The field of reproductive science has made incredible advancements in helping individuals and couples achieve their dream of having a child. From in vitro fertilization (IVF) to genetic testing, there are a variety of techniques and technologies that have revolutionized the way we approach fertility. One crucial aspect of reproductive science is the role of genetics. In this blog post, we will explore the significance of genetics in reproductive science and how it impacts the ability to conceive and have a healthy baby.
To understand the role of genetics in reproductive science, it is essential to first have a basic understanding of genetics. Genetics is the study of genes, DNA, and heredity. Genes are the building blocks of life and are responsible for determining physical traits, such as eye color and height. They also play a vital role in our health and can influence our risk for certain diseases.
Now, let’s delve into the various ways genetics plays a role in reproductive science:
1. Genetic Testing: Genetic testing is a crucial aspect of reproductive science. It involves analyzing a person’s DNA to identify any genetic abnormalities that may affect fertility or the health of a potential child. This type of testing can help identify genetic diseases, chromosomal abnormalities, and other factors that may affect the success of pregnancy. By identifying these issues early on, couples can make informed decisions about their reproductive options, such as using donor eggs or embryos, or pursuing adoption.
2. Inherited Fertility Issues: Some fertility issues are directly related to genetics and can be inherited from one or both parents. For example, women with a family history of early menopause may also experience early menopause, and men with a family history of low sperm count may also have trouble conceiving. In these cases, genetic testing can help identify the underlying cause and guide treatment options.
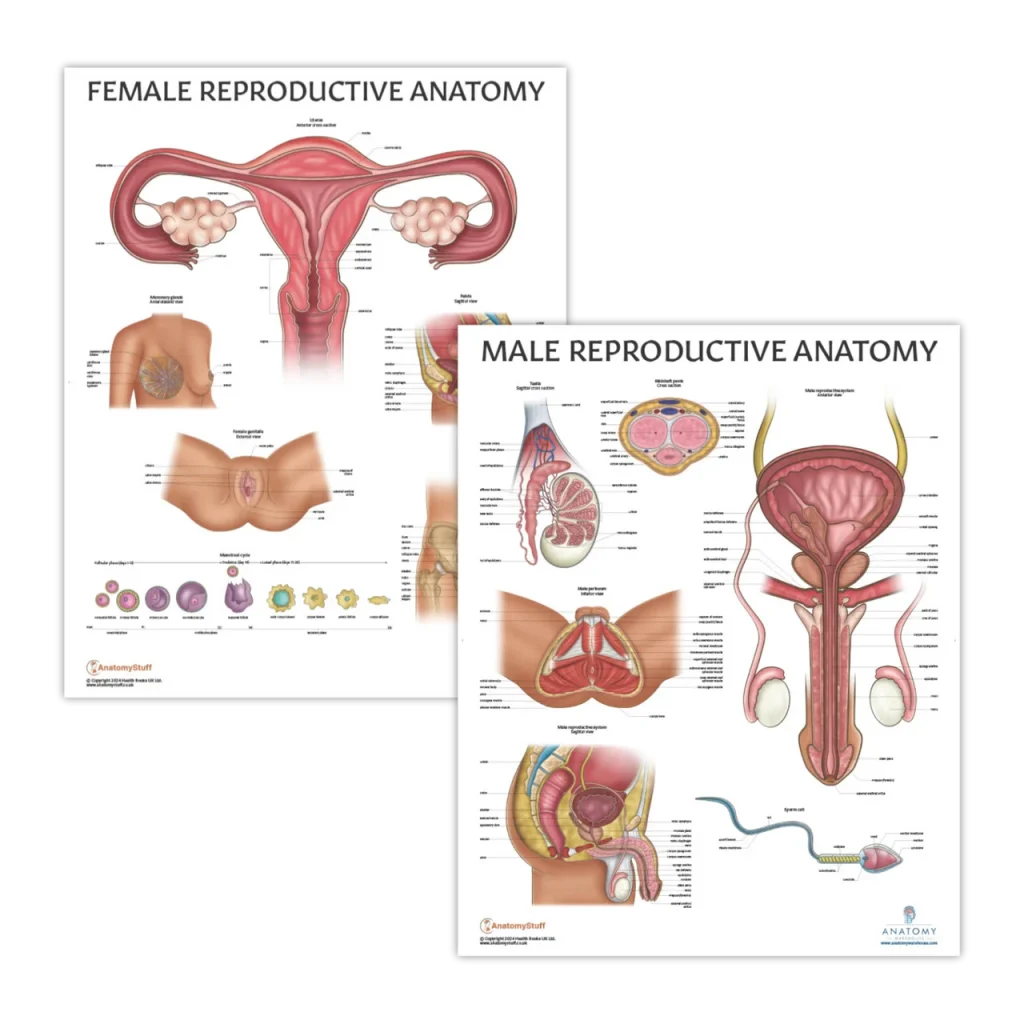
The Role of Genetics in Reproductive Science
3. Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT): PGT is a type of genetic testing that is performed on embryos created through IVF. This test can identify any genetic abnormalities in the embryo before it is transferred back into the uterus. PGT can help prevent the transfer of embryos with genetic disorders, thus increasing the chances of a successful pregnancy and reducing the risk of passing on a genetic disease to the child.
4. Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART): ART refers to a range of fertility treatments that help individuals and couples conceive. These treatments often include procedures such as IVF and intrauterine insemination (IUI). The success of ART can be influenced by genetic factors, such as egg quality and sperm health. By understanding a person’s genetic makeup, doctors can tailor ART treatments to increase the chances of a successful pregnancy.
5. Family Planning: Genetics also plays a crucial role in family planning. With the help of genetic counseling and testing, couples can make informed decisions about their family planning based on their genetic predispositions. For example, if a couple has a high risk of passing on a genetic disease to their child, they may choose to pursue alternative options, such as using donor eggs or embryos.
In conclusion, the role of genetics in reproductive science cannot be overstated. From identifying genetic disorders to guiding fertility treatments, genetics plays a crucial role in helping individuals and couples achieve their dream of having a child. With ongoing advancements in genetic testing and technology, we can expect even more significant breakthroughs in the field of reproductive science in the future.
5 Probable Search Queries:
1. How does genetics affect fertility?
2. What role does genetic testing play in reproductive science?
3. Can genetic testing help prevent genetic disorders in children?
4. How does preimplantation genetic testing work?
5. What is the impact of genetics on assisted reproductive technology?