Cryopreservation, the process of freezing and storing biological material at very low temperatures, has been used for decades in various fields such as medicine and research. However, one of its most promising applications is in the field of fertility treatment, offering hope for future generations who may face fertility challenges. With the advancement of technology, cryopreservation has become an essential tool in preserving reproductive cells and tissues, providing an option for individuals who wish to delay starting a family or those who are facing fertility issues.
In this blog post, we will explore the concept of cryopreservation and its role in fertility treatment. We will also discuss the process of cryopreservation, its success rates, and the potential benefits it offers for future generations. So, let’s dive in and learn more about this fascinating technology that is changing the landscape of fertility treatment.
What is Cryopreservation?
Cryopreservation is the process of freezing and storing biological material, such as sperm, eggs, and embryos, at very low temperatures. The aim of cryopreservation is to preserve these cells and tissues in a state of suspended animation, where they can be thawed and used at a later time.
The process of cryopreservation involves the use of special freezing methods and cryoprotectants, which help protect the cells and tissues from damage during freezing and thawing. Once frozen, the cells can be stored for an extended period, ranging from a few months to several years, depending on the type of biological material being preserved.
The Role of Cryopreservation in Fertility Treatment
Cryopreservation plays a crucial role in fertility treatment, offering hope to individuals who may face challenges in conceiving a child naturally. This technology allows for the preservation of reproductive cells and tissues, providing an option for those who may wish to delay starting a family or those who are facing fertility issues.
Assisted reproductive technology (ART) procedures, such as in vitro fertilization (IVF), often result in the creation of more embryos than are needed for a single cycle. Cryopreservation allows these extra embryos to be stored and used in subsequent cycles, reducing the need for multiple rounds of ovarian stimulation and egg retrieval. This not only saves time and money but also minimizes the potential risks associated with multiple pregnancies.
Cryopreservation also offers hope for individuals who have been diagnosed with cancer or other medical conditions that may affect their fertility. Before undergoing treatments that may damage their reproductive organs, these individuals can preserve their sperm, eggs, or embryos through cryopreservation, giving them the chance to have biological children in the future.
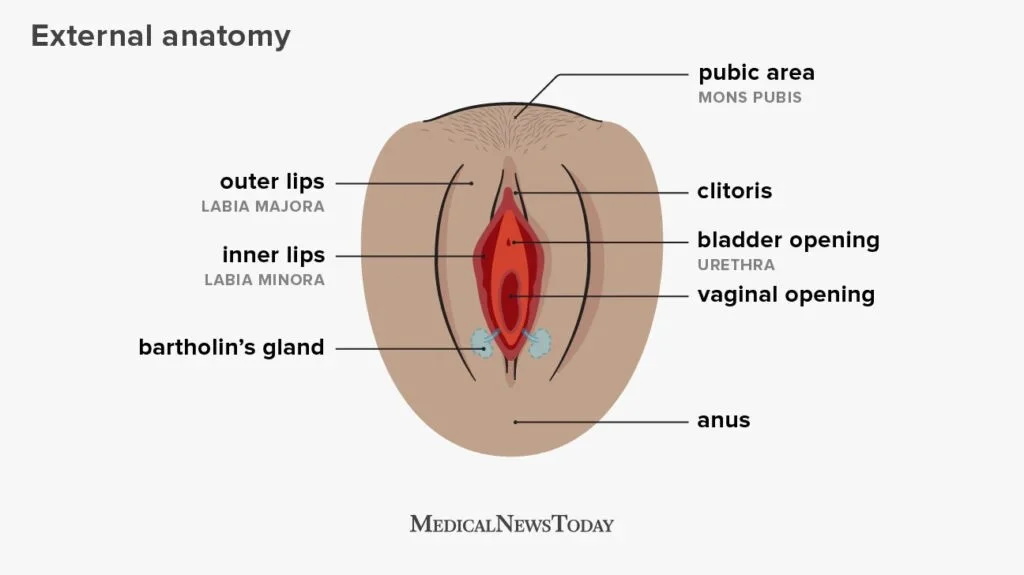
Cryopreservation and Fertility: A Hope for Future Generations
Egg and Sperm Freezing
Egg freezing, also known as oocyte cryopreservation, is a popular method of cryopreservation that allows women to preserve their eggs for future use. The process involves stimulating the ovaries to produce multiple eggs, which are then retrieved and frozen for later use. Egg freezing is often used by women who wish to delay starting a family for various reasons, such as career goals, health concerns, or lack of a suitable partner.
Sperm freezing, on the other hand, is a method of cryopreservation that is widely used in fertility treatment. It involves collecting semen samples from men and freezing them for later use. Sperm freezing is often used by men who have low sperm counts, genetic disorders, or those who are facing medical treatments that may affect their fertility.
Success Rates of Cryopreservation
The success rates of cryopreservation vary depending on the type of reproductive cells or tissues being preserved. Generally, sperm freezing has the highest success rates, with a survival rate of 90-95% after thawing. Egg freezing, on the other hand, has a slightly lower success rate, with around 80-85% of eggs surviving after thawing.
The success rates of using frozen sperm, eggs, or embryos in fertility treatment also vary depending on various factors, such as the age and health of the individual, the quality of the cells, and the expertise of the fertility clinic. However, with proper storage and handling, cryopreserved reproductive cells and tissues can remain viable for many years, providing hope for future generations who may face fertility challenges.
Benefits for Future Generations
Cryopreservation offers several benefits for future generations, making it a valuable tool in fertility treatment. By preserving reproductive cells and tissues, individuals can have the option to start a family at a later time when it is more convenient for them. This is particularly beneficial for women who face the challenge of declining fertility as they age.
Moreover, cryopreservation also offers hope for individuals who may face fertility challenges due to medical conditions or treatments. By preserving their reproductive cells or tissues, they can have a chance to have biological children in the future, providing a sense of hope and control over their fertility.
In conclusion, cryopreservation is a game-changer in the field of fertility treatment, offering hope for future generations who may face fertility challenges. With the advancement of technology, cryopreservation has become a reliable and safe method of preserving reproductive cells and tissues, providing individuals with the option to start a family when the time is right for them. As we continue to push the boundaries of medicine and technology, we can only hope for more breakthroughs in cryopreservation and its role in fertility treatment.
Search Queries:
1. What is cryopreservation and how does it work?
2. What are the success rates of cryopreservation in fertility treatment?
3. What are the benefits of cryopreservation for future generations?
4. How does egg freezing work and who can benefit from it?
5. Can sperm freezing be used for fertility treatment?