Embryo Transfer and Preimplantation Genetic Testing: Is It Necessary?
Embryo transfer and preimplantation genetic testing have become increasingly popular in the field of assisted reproductive technology (ART). These procedures involve the transfer of an embryo, created through in vitro fertilization (IVF), into the uterus of a woman in order to achieve pregnancy. Preimplantation genetic testing (PGT) is a technique used to screen embryos for genetic abnormalities, allowing for the selection of healthy embryos for transfer. While these procedures have proven to be effective in helping couples achieve pregnancy, the question remains: is it necessary? In this blog post, we will explore the benefits and considerations of embryo transfer and preimplantation genetic testing.
Embryo Transfer: The Basics
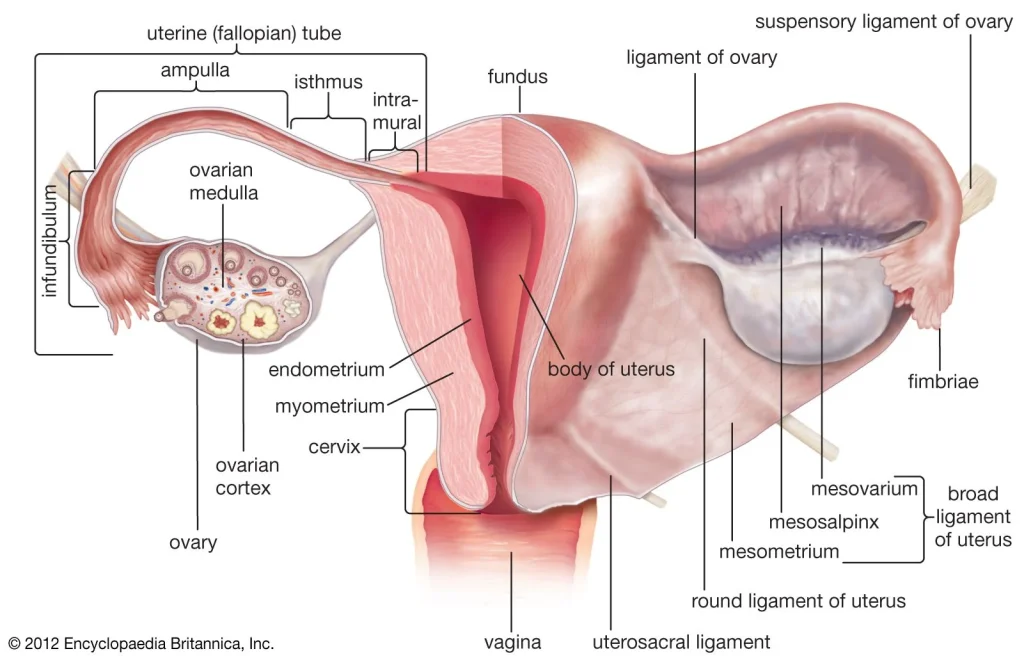
Embryo transfer is the process of placing a fertilized embryo into a woman’s uterus in order to establish a pregnancy. This procedure is commonly used in IVF, where the woman’s eggs are retrieved and fertilized with sperm in a laboratory setting. Once the embryos have developed, they are typically transferred into the woman’s uterus, where they will hopefully implant and continue to grow.
Embryo transfer is a crucial step in the IVF process, as it is the final stage of creating a viable pregnancy. The number of embryos transferred can vary, depending on factors such as the woman’s age, the quality of the embryos, and any previous failed IVF attempts. Generally, transferring multiple embryos increases the chances of pregnancy, but it also increases the likelihood of multiple pregnancies, which can come with their own set of risks.
Preimplantation Genetic Testing: What is it and Why is it Done?
Preimplantation genetic testing (PGT) is a technique used to screen embryos for genetic abnormalities before they are transferred into the uterus. This procedure is commonly used in cases where there is a known risk of passing on a genetic disorder to the child. PGT can also be used for family balancing, where the sex of the embryo is determined and only embryos of the desired sex are transferred.
There are two types of PGT: PGT-A (aneuploidy screening) and PGT-M (monogenic disorder screening). PGT-A screens for chromosomal abnormalities, such as Down syndrome, while PGT-M screens for specific genetic disorders, such as cystic fibrosis. These screenings involve removing a few cells from the embryo and analyzing them for genetic abnormalities. Only embryos that are deemed healthy are then transferred into the uterus.
Benefits of Embryo Transfer and Preimplantation Genetic Testing
Embryo transfer and preimplantation genetic testing have several benefits for couples struggling with infertility or those at risk of passing on genetic disorders. Some of the key benefits include:
1. Increased Chances of Pregnancy: By transferring multiple embryos, the chances of achieving pregnancy are significantly increased. Additionally, PGT can help ensure that only healthy embryos are transferred, further increasing the chances of a successful pregnancy.
2. Reduced Risk of Genetic Disorders: PGT can help identify and eliminate embryos with genetic disorders, reducing the risk of passing on a genetic disorder to the child.
3. Family Balancing: PGT can be used for family balancing, allowing couples to choose the sex of their child.
Embryo Transfer and Preimplantation Genetic Testing: Is It Necessary?
4. Peace of Mind: For couples with a family history of genetic disorders, PGT can offer peace of mind by ensuring that their child will not inherit the disorder.
Considerations for Embryo Transfer and Preimplantation Genetic Testing
While embryo transfer and preimplantation genetic testing have their benefits, there are also some important considerations to keep in mind before undergoing these procedures.
1. Cost: Both embryo transfer and preimplantation genetic testing can be expensive procedures, especially if multiple IVF cycles are required. It is important for couples to carefully consider the financial implications before proceeding with these treatments.
2. Ethical Concerns: The use of PGT for family balancing or sex selection can raise ethical concerns. Some may argue that this goes against the natural process of conception and may lead to gender imbalances in society.
3. False Positives/Negatives: While PGT is a highly accurate procedure, there is still a small margin for error. This means that there is a possibility of false positives or negatives, which can be emotionally distressing for couples.
4. Multiple Pregnancies: As mentioned earlier, transferring multiple embryos increases the chances of pregnancy but also the risk of multiple pregnancies. This can come with its own set of challenges and complications.
Is it Necessary?
The decision to undergo embryo transfer and preimplantation genetic testing is a personal one that should be made after careful consideration of all factors. For couples with a known risk of genetic disorders or those struggling with infertility, these procedures can offer hope and increase the chances of a successful pregnancy. However, for others, the cost, ethical concerns, and potential risks may outweigh the benefits.
Overall, embryo transfer and preimplantation genetic testing have proven to be valuable techniques in the world of assisted reproductive technology. They offer couples the opportunity to conceive a healthy child and can provide peace of mind for those at risk of passing on genetic disorders. However, it is important to carefully consider all factors and consult with a healthcare professional before making a decision.
Possible Search Queries:
1. “What is embryo transfer and preimplantation genetic testing?”
2. “Benefits and considerations of embryo transfer and preimplantation genetic testing”
3. “Is preimplantation genetic testing necessary for IVF?”
4. “Cost of embryo transfer and preimplantation genetic testing”
5. “Ethical concerns surrounding preimplantation genetic testing”
Summary:
Embryo transfer and preimplantation genetic testing are two procedures commonly used in assisted reproductive technology to help couples achieve pregnancy and screen for genetic disorders. While these procedures have their benefits, including increased chances of pregnancy and reduced risk of genetic disorders, there are also important considerations to keep in mind. These include the cost, ethical concerns, and potential risks associated with multiple pregnancies and false positives or negatives. Ultimately, the decision to undergo embryo transfer and preimplantation genetic testing is a personal one that should be made after careful consideration and consultation with a healthcare professional.