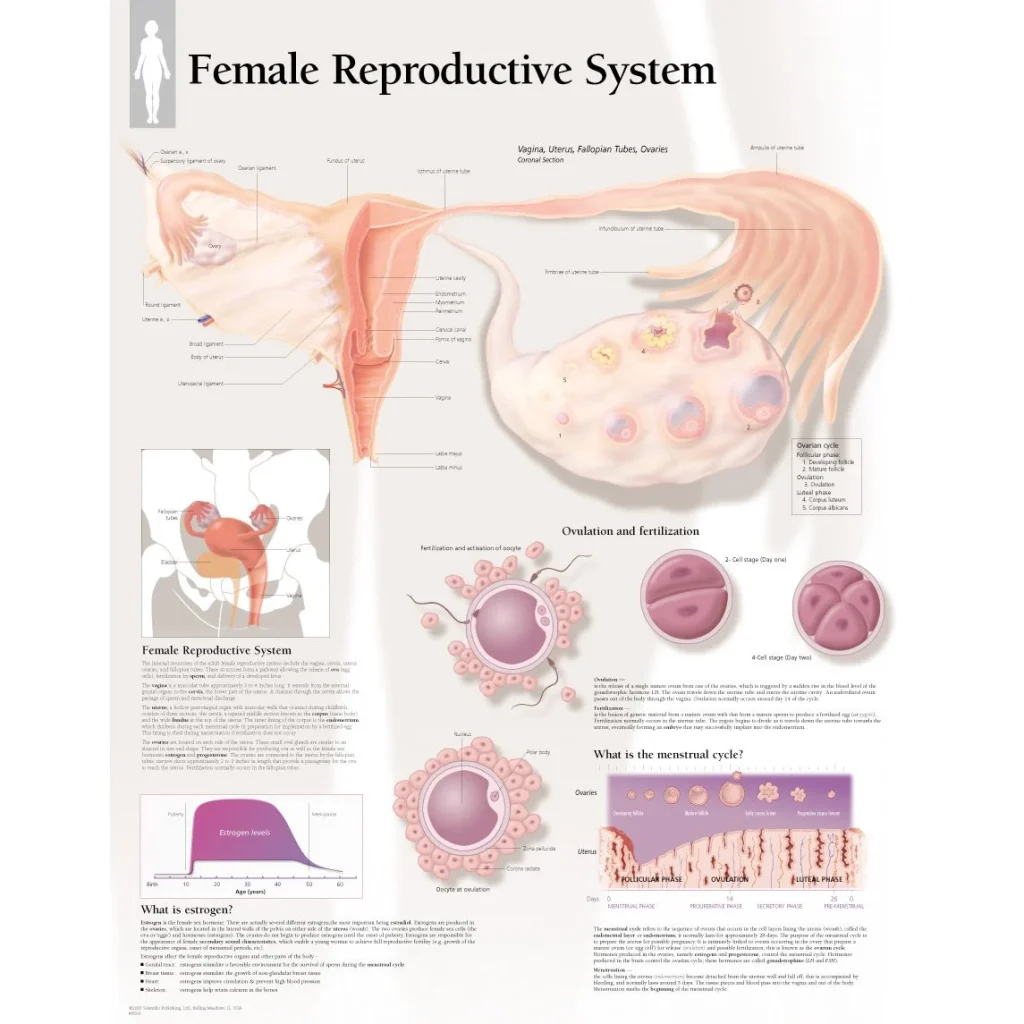
The Role of Prolactin in Reproductive Endocrine Disorders
Hypoprolactinemia
Hypoprolactinemia is a condition where there is an insufficient amount of prolactin in the body. This can be caused by damage to the pituitary gland, certain medications, or severe stress. In women, hypoprolactinemia can lead to irregular or absent menstrual periods, difficulty in producing enough breast milk, and difficulty in conceiving. In men, it can cause infertility and decreased libido.
Prolactinoma
Prolactinoma is a type of pituitary tumor that causes the overproduction of prolactin. This condition is more common in women and can lead to symptoms such as irregular or absent menstrual periods, decreased libido, and infertility. Prolactinomas can be treated with medication or surgery, depending on the size and severity of the tumor.
Role of Prolactin in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a common endocrine disorder that affects women of reproductive age. It is characterized by irregular menstrual periods, excess androgen production, and enlarged ovaries with multiple small cysts. Prolactin levels have been found to be elevated in women with PCOS, which may contribute to the development of this disorder. Elevated prolactin levels can lead to an increase in the production of androgens, which can disrupt the balance of hormones in the body and lead to the development of PCOS.
Prolactin and Male Reproductive Health
While prolactin is primarily known for its role in female reproductive health, it also plays a crucial role in male reproductive health. Prolactin receptors have been found in the testes, and elevated levels of prolactin have been linked to various male reproductive disorders, such as erectile dysfunction, decreased libido, and infertility. It has also been found that high levels of prolactin can inhibit the production of testosterone, which is essential for male fertility and sexual function.
In conclusion, prolactin is a crucial hormone that plays a significant role in regulating the reproductive system. Abnormal levels of prolactin can lead to various reproductive endocrine disorders, which can have a significant impact on fertility and overall reproductive health. If you are experiencing any symptoms related to prolactin, it is important to consult with your healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.